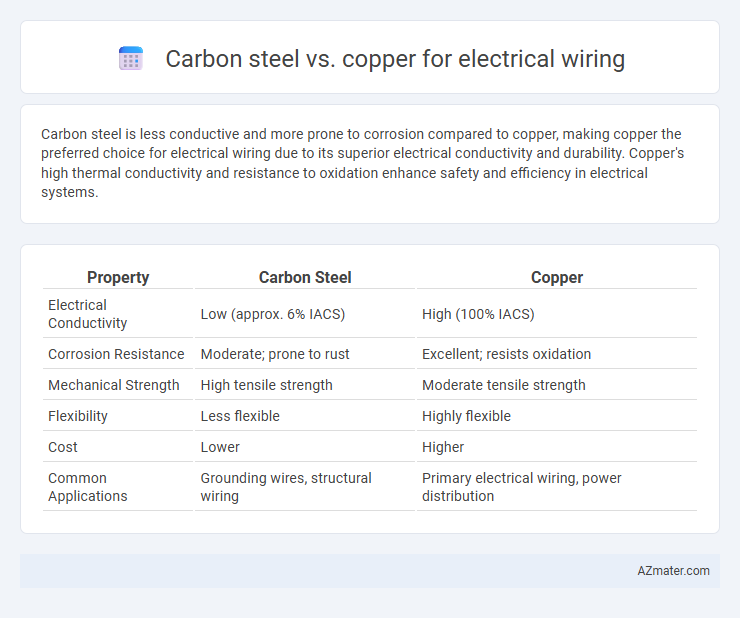
Carbon steel is less conductive and more prone to corrosion compared to copper, making copper the preferred choice for electrical wiring due to its superior electrical conductivity and durability. Copper's high thermal conductivity and resistance to oxidation enhance safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (approx. 6% IACS) | High (100% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to rust | Excellent; resists oxidation |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Applications | Grounding wires, structural wiring | Primary electrical wiring, power distribution |
Introduction to Electrical Wiring Materials
Carbon steel and copper serve distinct roles in electrical wiring due to their differing electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Copper is the preferred material for electrical wiring because of its high conductivity (approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m) and excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring efficient energy transmission and long service life. Carbon steel, with much lower conductivity and higher susceptibility to corrosion, is generally avoided in wiring but may be used in specific applications like structural support or protective enclosures where mechanical strength is prioritized over electrical performance.
Overview of Carbon Steel and Copper
Carbon steel contains iron and carbon, offering high tensile strength but has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, making it less efficient for electrical wiring. Copper is a highly conductive metal renowned for its excellent electrical and thermal properties, corrosion resistance, and ductility, which allows for easier installation and greater reliability in electrical systems. The choice between carbon steel and copper wiring depends on performance requirements, cost considerations, and environmental factors affecting conductivity and durability.
Electrical Conductivity: Carbon Steel vs Copper
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity, approximately 59.6 x 10^6 Siemens per meter, compared to carbon steel's much lower conductivity, which ranges around 1.45 x 10^6 Siemens per meter. This superior conductivity makes copper the preferred material for electrical wiring, ensuring efficient current flow and minimal energy loss. Carbon steel's limited conductivity results in higher resistance and energy dissipation, rendering it less suitable for standard electrical wiring applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Carbon steel offers superior mechanical strength compared to copper, making it more resistant to physical damage and wear in demanding electrical wiring environments. Copper excels in durability by resisting corrosion and maintaining conductivity over time, but its softer nature makes it more prone to deformation under mechanical stress. For applications requiring high tensile strength and impact resistance, carbon steel wiring provides enhanced longevity, while copper ensures sustained electrical performance through its excellent corrosion resistance.
Corrosion Resistance in Wiring Applications
Copper exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel, making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring in environments prone to moisture or chemical exposure. Carbon steel is susceptible to rust and oxidation, which can degrade conductivity and cause connection failures over time. Copper's stable oxide layer prevents corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability and consistent electrical performance in wiring applications.
Cost Comparison: Carbon Steel and Copper
Copper electrical wiring typically costs significantly more than carbon steel due to its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. Carbon steel, while less expensive, requires additional coatings or treatments to prevent rust and may involve higher maintenance costs over time. Overall, choosing carbon steel wiring can reduce upfront expenses but may lead to increased long-term costs compared to copper.
Installation and Flexibility
Carbon steel wiring offers enhanced durability and strength, making it well-suited for rigid installations but limits flexibility during complex routing. Copper wiring excels with superior electrical conductivity and exceptional flexibility, simplifying installation in intricate or tight spaces. The choice between carbon steel and copper hinges on specific project needs, balancing mechanical robustness versus ease of handling and installation.
Safety Considerations in Electrical Wiring
Copper offers superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, significantly reducing the risks of overheating and electrical fires in wiring applications. Carbon steel, while stronger mechanically, has higher electrical resistance and is more prone to oxidation, increasing potential safety hazards such as voltage drops and overheating. Proper insulation and grounding are critical when using carbon steel to mitigate safety concerns and ensure reliable electrical performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel, while less conductive than copper, offers a lower environmental footprint due to its abundant availability and recyclability, reducing the need for mining activities. Copper's superior electrical conductivity means less energy loss during transmission, but its extraction involves significant environmental degradation and high energy consumption. Sustainable wiring choices balance the lifecycle impacts, with steel favored for recyclability and copper prioritized where efficiency and energy savings offset mining impacts.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Wiring
Copper remains the preferred material for electrical wiring due to its superior electrical conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion, ensuring efficient and safe power transmission. Carbon steel, while stronger and less expensive, has higher electrical resistance and is prone to rust, making it less suitable for most wiring applications where reliability and performance are critical. Selecting the right material involves prioritizing conductivity and longevity, with copper consistently outperforming carbon steel in these key areas.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Copper for Electrical wiring
 azmater.com
azmater.com