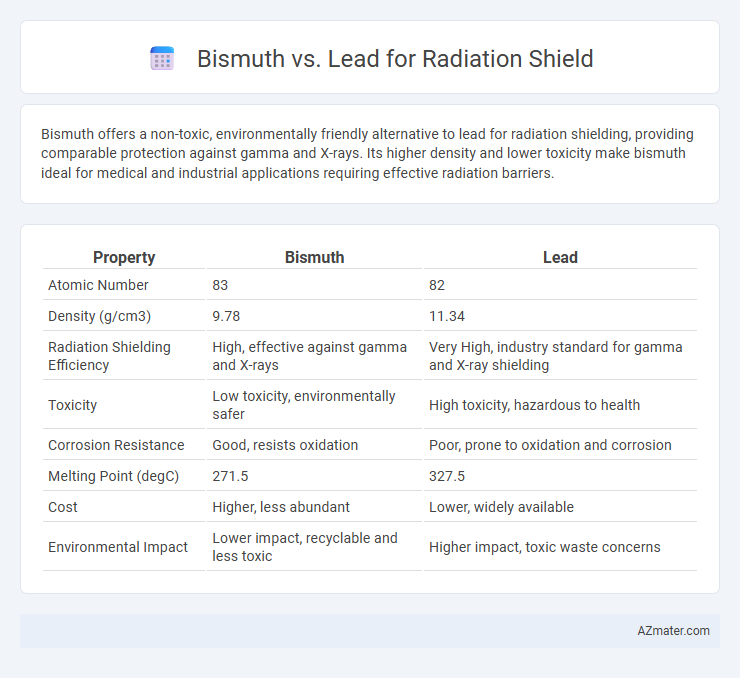
Bismuth offers a non-toxic, environmentally friendly alternative to lead for radiation shielding, providing comparable protection against gamma and X-rays. Its higher density and lower toxicity make bismuth ideal for medical and industrial applications requiring effective radiation barriers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 83 | 82 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 9.78 | 11.34 |
| Radiation Shielding Efficiency | High, effective against gamma and X-rays | Very High, industry standard for gamma and X-ray shielding |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity, environmentally safer | High toxicity, hazardous to health |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, resists oxidation | Poor, prone to oxidation and corrosion |
| Melting Point (degC) | 271.5 | 327.5 |
| Cost | Higher, less abundant | Lower, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Lower impact, recyclable and less toxic | Higher impact, toxic waste concerns |
Introduction to Radiation Shielding Materials
Bismuth and lead are prominent materials used for radiation shielding due to their high atomic numbers and density, which effectively attenuate ionizing radiation such as X-rays and gamma rays. Bismuth is favored for its non-toxic nature and comparable shielding efficiency, making it a safer alternative to lead, which poses significant health and environmental hazards due to its toxicity. Both materials are widely utilized in medical, industrial, and nuclear applications to protect human health and sensitive equipment from harmful radiation exposure.
Overview of Bismuth as a Shielding Material
Bismuth offers a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to lead for radiation shielding, with a high atomic number (83) that provides effective attenuation of gamma rays and X-rays. Its high density (9.78 g/cm3) closely matches lead's density, enhancing its capability to absorb ionizing radiation while reducing health hazards associated with lead toxicity. Bismuth's low thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical properties make it suitable for applications in medical, industrial, and nuclear radiation shielding.
Overview of Lead as a Shielding Material
Lead is widely used as a radiation shielding material due to its high density (11.34 g/cm3) and atomic number (82), which effectively attenuate gamma rays and X-rays. Its malleability and relatively low cost make it a practical choice for protective barriers in medical, industrial, and nuclear applications. However, concerns about lead's toxicity and environmental impact have prompted the search for safer alternatives in radiation shielding.
Density and Atomic Number Comparison
Bismuth has an atomic number of 83 and a density of approximately 9.78 g/cm3, whereas lead has a higher atomic number of 82 and a density of about 11.34 g/cm3. Despite lead's greater density, bismuth offers comparable radiation shielding efficiency due to its similar high atomic number and lower toxicity. The combination of bismuth's moderate density and high atomic number makes it a preferred alternative to lead in radiation shield applications, especially where environmental and health safety are priorities.
Radiation Attenuation Effectiveness
Bismuth exhibits superior radiation attenuation effectiveness compared to lead due to its higher atomic number (83) and density, enabling enhanced absorption of gamma rays and X-rays. Its non-toxic nature and comparable shielding capacity make it an ideal alternative in medical and industrial radiation protection applications. Bismuth's effective attenuation for photons in the 0.1 to 10 MeV energy range improves safety without the environmental and health hazards associated with lead.
Health and Environmental Considerations
Bismuth offers a safer alternative to lead for radiation shielding due to its non-toxic and environmentally benign properties, reducing health risks associated with lead exposure such as neurotoxicity and heavy metal poisoning. Bismuth's lower environmental impact stems from its non-leachable nature and recyclability, minimizing soil and water contamination compared to lead, which poses significant remediation challenges. In medical and industrial applications, bismuth-based shields provide effective gamma and X-ray attenuation while prioritizing occupational safety and sustainability standards.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Bismuth offers a cost-effective alternative to lead for radiation shielding due to its non-toxic nature and comparable density, reducing disposal and handling expenses. While lead remains more abundant and historically cheaper, increasing regulations on lead toxicity are driving up compliance costs, making bismuth more economically viable in the long term. Availability of bismuth is limited compared to lead, but growing mining operations and recycling advances are improving its supply stability for industrial shielding applications.
Applications in Medical and Industrial Fields
Bismuth offers superior radiation shielding in medical and industrial fields due to its non-toxic nature and high atomic number, effectively protecting against X-rays and gamma rays. Unlike lead, bismuth is environmentally friendly and ideal for use in medical devices such as protective aprons and imaging equipment, as well as industrial applications like radiography and nuclear facility shielding. Its comparable density to lead ensures efficient attenuation of radiation while eliminating concerns about lead toxicity and disposal regulations.
Ease of Fabrication and Handling
Bismuth offers superior ease of fabrication and handling compared to lead due to its non-toxic nature and lower environmental hazards, enabling safer processing and disposal. Its higher melting point and brittleness require specialized equipment, but it avoids the health risks associated with lead's toxicity. Consequently, bismuth-based radiation shields are often preferred in applications demanding safer material handling and regulatory compliance.
Future Trends in Radiation Shielding Materials
Bismuth is gaining traction as a preferred alternative to lead in radiation shielding due to its non-toxic nature and comparable density, enhancing environmental safety in medical and nuclear applications. Emerging composite materials incorporating bismuth nanoparticles demonstrate improved flexibility and reduced weight, meeting the demand for wearable and portable shielding solutions. Research trends emphasize eco-friendly, high-performance bismuth-based shields combining effective gamma and X-ray absorption with sustainable manufacturing processes.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Lead for Radiation shield
 azmater.com
azmater.com