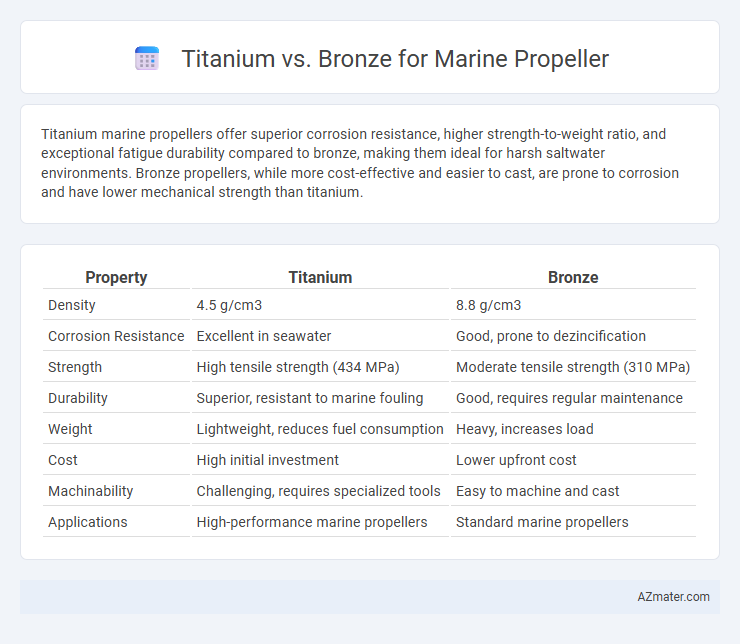
Titanium marine propellers offer superior corrosion resistance, higher strength-to-weight ratio, and exceptional fatigue durability compared to bronze, making them ideal for harsh saltwater environments. Bronze propellers, while more cost-effective and easier to cast, are prone to corrosion and have lower mechanical strength than titanium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cm3 | 8.8 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in seawater | Good, prone to dezincification |
| Strength | High tensile strength (434 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (310 MPa) |
| Durability | Superior, resistant to marine fouling | Good, requires regular maintenance |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces fuel consumption | Heavy, increases load |
| Cost | High initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Machinability | Challenging, requires specialized tools | Easy to machine and cast |
| Applications | High-performance marine propellers | Standard marine propellers |
Introduction: Importance of Material Choice for Marine Propellers
Material choice for marine propellers significantly impacts performance, durability, and corrosion resistance in harsh ocean environments. Titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional resistance to seawater corrosion compared to bronze, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Bronze remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and good wear resistance, balancing affordability with adequate marine durability.
Overview of Titanium and Bronze Alloys
Titanium alloys offer superior strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and outstanding fatigue performance, making them highly suitable for marine propellers exposed to harsh seawater environments. Bronze alloys, particularly manganese and aluminum bronzes, are traditionally favored for their good corrosion resistance, ease of casting, and cost-effectiveness, though they generally exhibit lower strength and higher weight compared to titanium. The choice between titanium and bronze alloys hinges on balancing durability, maintenance requirements, and initial investment in marine propulsion applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium vs Bronze in Marine Environments
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to bronze in marine environments due to its stable oxide layer that prevents seawater penetration and pitting. Bronze alloys, while corrosion-resistant, are more susceptible to dezincification and galvanic corrosion when exposed to saltwater, reducing their service life. This makes titanium an optimal choice for marine propellers requiring long-term durability and minimal maintenance in harsh ocean conditions.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium marine propellers offer superior strength with a tensile strength of approximately 900 MPa compared to bronze's 400-600 MPa range, resulting in enhanced resistance to impact and deformation. Titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance against seawater significantly extends propeller lifespan, reducing maintenance frequency and costs. Bronze propellers, while cost-effective, are more prone to corrosion and mechanical wear, making titanium the preferred choice for high-performance and long-term durability in marine applications.
Weight Differences and Impact on Performance
Titanium marine propellers weigh significantly less than bronze counterparts, with titanium offering up to 40% weight reduction due to its lower density and high strength-to-weight ratio. This weight difference enhances vessel acceleration, maneuverability, and fuel efficiency by reducing rotational inertia and overall mass. The lighter titanium propeller also minimizes vibration and stress on the propulsion system, leading to improved performance and longer service life.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Titanium marine propellers have a higher initial investment cost, typically ranging from 3 to 5 times that of bronze propellers, due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes. However, titanium offers superior corrosion resistance, reduced maintenance expenses, and extended service life, resulting in lower total ownership costs over time. Bronze propellers require more frequent repairs and replacements, increasing long-term operational expenses despite their lower upfront price.
Maintenance and Lifespan Expectations
Titanium marine propellers offer superior corrosion resistance and require less maintenance compared to bronze counterparts due to their inert oxide layer that prevents seawater degradation. Bronze propellers, while cost-effective, are prone to galvanic corrosion and biofouling, demanding regular cleaning and protective coatings to maintain performance. Titanium's extended lifespan, often doubling that of bronze, results in long-term economic benefits despite higher initial costs, making it ideal for marine applications requiring durability and low upkeep.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Titanium marine propellers offer superior corrosion resistance in saltwater environments, significantly reducing the frequency of replacements compared to bronze, which is more prone to marine corrosion and biofouling. The production of titanium, despite higher initial energy costs, results in longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements, minimizing environmental disruption and lifecycle carbon footprint. Bronze propellers, while cheaper and recyclable, often require more frequent inspections and treatments involving toxic antifouling paints, contributing to marine pollution over time.
Application Suitability: Commercial vs Recreational Marine Vessels
Titanium marine propellers offer exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making them highly suitable for commercial vessels operating in harsh, saltwater environments where durability and reliability are critical. Bronze propellers, while cost-effective and easier to repair, are more commonly preferred for recreational marine vessels due to moderate corrosion resistance and adequate performance in less demanding conditions. The choice between titanium and bronze hinges on the vessel's operational intensity and budget, with titanium favored for heavy-duty commercial use and bronze often sufficient for recreational applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Marine Propellers
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and longevity compared to bronze, making it ideal for high-performance and long-lasting marine propellers. Bronze, known for its cost-effectiveness and ease of casting, remains a reliable choice for standard applications where budget constraints exist. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental exposure, and budget considerations for optimal marine propulsion efficiency.
Infographic: Titanium vs Bronze for Marine Propeller
 azmater.com
azmater.com