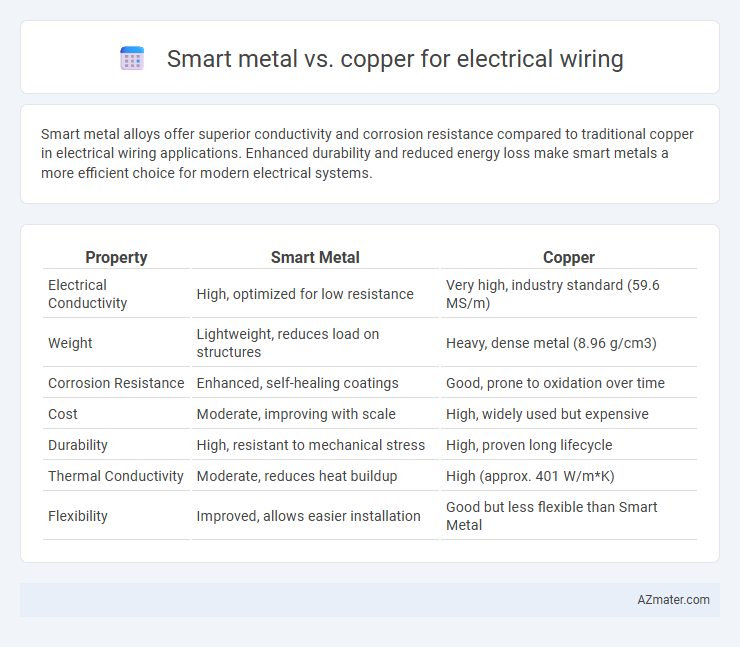
Smart metal alloys offer superior conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to traditional copper in electrical wiring applications. Enhanced durability and reduced energy loss make smart metals a more efficient choice for modern electrical systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Metal | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, optimized for low resistance | Very high, industry standard (59.6 MS/m) |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces load on structures | Heavy, dense metal (8.96 g/cm3) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Enhanced, self-healing coatings | Good, prone to oxidation over time |
| Cost | Moderate, improving with scale | High, widely used but expensive |
| Durability | High, resistant to mechanical stress | High, proven long lifecycle |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate, reduces heat buildup | High (approx. 401 W/m*K) |
| Flexibility | Improved, allows easier installation | Good but less flexible than Smart Metal |
Introduction to Electrical Wiring Materials
Smart metal alloys in electrical wiring offer enhanced conductivity, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties compared to traditional copper wires. Copper remains the standard due to its high electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance, ensuring efficient energy transmission. Advances in smart metal technology aim to provide cost-effective, durable alternatives with improved mechanical strength and flexibility for modern electrical systems.
What is Smart Metal?
Smart Metal refers to advanced conductive materials engineered to offer superior electrical performance, durability, and corrosion resistance compared to traditional metals like copper. Unlike copper, Smart Metal often incorporates nanotechnology or composite blends, enhancing conductivity and reducing energy loss in electrical wiring applications. These materials provide improved efficiency and longevity, making them a promising alternative for modern electrical infrastructure.
Copper: The Traditional Choice
Copper remains the traditional choice for electrical wiring due to its excellent electrical conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance, ensuring efficient and long-lasting performance. Its high thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat effectively, reducing the risk of overheating in electrical circuits. While smart metals offer innovative features, copper's proven reliability and widespread availability make it the preferred material in most residential and commercial wiring applications.
Conductivity Comparison: Smart Metal vs Copper
Smart metal alloys used in electrical wiring often feature enhanced conductivity properties tailored for specific applications, with some formulations approaching but typically not surpassing the electrical conductivity of pure copper, which is approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m (siemens per meter) at room temperature. Copper remains the industry standard for wiring due to its superior electrical conductivity, excellent thermal conductivity, and mechanical reliability, providing efficient current flow with minimal resistive losses. While smart metals may offer benefits such as reduced weight, corrosion resistance, or flexibility, copper's unmatched conductivity ensures its continued preference in high-performance electrical wiring systems.
Durability and Longevity
Smart metal wiring, often consisting of advanced alloys or coated materials, offers enhanced durability compared to traditional copper wiring due to its improved resistance to corrosion, fatigue, and thermal stress. Copper, while highly conductive and reliable, can be prone to oxidation and mechanical wear over time, potentially reducing lifespan in harsh environments. The longevity of smart metal wiring surpasses copper in demanding applications, making it a preferred choice for sustainable and long-lasting electrical systems.
Cost Analysis: Smart Metal vs Copper
Smart metal offers a cost advantage over copper for electrical wiring due to lower raw material expenses and reduced weight, which decrease transportation and installation costs. While copper provides superior conductivity and durability, its higher market price significantly increases overall project budgets. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance and efficiency, smart metal often proves more economical for large-scale electrical applications.
Safety and Fire Resistance
Smart metal wiring incorporates advanced alloys that provide superior fire resistance and enhanced thermal stability compared to traditional copper wiring, reducing the risk of electrical fires. Copper, while highly conductive, is more prone to oxidation and overheating under high load conditions, which can compromise safety over time. Smart metal's improved resistance to corrosion and heat makes it a safer choice for modern electrical systems focused on minimizing fire hazards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart metals for electrical wiring often incorporate advanced alloys or coatings designed to reduce energy loss and extend lifespan, resulting in lower resource consumption and waste compared to traditional copper wiring. Copper remains highly recyclable with a well-established recycling infrastructure, reducing the need for virgin mining, yet its extraction and processing pose significant environmental challenges including habitat disruption and high energy use. Choosing smart metals engineered for durability and conductivity can enhance sustainability by minimizing environmental impact and conserving natural resources over the lifecycle of electrical systems.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Smart metal wiring offers easier installation due to its lightweight properties and enhanced flexibility compared to traditional copper wiring, reducing labor time and effort. Copper wiring requires more careful handling because of its rigidity and susceptibility to damage during installation, which can increase maintenance needs. Maintenance for smart metal systems often involves fewer inspections and replacements, as their advanced corrosion resistance and durability lower the risk of electrical faults over time.
Future Trends in Electrical Wiring Technologies
Smart metal alloys, incorporating materials like graphene-enhanced copper, are emerging as future trends in electrical wiring due to their superior conductivity, flexibility, and corrosion resistance compared to traditional copper wiring. Innovations in smart metals enable self-healing and real-time diagnostic capabilities, improving the reliability and lifespan of electrical systems in smart grids and IoT applications. The integration of advanced materials with copper aims to optimize electrical performance while supporting sustainability and energy efficiency in next-generation wiring technologies.
Infographic: Smart metal vs Copper for Electrical wiring
 azmater.com
azmater.com