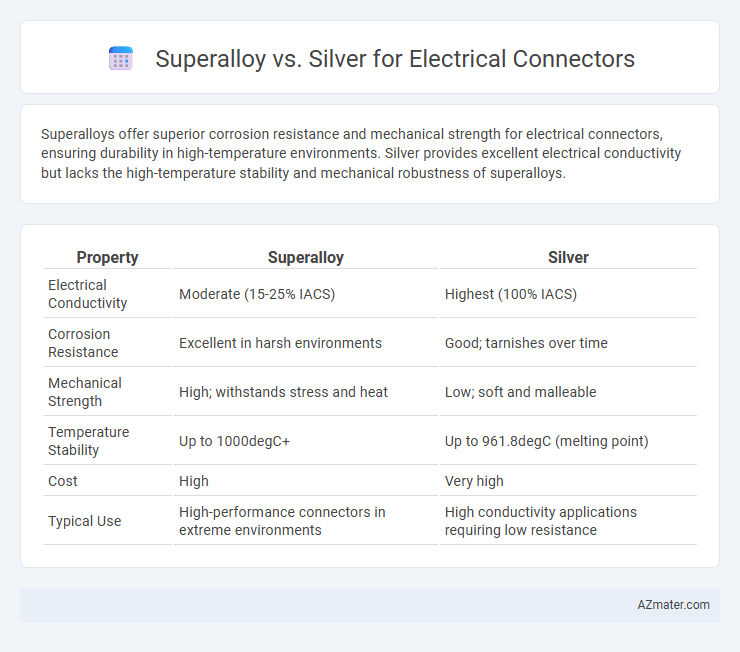
Superalloys offer superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength for electrical connectors, ensuring durability in high-temperature environments. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity but lacks the high-temperature stability and mechanical robustness of superalloys.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superalloy | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate (15-25% IACS) | Highest (100% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in harsh environments | Good; tarnishes over time |
| Mechanical Strength | High; withstands stress and heat | Low; soft and malleable |
| Temperature Stability | Up to 1000degC+ | Up to 961.8degC (melting point) |
| Cost | High | Very high |
| Typical Use | High-performance connectors in extreme environments | High conductivity applications requiring low resistance |
Introduction to Superalloy and Silver in Electrical Connectors
Superalloy and silver are both essential materials in electrical connectors, each offering distinct advantages based on their electrical and mechanical properties. Superalloys, typically nickel-based, exhibit exceptional resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and mechanical stress, making them ideal for demanding aerospace and industrial connector applications. Silver, known for its superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal properties, is commonly used in connectors requiring minimal signal loss and efficient current flow.
Material Properties Comparison: Superalloy vs Silver
Superalloy offers superior mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability compared to silver, making it ideal for harsh environments in electrical connectors. Silver excels in electrical conductivity, boasting the highest conductivity among metals, but its softness and susceptibility to tarnishing limit durability. Selecting between superalloy and silver depends on prioritizing electrical performance versus mechanical robustness in connector applications.
Electrical Conductivity: Silver vs Superalloy
Silver offers exceptional electrical conductivity of approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it one of the best materials for minimizing resistance in electrical connectors. Superalloys, composed primarily of nickel, cobalt, or iron with various alloying elements, typically exhibit conductivity values significantly lower than silver, often less than 10 x 10^6 S/m. The superior conductivity of silver ensures enhanced signal integrity and reduced power loss, while superalloys prioritize mechanical strength and corrosion resistance over electrical performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Superalloys offer superior mechanical strength compared to silver, with tensile strengths often exceeding 1000 MPa, making them ideal for high-stress electrical connectors in aerospace and industrial applications. Silver, while exhibiting excellent electrical conductivity of about 63 x 10^6 S/m, lacks comparable durability and tends to deform under mechanical stress, limiting its use in environments demanding robust, wear-resistant connections. The corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability of superalloys significantly enhance connector lifespan, outperforming silver in durability for heavy-duty and long-term electrical contact scenarios.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Superalloy connectors exhibit superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to silver, making them ideal for harsh environments where durability is critical. Silver offers excellent electrical conductivity but is prone to tarnishing and corrosion, especially in the presence of sulfur or moisture. The enhanced resistance of superalloys ensures longer lifespan and reliability in industrial and aerospace electrical applications.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Superalloys exhibit superior thermal stability compared to silver, maintaining mechanical integrity and electrical conductivity at temperatures exceeding 700degC, whereas silver's performance degrades rapidly above 200degC due to oxidation and softening. The enhanced thermal performance of superalloys ensures reliable, long-term operation in high-temperature environments such as aerospace and power generation connectors. Silver, while highly conductive at lower temperatures, lacks the resilience needed for high-heat applications, making superalloys the preferred choice for connectors enduring extreme thermal stress.
Cost Analysis: Superalloy vs Silver
Superalloy electrical connectors typically offer a lower cost option compared to silver connectors due to their base metal composition and reduced raw material expenses. Silver connectors, while more expensive, provide superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, justifying their higher initial investment in high-performance applications. Cost analysis should factor in long-term reliability and maintenance savings where silver's efficiency may offset upfront costs.
Applications in Industry: Where Each Material Excels
Superalloy connectors excel in high-temperature and corrosive environments such as aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing due to their exceptional strength and oxidation resistance. Silver connectors dominate in electronics, telecommunications, and precision instruments where superior electrical conductivity and low contact resistance are critical. Industries requiring durability under extreme conditions favor superalloys, while high-frequency signal and low-resistance applications benefit from silver's conductive properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Superalloy electrical connectors, often composed of nickel, cobalt, and chromium, offer superior corrosion resistance and durability, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing environmental waste. Silver connectors provide excellent electrical conductivity but require more frequent maintenance and eventual recycling due to tarnishing and wear, potentially increasing environmental burden. Sustainable practices favor superalloy connectors for long-term use, while silver's recyclability supports circular economy efforts in electronic waste management.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Connectors
Superalloy offers exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength at elevated temperatures, and excellent mechanical durability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in harsh environments. Silver provides superior electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, ensuring efficient signal transmission and minimal power loss in connectors, especially in low-current or sensitive applications. Selecting between superalloy and silver depends on balancing the need for durability and environmental resistance against the priority of electrical efficiency and conductivity.
Infographic: Superalloy vs Silver for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com