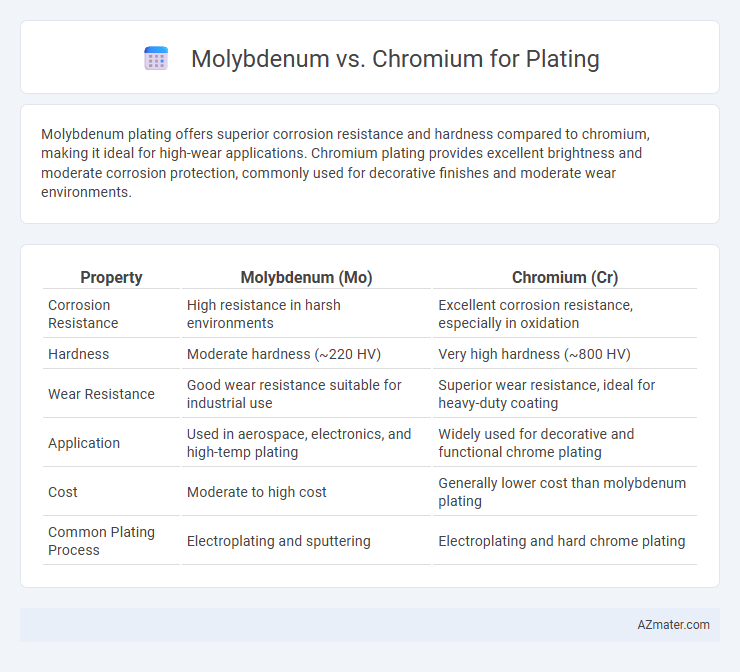
Molybdenum plating offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness compared to chromium, making it ideal for high-wear applications. Chromium plating provides excellent brightness and moderate corrosion protection, commonly used for decorative finishes and moderate wear environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum (Mo) | Chromium (Cr) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance in harsh environments | Excellent corrosion resistance, especially in oxidation |
| Hardness | Moderate hardness (~220 HV) | Very high hardness (~800 HV) |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear resistance suitable for industrial use | Superior wear resistance, ideal for heavy-duty coating |
| Application | Used in aerospace, electronics, and high-temp plating | Widely used for decorative and functional chrome plating |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost | Generally lower cost than molybdenum plating |
| Common Plating Process | Electroplating and sputtering | Electroplating and hard chrome plating |
Introduction to Plating Metals
Molybdenum and chromium are key metals used in plating due to their distinct properties enhancing surface durability and corrosion resistance. Molybdenum plating offers superior hardness and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for high-stress environments, while chromium plating provides a bright, decorative finish combined with corrosion protection. Both metals contribute significantly to extending the lifespan and performance of industrial components through advanced plating techniques.
Overview of Molybdenum Plating
Molybdenum plating offers excellent wear resistance, high hardness, and superior corrosion protection, making it ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. Unlike chromium plating, molybdenum provides a more uniform coating with better thermal stability and reduced risk of cracking under mechanical stress. Its ability to enhance surface lubricity and withstand extreme temperatures makes molybdenum plating a preferred choice for high-performance and harsh environment applications.
Overview of Chromium Plating
Chromium plating provides a hard, highly corrosion-resistant surface commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. It offers excellent wear resistance, low friction, and a bright, reflective finish that enhances both performance and aesthetics. This plating method typically involves electrodeposition of chromium onto a substrate, creating a durable layer that protects underlying metals from oxidation and chemical damage.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Molybdenum and chromium both exhibit high corrosion resistance, but molybdenum offers superior resistance to alkaline environments while chromium excels in acidic conditions. Chromium forms a hard, adherent oxide layer that provides excellent wear resistance and aesthetic appeal, whereas molybdenum contributes enhanced toughness and high-temperature stability in plating applications. The differing chemical reactivity and oxide formation of these metals influence their suitability for specific industrial plating uses, such as stainless steel reinforcements for molybdenum and decorative or protective coatings for chromium.
Durability and Hardness
Molybdenum plating offers superior hardness, typically reaching 1400-1800 HV, making it highly resistant to wear and abrasion in industrial applications. Chromium plating provides excellent durability with hardness levels around 1000-1200 HV, contributing to strong corrosion resistance and improved surface finish. While molybdenum excels in toughness and thermal stability, chromium is often preferred for its corrosion protection and aesthetic appeal in decorative and automotive plating.
Corrosion Resistance: Molybdenum vs Chromium
Molybdenum plating exhibits superior corrosion resistance in acidic and high-temperature environments compared to chromium, making it ideal for harsh industrial applications. Chromium plating offers excellent corrosion protection in moderate conditions with a distinctive shiny finish and high hardness. Selecting between molybdenum and chromium depends on balancing corrosion resistance requirements with aesthetic and wear-resistant properties.
Aesthetic and Surface Finish Differences
Molybdenum plating offers a smoother, more uniform surface finish with excellent resistance to wear and corrosion, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and a sleek look. Chromium plating provides a highly reflective, mirror-like aesthetic with superior hardness and excellent resistance to tarnish and oxidation. While chromium excels in decorative appeal with its bright, shiny finish, molybdenum plating is preferred for functional, wear-resistant surfaces with a more subdued metallic appearance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Molybdenum plating offers superior environmental benefits compared to chromium plating due to its lower toxicity and reduced hazardous waste generation, making it a safer choice for industrial applications. Chromium plating, especially hexavalent chromium, poses significant health risks such as respiratory issues and carcinogenic effects, leading to stringent regulatory controls and costly waste management processes. Choosing molybdenum minimizes environmental impact and enhances workplace safety by eliminating the need for carcinogenic chromium compounds and their associated disposal challenges.
Cost and Economic Factors
Molybdenum plating typically incurs higher costs due to its complex deposition process and limited availability compared to chromium, which benefits from well-established, cost-effective electroplating methods. Chromium plating offers superior economic advantages with faster plating times, lower material waste, and widespread industrial adoption, making it more accessible for large-scale applications. Cost-efficiency in chromium plating drives its preference in automotive and decorative industries, while molybdenum's expense limits its use to specialized sectors requiring enhanced wear resistance or corrosion protection.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Molybdenum plating offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for aerospace components, chemical processing equipment, and electrical contacts. Chromium plating excels in hardness and wear resistance, widely used in automotive parts, decorative finishes, and industrial machinery. Both metals serve critical roles in enhancing durability and performance across manufacturing, electronics, and energy sectors.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com