Chromium enhances tool hardness and corrosion resistance, while vanadium improves wear resistance and toughness in tool making. Combining both elements optimizes steel performance for cutting and industrial tools.
Table of Comparison
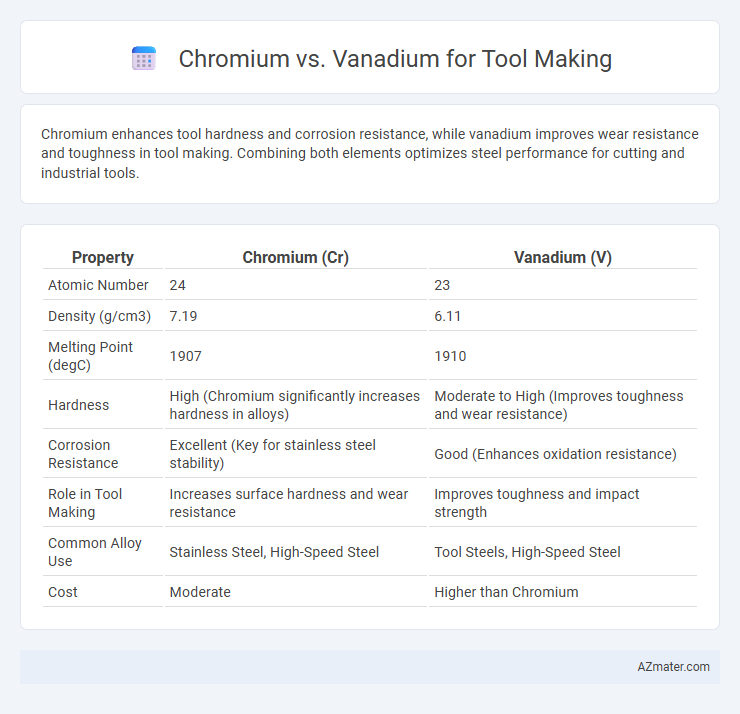
| Property | Chromium (Cr) | Vanadium (V) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 24 | 23 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 7.19 | 6.11 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 1907 | 1910 |
| Hardness | High (Chromium significantly increases hardness in alloys) | Moderate to High (Improves toughness and wear resistance) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Key for stainless steel stability) | Good (Enhances oxidation resistance) |
| Role in Tool Making | Increases surface hardness and wear resistance | Improves toughness and impact strength |
| Common Alloy Use | Stainless Steel, High-Speed Steel | Tool Steels, High-Speed Steel |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than Chromium |
Introduction to Chromium and Vanadium in Tool Making
Chromium enhances tool steel hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance by forming stable carbides, critical for cutting and shaping applications. Vanadium improves toughness, grain refinement, and thermal stability, contributing to tools that endure high impact and maintain sharpness under stress. Both elements play complementary roles in alloy formulations, optimizing tool performance for diverse industrial uses.
Chemical Properties: Chromium vs. Vanadium
Chromium exhibits high corrosion resistance and hardness due to its ability to form a stable oxide layer, making it valuable for enhancing surface durability in tool steels. Vanadium contributes to improved tensile strength and wear resistance by forming hard vanadium carbides that refine grain structure in alloys. Both elements significantly enhance tool performance, with chromium emphasizing oxidation resistance and vanadium focusing on toughness and hardness through carbide precipitation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Chromium significantly enhances tool steel's hardness and corrosion resistance, improving wear resistance and extending tool lifespan in demanding applications. Vanadium refines grain structure and increases toughness, providing superior impact resistance and preventing deformation under high stress. Combining these elements often results in tools with balanced mechanical strength and exceptional durability for heavy-duty industrial use.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Chromium significantly enhances corrosion resistance in tool steels by forming a thin, stable oxide layer that prevents surface degradation, making it ideal for tools exposed to harsh environments. Vanadium primarily contributes to wear resistance and toughness but offers limited improvement in oxidation resistance compared to chromium. Tools with higher chromium content maintain their structural integrity longer in corrosive and high-temperature conditions, whereas vanadium-rich alloys excel in durability but require protective coatings to prevent oxidation.
Impact on Hardness and Wear Resistance
Chromium significantly enhances hardness and wear resistance in tool steels by forming hard carbides that improve surface durability. Vanadium contributes to fine grain structure refinement, which elevates toughness while increasing wear resistance through stable carbide formation. Combining chromium and vanadium in tool alloys results in superior hardness and prolonged tool life due to synergistic effects on microstructure and carbide distribution.
Cost and Availability for Manufacturers
Chromium is generally more abundant and cost-effective than vanadium, making it a preferred choice for large-scale tool manufacturing where budget constraints are critical. Vanadium, though more expensive, offers superior strength and wear resistance, justifying its use in specialized or high-performance tools. Manufacturers must balance raw material costs with the desired tool durability and application requirements when selecting between chromium and vanadium.
Chromium vs. Vanadium in Steel Alloys
Chromium in steel alloys enhances corrosion resistance, hardness, and wear resistance, making it ideal for tools requiring durability and prolonged edge retention. Vanadium contributes to grain refinement and increases toughness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength in steel, which is crucial for impact-resistant and high-performance cutting tools. The combination of chromium and vanadium in tool steels optimizes hardness, toughness, and corrosion resistance for diverse industrial applications.
Applications: Which Tools Use Chromium or Vanadium?
Chromium is extensively used in cutting tools, drill bits, and saw blades due to its excellent hardness and corrosion resistance, enhancing tool durability under high-stress conditions. Vanadium is commonly found in impact tools, wrenches, and high-performance steels, where its ability to refine grain structure improves toughness and wear resistance. Tools requiring a balance of strength and resistance to abrasion often incorporate both elements to optimize performance and lifespan.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Chromium and vanadium both enhance tool steel durability, but chromium offers superior corrosion resistance, reducing environmental impact from rust and wear debris. Vanadium, while improving hardness and wear resistance, requires careful handling during alloying due to its toxic dust and fumes, posing greater safety risks in manufacturing. Choosing chromium-rich alloys mitigates environmental pollution and enhances worker safety in tool production processes.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Tools
Chromium enhances hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for tools exposed to moisture and wear, while vanadium improves toughness and fatigue resistance, ensuring durability under impact and repeated use. Selecting the right metal depends on the desired balance between hardness and toughness, with chromium alloys favored for cutting and abrasive tools, and vanadium alloys preferred for high-impact applications. Understanding these properties helps optimize tool performance and longevity in specific working conditions.
Infographic: Chromium vs Vanadium for Tool Making
 azmater.com
azmater.com