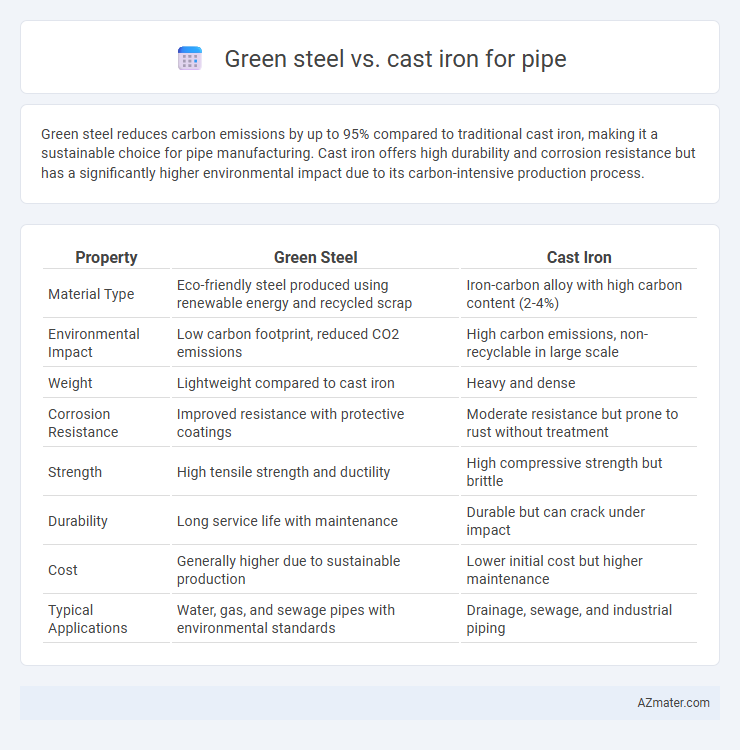
Green steel reduces carbon emissions by up to 95% compared to traditional cast iron, making it a sustainable choice for pipe manufacturing. Cast iron offers high durability and corrosion resistance but has a significantly higher environmental impact due to its carbon-intensive production process.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Steel | Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Eco-friendly steel produced using renewable energy and recycled scrap | Iron-carbon alloy with high carbon content (2-4%) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, reduced CO2 emissions | High carbon emissions, non-recyclable in large scale |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to cast iron | Heavy and dense |
| Corrosion Resistance | Improved resistance with protective coatings | Moderate resistance but prone to rust without treatment |
| Strength | High tensile strength and ductility | High compressive strength but brittle |
| Durability | Long service life with maintenance | Durable but can crack under impact |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable production | Lower initial cost but higher maintenance |
| Typical Applications | Water, gas, and sewage pipes with environmental standards | Drainage, sewage, and industrial piping |
Overview of Green Steel and Cast Iron Pipes
Green steel pipes utilize eco-friendly production methods that reduce carbon emissions by using renewable energy and recycled materials, resulting in a sustainable alternative to traditional steel. Cast iron pipes, known for their durability and corrosion resistance, have been widely used in plumbing and infrastructure but involve energy-intensive smelting processes with higher carbon footprints. The choice between green steel and cast iron pipes depends on balancing sustainability goals with durability requirements and application-specific performance factors.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Green steel for pipes primarily consists of recycled scrap steel combined with renewable energy-driven production methods, reducing carbon emissions significantly compared to traditional cast iron. Cast iron pipes are made from iron-carbon alloys with 2-4% carbon content, produced through melting and casting processes that involve higher energy consumption and carbon footprint. The manufacturing of green steel employs electric arc furnaces powered by clean energy, whereas cast iron pipes are formed by casting molten iron into molds, resulting in differences in durability, flexibility, and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green steel production significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing hydrogen or electric arc furnace methods powered by renewable energy, unlike traditional cast iron manufacturing which relies heavily on coke and coal, generating substantial CO2 pollution. Green steel's lower environmental footprint includes decreased air pollutants, energy consumption, and waste byproducts, contributing to sustainable infrastructure development. Cast iron pipes, while durable, embody higher embedded carbon and pose recycling challenges, making green steel a more eco-friendly choice for pipe materials in reducing industrial greenhouse gas emissions.
Strength and Durability Differences
Green steel pipes demonstrate superior strength and durability compared to cast iron due to their refined microstructure and enhanced corrosion resistance. The tensile strength of green steel can exceed 700 MPa, while cast iron typically ranges between 200-400 MPa, leading to better load-bearing capacity and impact resistance in green steel pipes. Furthermore, green steel's resistance to cracking and wear extends the service life of pipes significantly beyond that of cast iron, especially in corrosive or high-stress environments.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Green steel pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to cast iron due to advanced alloying techniques and protective coatings that reduce oxidation and rust formation. Cast iron pipes, while durable, are more prone to corrosion in harsh environments, which shortens their service life and increases maintenance costs. The enhanced longevity of green steel makes it a preferred choice in infrastructure projects demanding extended durability and minimal degradation.
Cost Analysis: Green Steel vs Cast Iron
Green steel offers a lower lifecycle cost compared to cast iron pipes due to reduced maintenance and longer durability despite higher initial expenses. Cast iron pipes require frequent repairs and are prone to corrosion, increasing overall operational costs over time. Energy-efficient production of green steel contributes to cost savings by minimizing environmental compliance fees and potential carbon taxes.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Green steel pipes offer significant installation advantages over cast iron, as their lighter weight and higher strength simplify handling and reduce labor costs. Cast iron pipes require specialized equipment due to their brittleness and heavy weight, increasing the complexity and risk during installation. Maintenance for green steel is minimal because of its corrosion resistance and durability, whereas cast iron demands regular inspections and repairs to address rust and cracking.
Suitability for Various Applications
Green steel exhibits superior environmental benefits and enhanced mechanical properties, making it highly suitable for applications requiring corrosion resistance and lightweight strength, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. Cast iron, known for its excellent compressive strength and durability, remains ideal for heavy-duty piping systems in municipal water infrastructure and sewage management. Choosing between green steel and cast iron depends on factors like environmental impact, mechanical requirements, and the specific demands of the pipe application.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Green steel pipes offer superior compliance with evolving environmental regulations such as the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and increasingly strict ISO 14001 standards, promoting sustainable production. Cast iron pipes often face challenges meeting these green standards due to higher carbon emissions in their manufacturing processes, limiting their acceptance in eco-conscious infrastructure projects. Adhering to industry benchmarks like ASTM A1011 for green steel ensures pipelines meet both durability and eco-compliance demands, surpassing traditional cast iron alternatives.
Future Trends in Sustainable Piping Solutions
Green steel, produced using low-carbon or hydrogen-based processes, is transforming sustainable piping solutions by significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional cast iron pipes. Future trends indicate a growing shift towards green steel pipes in infrastructure projects due to their superior durability, recyclability, and lower environmental impact. Innovations in green steel manufacturing technologies are expected to further enhance cost-effectiveness and promote widespread adoption in the sustainable piping industry.
Infographic: Green steel vs Cast iron for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com