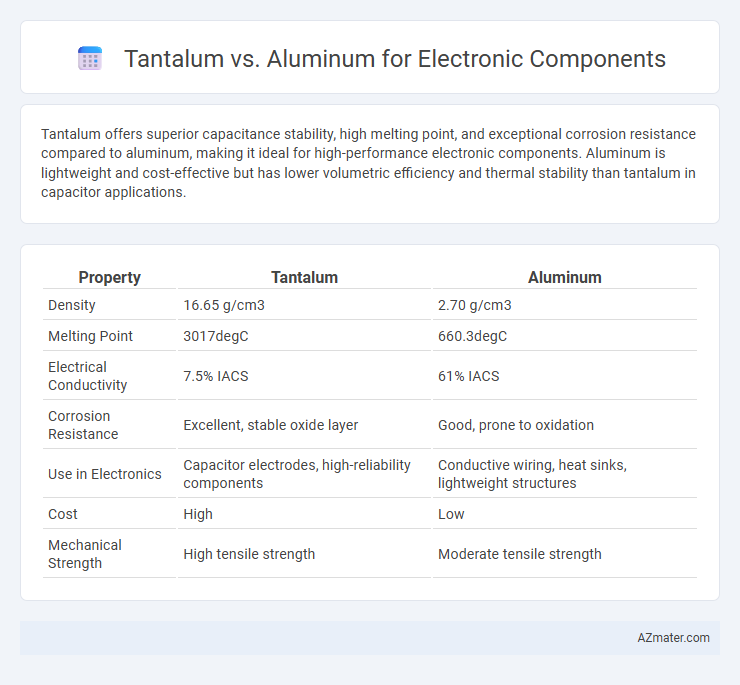
Tantalum offers superior capacitance stability, high melting point, and exceptional corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-performance electronic components. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective but has lower volumetric efficiency and thermal stability than tantalum in capacitor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 16.65 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 3017degC | 660.3degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | 7.5% IACS | 61% IACS |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, stable oxide layer | Good, prone to oxidation |
| Use in Electronics | Capacitor electrodes, high-reliability components | Conductive wiring, heat sinks, lightweight structures |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
Introduction to Tantalum and Aluminum in Electronics
Tantalum is a rare, corrosion-resistant metal widely used in electronic components such as capacitors due to its high capacitance per volume and stability at elevated temperatures. Aluminum, abundant and lightweight, serves as a versatile material in electronics for heat sinks, capacitors, and conductive pathways, offering cost-efficiency and excellent thermal conductivity. The distinct electrical properties and application-specific advantages of tantalum and aluminum make them critical choices in electronic design and manufacturing.
Material Properties Overview: Tantalum vs Aluminum
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting point (approximately 3017degC) compared to aluminum's melting point of about 660degC, making it ideal for high-temperature electronic components. Aluminum provides excellent thermal and electrical conductivity with a lower density (2.7 g/cm3) than tantalum's density of 16.69 g/cm3, offering weight advantages in portable devices. The choice between tantalum and aluminum depends on the specific electronic application's requirements for durability, thermal management, and weight constraints.
Capacitance Rates: Tantalum vs Aluminum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume compared to aluminum capacitors, making them ideal for applications requiring compact size and stable capacitance. Aluminum capacitors generally provide higher capacitance values but with larger physical size and higher equivalent series resistance (ESR). The volumetric efficiency and low ESR of tantalum capacitors make them preferable for precision electronic components where capacitance stability and reliability are critical.
Size and Form Factor Comparison
Tantalum capacitors offer a smaller size and higher volumetric efficiency compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, making them ideal for compact electronic components. Their solid-state construction allows for thinner profiles and more stable form factors, which are critical in miniaturized circuit designs like smartphones and wearables. Aluminum capacitors, while bulkier, provide higher capacitance values but occupy more space, limiting their use in applications where size and form factor are paramount.
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) Differences
Tantalum capacitors typically exhibit significantly lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, resulting in improved performance in high-frequency applications. The lower ESR of tantalum components enhances efficiency and reduces heat generation, making them ideal for sensitive electronic circuits requiring stable capacitance and reliable energy delivery. In contrast, aluminum capacitors generally have higher ESR, which can lead to increased losses and reduced lifespan under high ripple current conditions.
Reliability and Lifespan in Electronic Applications
Tantalum capacitors exhibit superior reliability and longer lifespan compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, primarily due to their stable oxide layer and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), which reduces heat generation and failure rates in electronic applications. Aluminum capacitors, while cost-effective and available in higher capacitance values, are more prone to electrolyte drying and leakage over time, leading to reduced performance and shorter operational life. Engineers often select tantalum capacitors for critical, long-term stability in devices where durability and consistent performance are paramount.
Cost Considerations: Tantalum vs Aluminum
Tantalum capacitors typically cost more per unit than aluminum electrolytic capacitors due to higher raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes. Aluminum capacitors offer a cost-effective solution for applications requiring large capacitance values but may require larger physical sizes and have shorter lifespans. Evaluating total cost of ownership should account for performance, reliability, and application-specific requirements beyond initial component price.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Tantalum capacitors exhibit superior performance in high-temperature environments due to their stable electrical characteristics, higher melting point (2996degC), and excellent dielectric properties, ensuring reliability in harsh conditions. Aluminum capacitors, with a lower melting point (660degC) and increased leakage current under heat stress, may suffer from reduced lifespan and performance degradation at elevated temperatures. The inherent material properties of tantalum enable it to maintain capacitance and withstand thermal cycling, making it preferable for aerospace, automotive, and industrial electronic components exposed to extreme heat.
Common Applications for Each Material
Tantalum is widely used in electronic components such as capacitors and high-temperature resistant circuits due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high melting point. Aluminum finds common applications in heat sinks, circuit boards, and conductive pathways because of its lightweight nature and superior thermal and electrical conductivity. Both materials serve critical roles in electronic device manufacturing, with tantalum preferred for reliability in high-stress environments and aluminum for efficient heat dissipation.
Choosing the Right Component for Your Project
Tantalum capacitors offer superior capacitance stability, higher volumetric efficiency, and better performance at low voltages compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, making them ideal for compact, high-reliability electronic applications. Aluminum capacitors excel in cost-effectiveness and high voltage tolerance, making them suitable for power supply filtering and bulk energy storage where size is less critical. Selecting between tantalum and aluminum depends on project requirements such as operating voltage, temperature range, lifespan, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Aluminum for Electronic Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com