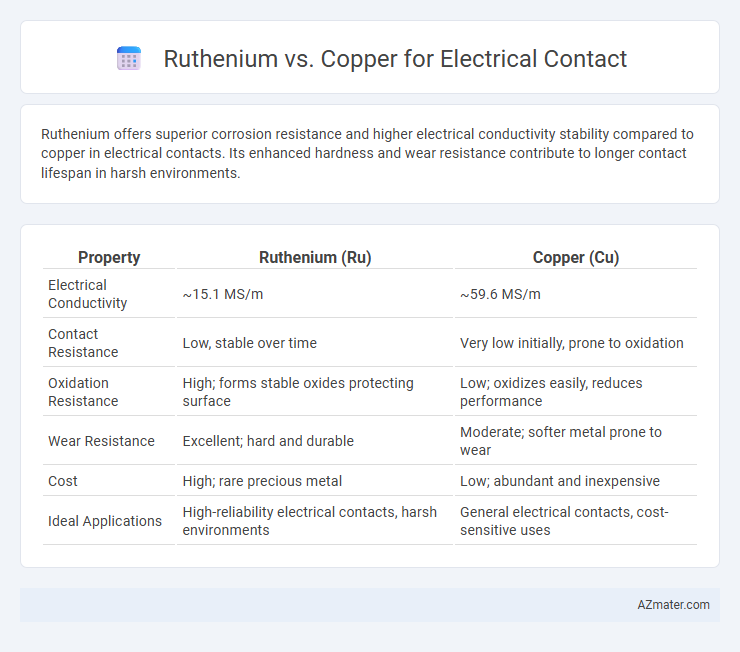
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher electrical conductivity stability compared to copper in electrical contacts. Its enhanced hardness and wear resistance contribute to longer contact lifespan in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Copper (Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~15.1 MS/m | ~59.6 MS/m |
| Contact Resistance | Low, stable over time | Very low initially, prone to oxidation |
| Oxidation Resistance | High; forms stable oxides protecting surface | Low; oxidizes easily, reduces performance |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent; hard and durable | Moderate; softer metal prone to wear |
| Cost | High; rare precious metal | Low; abundant and inexpensive |
| Ideal Applications | High-reliability electrical contacts, harsh environments | General electrical contacts, cost-sensitive uses |
Introduction to Electrical Contacts
Ruthenium exhibits superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts. Its high hardness and wear resistance reduce contact degradation and ensure stable, low-resistance connections in demanding environments. Copper offers excellent conductivity and is cost-effective but is more prone to oxidation and wear, limiting its durability in electrical contact applications.
Overview of Ruthenium and Copper Materials
Ruthenium, a rare transition metal, exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and superior hardness, making it highly suitable for durable electrical contacts that require long-term reliability. Copper, renowned for its exceptional electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, remains the standard choice for electrical contacts but is more prone to oxidation and wear under harsh conditions. The distinct material properties of ruthenium and copper dictate their applications, with ruthenium favored in high-performance, high-reliability environments and copper preferred for general-purpose electrical connections.
Conductivity Comparison: Ruthenium vs Copper
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity at approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m, making it the standard choice for electrical contacts where efficiency is critical. Ruthenium's conductivity is significantly lower, around 2.2 x 10^6 S/m, but it offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments. The trade-off between ruthenium's wear resistance and copper's high conductivity often dictates material selection based on application-specific performance requirements.
Wear Resistance and Durability in Electrical Contacts
Ruthenium exhibits superior wear resistance and durability compared to copper in electrical contacts due to its high hardness and corrosion resistance, which minimize surface degradation during repeated electrical cycling. Copper, while highly conductive, is softer and more prone to wear and oxidation, leading to increased contact resistance and reduced lifespan in demanding applications. The enhanced mechanical and chemical stability of ruthenium-coated contacts ensures reliable long-term performance in high-load and high-frequency electrical environments.
Corrosion Resistance: How Ruthenium and Copper Perform
Ruthenium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, maintaining stable electrical conductivity in harsh environments due to its inert oxide layer formation. Copper, while highly conductive, is prone to oxidation and corrosion, leading to contact degradation and increased electrical resistance over time. This inherent corrosion resistance makes ruthenium a preferred material for electrical contacts in demanding industrial and automotive applications.
Cost Analysis: Ruthenium vs Copper
Ruthenium electrical contacts offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to copper, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs despite ruthenium's higher upfront price, which ranges around $600 per ounce versus copper's approximately $4 per pound. The cost analysis must weigh ruthenium's premium material costs against savings from minimized downtime, improved reliability, and fewer replacements in critical applications such as aerospace and high-performance electronics. Copper's lower initial expense suits general use with less demanding environments, while ruthenium's enhanced performance justifies its investment in high-stress, longevity-focused electrical contacts.
Applications in Industry
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains excellent conductivity under high-temperature conditions, making it ideal for electrical contacts in aerospace and automotive industries. Copper, while highly conductive and cost-effective, is prone to oxidation and wear, limiting its use in harsh environments but remaining prevalent in low-stress electrical connectors and power distribution systems. Industrial applications favor ruthenium-plated contacts for high-reliability switches and relays, whereas copper dominates bulk electrical wiring and general-purpose connectors due to its affordability and conductivity.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Ruthenium offers superior performance compared to copper for electrical contacts in high-temperature environments due to its high melting point of 2334degC and excellent oxidation resistance, which ensures stable conductivity under thermal stress. Copper's lower melting point of 1085degC and susceptibility to oxidation limit its reliability and lifespan in elevated temperatures. The robustness of ruthenium contacts reduces contact resistance variations and extends the service life in applications such as aerospace and industrial electronics operating above 200degC.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan in electrical contacts compared to copper, reducing material waste and frequency of replacements. Copper mining and refining have higher environmental footprints due to energy-intensive processes and significant land disturbance, while ruthenium, as a platinum-group metal, benefits from recycling initiatives that improve sustainability. Selecting ruthenium for electrical contacts supports eco-friendly applications by minimizing resource consumption and enhancing durability in demanding environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh environments. Copper provides cost-effective, high conductivity but may suffer from oxidation and wear in demanding applications. Selecting between ruthenium and copper depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints for optimal contact longevity and efficiency.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Copper for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com