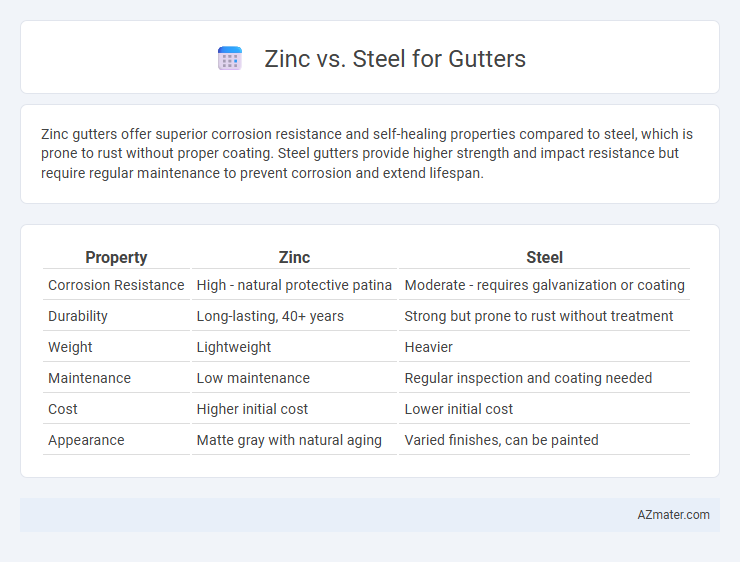
Zinc gutters offer superior corrosion resistance and self-healing properties compared to steel, which is prone to rust without proper coating. Steel gutters provide higher strength and impact resistance but require regular maintenance to prevent corrosion and extend lifespan.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zinc | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High - natural protective patina | Moderate - requires galvanization or coating |
| Durability | Long-lasting, 40+ years | Strong but prone to rust without treatment |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Regular inspection and coating needed |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Appearance | Matte gray with natural aging | Varied finishes, can be painted |
Introduction: Zinc vs Steel Gutters
Zinc gutters offer superior corrosion resistance and a natural patina that enhances longevity, making them ideal for climates with frequent moisture. Steel gutters provide exceptional strength and affordability but require regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion. Choosing between zinc and steel depends on budget, durability needs, and environmental exposure.
Material Composition and Properties
Zinc gutters consist primarily of pure zinc or a zinc-titanium alloy, offering high resistance to corrosion and self-healing properties due to the formation of a protective patina. Steel gutters, often galvanized or coated with zinc, provide superior strength and durability but require maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion over time. The choice between zinc and steel hinges on balancing zinc's low maintenance and aesthetic aging with steel's robustness and structural support capabilities.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Zinc gutters offer superior durability with a lifespan of up to 80-100 years due to natural corrosion resistance and self-healing properties from patina formation. Steel gutters typically last 20-50 years but require regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in harsh weather conditions. The long-term performance of zinc makes it a more cost-effective and low-maintenance option compared to steel for gutter systems.
Corrosion Resistance: Steel vs Zinc
Zinc offers superior corrosion resistance for gutters due to its natural ability to form a protective patina that shields the metal from moisture and air. Steel gutters require galvanized coatings or paint treatments to prevent rust, which can wear away over time and lead to corrosion. The longevity of zinc gutters in harsh weather conditions typically surpasses that of steel, making zinc a more durable choice for corrosion resistance.
Maintenance Requirements
Zinc gutters require minimal maintenance due to their natural patina, which protects against corrosion and reduces the need for frequent cleaning or painting. Steel gutters, especially those not galvanized or coated, demand regular inspections and maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, including periodic painting or rust treatment. Proper maintenance of steel gutters ensures longevity but typically involves higher time and cost investments compared to zinc.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finish Options
Zinc gutters offer a natural, matte finish that patinas over time, creating a distinctive, elegant look often favored in historic and modern architecture for its unique aesthetic appeal. Steel gutters provide a wide range of finish options, including smooth, glossy, and textured coatings in various colors, allowing for greater customization to match diverse architectural styles. While zinc emphasizes a timeless, evolving appearance, steel offers vibrant and consistent aesthetics with durable paint finishes resistant to chipping and fading.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc gutters offer superior environmental benefits due to their natural corrosion resistance, longevity of over 80 years, and high recyclability rate of 95%, significantly reducing landfill waste. Steel gutters, while strong and durable, typically last around 20-40 years and often require protective coatings that can contain harmful chemicals, impacting sustainability. Recycled steel options exist but have lower overall recyclability compared to zinc, making zinc a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious construction.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Zinc gutters typically have a higher upfront cost compared to steel due to the premium price of zinc material and its specialized installation requirements. Over the long term, zinc offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, resulting in lower maintenance and replacement expenses, whereas steel gutters may incur higher costs from frequent repairs and rust treatment. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors zinc for long-term savings despite the initial investment, especially in environments prone to moisture and wear.
Installation Considerations
Zinc gutters require specialized installation techniques due to their need for precise soldering and soft metal handling, which ensures long-term durability and weather resistance. Steel gutters, in contrast, are heavier and often demand robust support brackets and rust-resistant coatings during installation to prevent corrosion. Professional expertise is crucial for both materials to achieve proper alignment, secure fastening, and effective water drainage.
Best Applications for Zinc and Steel Gutters
Zinc gutters offer superior corrosion resistance and self-healing patinas, making them ideal for coastal and industrial environments where durability against harsh weather and pollutants is essential. Steel gutters provide exceptional strength and impact resistance, making them perfect for areas with heavy snowfall or where mechanical damage is a concern. The choice between zinc and steel gutters depends on environmental exposure and maintenance preferences, with zinc favored for longevity and aesthetics while steel suits high-impact, load-bearing applications.
Infographic: Zinc vs Steel for Gutter
 azmater.com
azmater.com