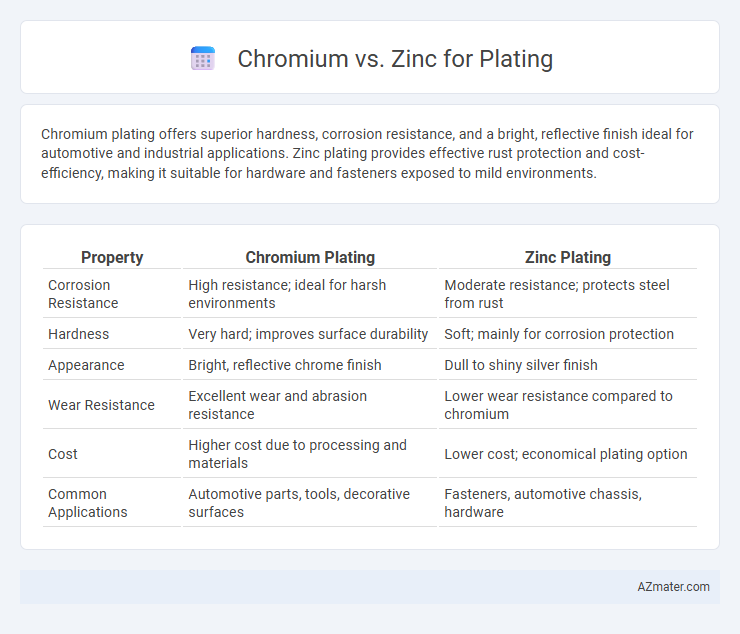
Chromium plating offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and a bright, reflective finish ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Zinc plating provides effective rust protection and cost-efficiency, making it suitable for hardware and fasteners exposed to mild environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chromium Plating | Zinc Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance; ideal for harsh environments | Moderate resistance; protects steel from rust |
| Hardness | Very hard; improves surface durability | Soft; mainly for corrosion protection |
| Appearance | Bright, reflective chrome finish | Dull to shiny silver finish |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear and abrasion resistance | Lower wear resistance compared to chromium |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing and materials | Lower cost; economical plating option |
| Common Applications | Automotive parts, tools, decorative surfaces | Fasteners, automotive chassis, hardware |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Chromium vs Zinc
Chromium and zinc are widely used metals in plating processes to enhance corrosion resistance and surface durability. Chromium plating offers exceptional hardness and a bright, reflective finish, making it ideal for automotive and decorative applications. Zinc plating provides effective sacrificial protection against rust, commonly applied to steel components in industrial and construction settings.
Chemical Properties of Chromium and Zinc
Chromium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and hardness due to its ability to form a stable, adherent oxide layer, making it ideal for decorative and protective plating. Zinc offers excellent sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially to the underlying metal, thanks to its more negative electrochemical potential in comparison to steel. The chemical stability of chromium allows for greater durability in harsh environments, whereas zinc's reactivity ensures effective galvanic protection in automotive and industrial applications.
Plating Processes: Differences in Application
Chromium plating involves a hard, corrosion-resistant layer applied through electroplating using chromium electrolyte solutions, offering enhanced wear resistance and decorative appeal. Zinc plating, typically performed via electroplating or mechanical plating, provides sacrificial protection by forming a barrier that prevents rust on steel substrates, commonly used for corrosion resistance in automotive and construction industries. The application differences lie in chromium's thin, hard coating ideal for high-durability surfaces versus zinc's thicker, sacrificial coating optimized for anti-corrosion protection.
Corrosion Resistance: Chromium vs Zinc
Chromium plating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc due to its dense, hard, and inert surface that prevents oxidation and rust formation. Zinc plating acts as a sacrificial barrier, protecting steel by corroding preferentially, but it is less durable in harsh environments and requires maintenance or additional coatings. For long-term protection against corrosion, chromium plating is preferred in automotive and industrial applications requiring a sleek, corrosion-resistant finish.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics Comparison
Chromium plating delivers a brighter, mirror-like surface finish with superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for decorative and automotive applications where aesthetics are paramount. Zinc plating provides a duller, matte finish that excels in rust prevention but lacks the high-gloss appeal of chromium. The choice between chromium and zinc plating significantly impacts the final appearance and durability of coated metal products.
Durability and Longevity of Chromium and Zinc Plating
Chromium plating offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-wear applications and environments exposed to moisture and chemicals. Zinc plating provides good corrosion protection but tends to wear faster and is less resistant to harsh conditions compared to chromium. The longevity of chromium plating typically exceeds zinc by delivering a harder surface that maintains appearance and performance over extended periods.
Cost Analysis: Chromium vs Zinc Plating
Chromium plating typically incurs higher costs due to expensive raw materials and more complex processing requirements compared to zinc plating. Zinc plating offers a more economical solution with lower material expenses and simpler application methods, making it suitable for large-scale, cost-sensitive projects. Despite its affordability, zinc plating provides reliable corrosion resistance, whereas chromium plating is often chosen when superior hardness and aesthetic appeal justify the additional investment.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Chromium plating, especially hexavalent chromium, poses significant environmental hazards due to its toxicity and carcinogenic properties, requiring strict regulation and waste management protocols. Zinc plating is generally safer, offering corrosion resistance with lower toxicity and less hazardous waste, making it a more environmentally friendly alternative. Transitioning to trivalent chromium and advanced zinc coatings reduces health risks for workers and minimizes ecological impact.
Common Industries and Applications
Chromium and zinc plating serve critical roles in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries by providing corrosion resistance and enhancing surface durability. Chromium plating is preferred for high-wear applications such as engine components, decorative trims, and hydraulic cylinders due to its hardness and resistance to oxidation. Zinc plating is commonly used in fasteners, automotive chassis, and electrical equipment, offering sacrificial protection against rust in industrial and outdoor environments.
Choosing the Right Plating: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right plating between chromium and zinc depends on factors such as corrosion resistance, application environment, and aesthetic preferences. Chromium plating offers superior hardness and a shiny, mirror-like finish ideal for decorative and wear-resistant applications, while zinc plating provides excellent rust protection, especially in outdoor or automotive environments due to its sacrificial corrosion properties. Cost considerations and required durability also influence the decision, with zinc generally being more economical and chromium favored for high-end finishes.
Infographic: Chromium vs Zinc for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com