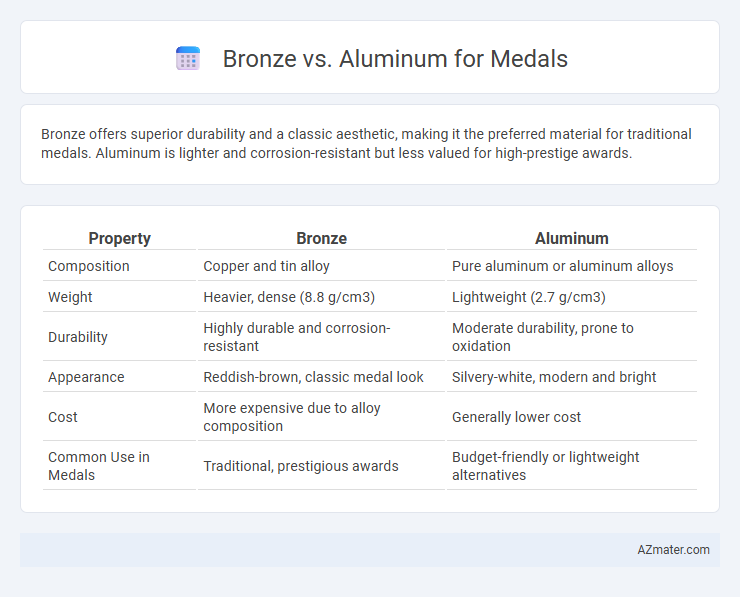
Bronze offers superior durability and a classic aesthetic, making it the preferred material for traditional medals. Aluminum is lighter and corrosion-resistant but less valued for high-prestige awards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and tin alloy | Pure aluminum or aluminum alloys |
| Weight | Heavier, dense (8.8 g/cm3) | Lightweight (2.7 g/cm3) |
| Durability | Highly durable and corrosion-resistant | Moderate durability, prone to oxidation |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown, classic medal look | Silvery-white, modern and bright |
| Cost | More expensive due to alloy composition | Generally lower cost |
| Common Use in Medals | Traditional, prestigious awards | Budget-friendly or lightweight alternatives |
Introduction to Medal Materials
Bronze and aluminum are two common materials used for medals, each offering distinct properties. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, is valued for its durability, traditional appearance, and ability to develop a rich patina over time. Aluminum, known for its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, provides a modern alternative that allows for easier customization and cost-effective production.
Historical Significance of Bronze and Aluminum Medals
Bronze medals have a rich historical significance dating back to ancient civilizations where bronze was commonly used for crafting durable awards and artifacts, symbolizing strength and resilience. Aluminum medals, introduced in the 20th century, represent modern advancements in lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, often associated with industrial progress and innovation. The use of bronze in medals continues to evoke tradition and heritage, while aluminum highlights contemporary values of efficiency and sustainability in award design.
Physical Properties: Bronze vs Aluminum
Bronze exhibits higher density and superior hardness compared to aluminum, making it more durable and resistant to wear for medal crafting. Aluminum offers lighter weight and excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for medals where ease of handling and longevity are priorities. The thermal conductivity of aluminum is significantly greater than bronze, influencing cooling and casting processes during medal production.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Bronze medals offer superior durability due to their resistance to corrosion and wear, making them ideal for long-term preservation. Aluminum medals, while lightweight and resistant to rust, are generally softer and prone to scratching or denting over time. The robustness of bronze ensures medals maintain their appearance and structural integrity better than aluminum in demanding conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finish
Bronze medals exhibit a rich, warm color with a classic, timeless patina that evolves over time, enhancing their aesthetic appeal. Aluminum medals offer a sleek, modern finish with a lightweight, silver-toned appearance that resists corrosion and maintains a consistent shine. The choice between bronze and aluminum medals often depends on desired visual impact and longevity of the finish.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Bronze medals generally offer better cost efficiency due to lower raw material costs and widespread availability of copper and tin alloys, making them a budget-friendly choice for mass production. Aluminum medals, while lightweight and corrosion-resistant, tend to be more expensive per unit because of fluctuating aluminum market prices and processing complexities. Availability of bronze alloys is more stable globally, ensuring consistent supply chains compared to aluminum, which can face regional production bottlenecks affecting overall cost and delivery timelines.
Weight Differences and Athlete Experience
Bronze medals typically weigh more than aluminum medals, with bronze averaging around 350 grams compared to aluminum's lighter weight of approximately 150 grams, significantly impacting the physical sensation athletes experience. The heavier bronze medal often conveys a sense of prestige and durability, contributing to a more substantial and memorable athlete experience during ceremonies. Aluminum medals, being lighter and sometimes perceived as less prestigious, may affect the emotional impact and tactile satisfaction for competitors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bronze medals, primarily composed of copper and tin, have a higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive mining and smelting processes that contribute to significant carbon emissions and habitat disruption. Aluminum medals, derived from bauxite ore, can be more sustainable when recycled, as aluminum recycling consumes up to 95% less energy compared to primary production, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Selecting recycled aluminum medals supports circular economy principles, minimizing resource depletion and lowering ecological footprints in large-scale sporting events.
Modern Trends in Medal Manufacturing
Modern trends in medal manufacturing favor aluminum over bronze due to aluminum's lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for mass production and international events. Bronze remains popular for its classic aesthetic and durability, often chosen for prestigious awards and commemorative pieces that emphasize tradition and longevity. Advances in anodizing and surface texturing techniques for aluminum enable versatile design options, enhancing its appeal in contemporary medal crafting.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Event
Choosing the right metal for your event medals depends on factors like budget, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Bronze offers a classic, prestigious look with excellent durability and a rich, warm tone, making it ideal for traditional or high-profile ceremonies. Aluminum is lightweight, more affordable, and resistant to corrosion, perfect for large-scale events or casual competitions where cost-effectiveness and ease of handling are priorities.
Infographic: Bronze vs Aluminum for Medal
 azmater.com
azmater.com