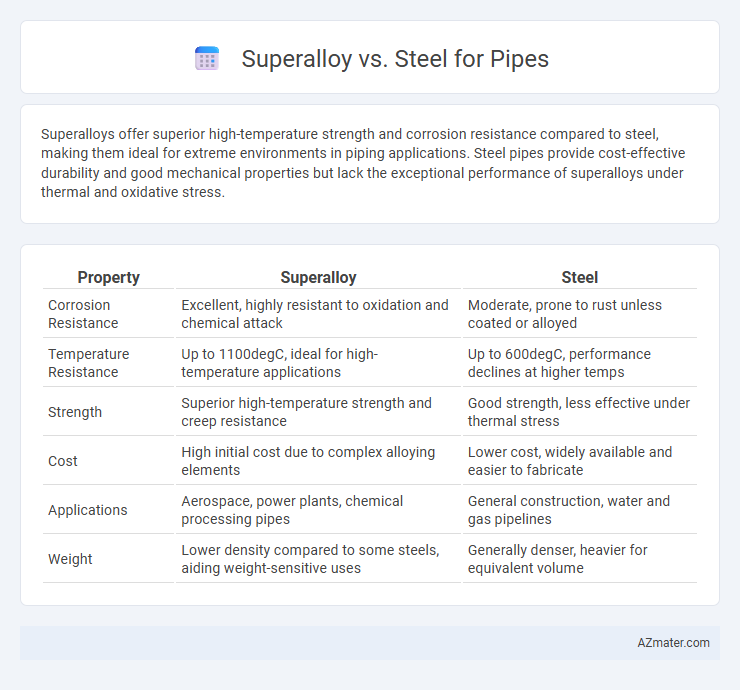
Superalloys offer superior high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance compared to steel, making them ideal for extreme environments in piping applications. Steel pipes provide cost-effective durability and good mechanical properties but lack the exceptional performance of superalloys under thermal and oxidative stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superalloy | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to oxidation and chemical attack | Moderate, prone to rust unless coated or alloyed |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1100degC, ideal for high-temperature applications | Up to 600degC, performance declines at higher temps |
| Strength | Superior high-temperature strength and creep resistance | Good strength, less effective under thermal stress |
| Cost | High initial cost due to complex alloying elements | Lower cost, widely available and easier to fabricate |
| Applications | Aerospace, power plants, chemical processing pipes | General construction, water and gas pipelines |
| Weight | Lower density compared to some steels, aiding weight-sensitive uses | Generally denser, heavier for equivalent volume |
Introduction to Superalloy and Steel Pipes
Superalloy pipes are engineered from high-performance metal alloys that exhibit exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, making them ideal for extreme environments such as aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing. Steel pipes, primarily composed of iron and carbon, provide cost-effective strength and durability with varying grades tailored for construction, plumbing, and oil and gas applications. The choice between superalloy and steel pipes depends on operating conditions, with superalloys favored for high-temperature and corrosive settings while steel remains preferred for general-purpose uses.
Composition and Material Properties Comparison
Superalloys typically contain high percentages of nickel, cobalt, and chromium, enhancing their resistance to oxidation, corrosion, and high-temperature strength compared to steel, which is primarily iron with carbon and varying amounts of manganese, silicon, and trace elements. The microstructure of superalloys is engineered for exceptional creep resistance and mechanical stability at elevated temperatures, whereas steel pipes offer adequate strength and toughness at lower temperatures with cost-effectiveness. Consequently, superalloy pipes are preferred in extreme environments like aerospace and power generation, while steel pipes are commonly used in general industrial applications requiring standard mechanical properties.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Superalloys exhibit superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to conventional steel, making them ideal for high-stress pipe applications in extreme environments. Their high creep resistance and oxidation tolerance ensure long-term performance under elevated temperatures and corrosive conditions. Steel pipes, while cost-effective and strong for general use, often lack the advanced fatigue resistance and thermal stability inherent to superalloy materials.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Superalloys exhibit superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to steel, making them ideal for high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments in piping applications. Their alloying elements such as nickel, chromium, and cobalt create a stable oxide layer that prevents degradation under extreme conditions. Steel, while cost-effective, is more prone to rust and oxidation, requiring additional coatings or treatments to achieve similar protective properties.
Temperature and Pressure Performance
Superalloys exhibit superior temperature resistance compared to steel, maintaining mechanical strength and corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 1,000degC, whereas steel typically softens and loses durability above 600degC. Under high-pressure conditions, superalloys outperform most steel grades due to their enhanced creep resistance and ability to withstand thermal fatigue in extreme environments such as gas turbines and chemical reactors. The combination of nickel, cobalt, or iron in superalloys provides tailored microstructures that enable sustained performance in high-stress, high-temperature applications where conventional steel pipes would fail.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Superalloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to steel, leading to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in piping systems used in extreme environments such as aerospace and chemical processing. Despite higher initial material and fabrication expenses, the overall economic impact favors superalloys when lifecycle costs, including downtime and replacement frequency, are significantly lower than steel counterparts. Cost considerations must balance upfront investment with long-term performance benefits, where superalloys deliver enhanced reliability that can justify premium pricing in critical applications.
Applications in Industrial Sectors
Superalloys offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to steel, making them ideal for aerospace, chemical processing, and power generation industries where extreme conditions prevail. Steel pipes are widely used in construction, water supply, and oil and gas sectors due to their cost-effectiveness and adequate mechanical properties for moderate environments. The choice between superalloy and steel pipes depends on specific industrial requirements such as temperature, pressure, and exposure to corrosive substances.
Fabrication, Welding, and Machinability
Superalloys offer superior high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance compared to steel, but their fabrication requires specialized techniques due to increased hardness and toughness. Welding superalloy pipes demands precise control of heat input and filler materials to prevent cracking and maintain mechanical properties, contrasting with steel's more straightforward welding process. Machining superalloys is more challenging because of their work-hardening behavior and toughness, necessitating advanced tooling and slower cutting speeds, whereas steel is generally easier and more cost-effective to machine.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Superalloy pipes exhibit superior longevity compared to steel due to their exceptional resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and mechanical stress, which significantly reduces the frequency of replacement and repairs. Steel pipes, although cost-effective initially, often require more frequent maintenance and inspections to address rust, wear, and fatigue, especially in harsh industrial environments. The enhanced durability of superalloy materials translates into lower long-term maintenance costs and improved operational reliability in critical applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Pipe Needs
Superalloys offer superior corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and excellent mechanical properties compared to steel, making them ideal for extreme environments such as aerospace and chemical processing industries. Steel remains a cost-effective choice with good tensile strength and versatility for general-purpose piping applications, especially where temperatures and corrosive conditions are moderate. Selecting between superalloy and steel depends on specific operational demands like pressure, temperature, and exposure to corrosive media to ensure optimal pipe performance and longevity.
Infographic: Superalloy vs Steel for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com