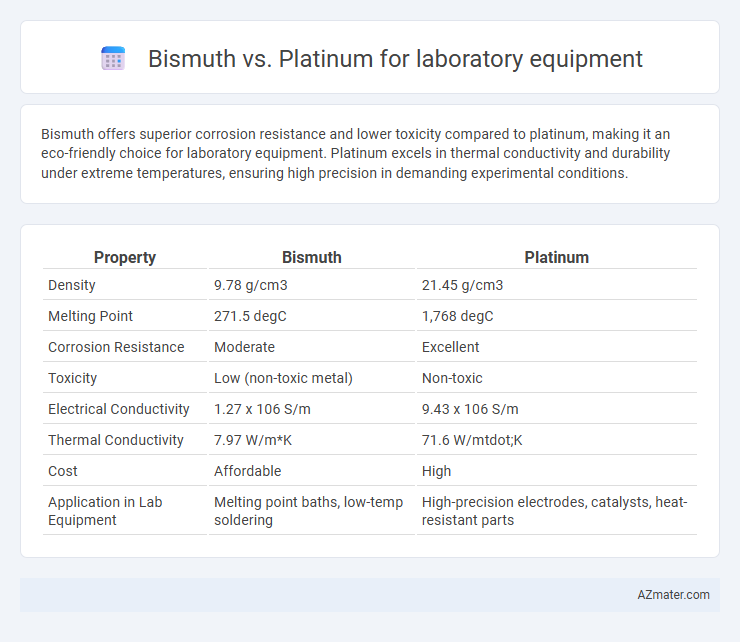
Bismuth offers superior corrosion resistance and lower toxicity compared to platinum, making it an eco-friendly choice for laboratory equipment. Platinum excels in thermal conductivity and durability under extreme temperatures, ensuring high precision in demanding experimental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth | Platinum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 9.78 g/cm3 | 21.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 271.5 degC | 1,768 degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Toxicity | Low (non-toxic metal) | Non-toxic |
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.27 x 106 S/m | 9.43 x 106 S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 7.97 W/m*K | 71.6 W/mtdot;K |
| Cost | Affordable | High |
| Application in Lab Equipment | Melting point baths, low-temp soldering | High-precision electrodes, catalysts, heat-resistant parts |
Introduction to Bismuth and Platinum in Laboratory Equipment
Bismuth and platinum serve distinct roles in laboratory equipment due to their unique physical and chemical properties. Bismuth, known for its low toxicity and excellent thermal stability, is often utilized in alloys, low-melting alloys, and as a protective coating in specialized laboratory tools. Platinum's exceptional resistance to corrosion, high melting point, and catalytic properties make it essential for crucibles, electrodes, and reaction vessels in high-temperature and electrochemical experiments.
Physical Properties: Bismuth vs Platinum
Bismuth exhibits a low thermal conductivity of 7.97 W/m*K and a melting point of 271.5degC, making it suitable for applications requiring thermal insulation. Platinum offers superior physical properties, including a high melting point of 1768.3degC and exceptional chemical stability, ideal for high-temperature laboratory equipment. The density of bismuth is 9.78 g/cm3, significantly lower than platinum's density of 21.45 g/cm3, influencing equipment weight and durability considerations.
Chemical Durability and Reactivity
Bismuth offers excellent chemical durability with low reactivity, making it resistant to many acids and ideal for corrosion-prone laboratory equipment. Platinum exhibits superior chemical inertness and exceptional resistance to oxidation and most chemicals, ensuring long-lasting performance in highly reactive environments. Both metals provide unique advantages, but platinum's unmatched stability under aggressive conditions often positions it as the preferred choice for critical laboratory applications.
Thermal Stability and Conductivity
Bismuth exhibits lower thermal conductivity and moderate thermal stability compared to platinum, making it less efficient for applications requiring rapid heat dissipation. Platinum offers exceptional thermal stability with a melting point of 1768degC and high thermal conductivity around 71.6 W/m*K, ensuring precise temperature control in laboratory equipment. The superior conductivity and heat resistance of platinum make it the preferred choice for high-performance scientific instruments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Bismuth offers a significantly lower cost compared to platinum, with bismuth metals priced at a fraction of platinum's market rate, making it a cost-effective alternative for laboratory equipment. The economic viability of bismuth is enhanced by its abundance and lower extraction costs, reducing overall expenses in equipment fabrication and maintenance. Although platinum exhibits superior chemical stability and resistance, bismuth's affordability provides a practical option for budget-conscious laboratory settings without compromising basic performance requirements.
Applications in Analytical Instruments
Bismuth offers a non-toxic, cost-effective alternative to platinum in laboratory analytical instruments, particularly in electrochemical sensors and electrodes for trace metal detection. Platinum remains superior in durability and catalytic activity, making it essential for high-precision applications like mass spectrometry and chromatography detectors. The choice between bismuth and platinum depends on the specific analytical requirements, balancing sensitivity, biocompatibility, and budget constraints.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Bismuth offers significant environmental advantages over platinum in laboratory equipment due to its lower toxicity and greater abundance, reducing ecological impact and resource depletion. Platinum's extraction and recycling often involve energy-intensive processes and hazardous chemicals, increasing environmental and occupational health risks. Choosing bismuth minimizes exposure to toxic heavy metals, promoting safer working conditions and sustainable laboratory practices.
Availability and Sourcing Challenges
Bismuth is relatively abundant in the Earth's crust and often sourced as a byproduct of lead, copper, and tin refining, making its availability more stable and cost-effective for laboratory equipment manufacturing. In contrast, platinum is a rare precious metal with limited global reserves primarily concentrated in South Africa and Russia, leading to high prices and supply vulnerabilities due to geopolitical factors. The sourcing challenges of platinum involve complex extraction processes, ethical concerns, and market fluctuations, which can delay procurement and increase overall costs compared to bismuth-based materials.
Performance in Specialized Laboratory Settings
Bismuth demonstrates excellent corrosion resistance and low toxicity, making it suitable for specialized laboratory equipment in biochemical and pharmaceutical research. Platinum offers superior catalytic properties, unmatched thermal stability, and exceptional durability under high-temperature and oxidative conditions, ideal for precision analytical instruments. The choice between bismuth and platinum hinges on specific laboratory requirements such as chemical inertness, temperature tolerance, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Material: Bismuth or Platinum?
Bismuth offers excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness for laboratory equipment, making it ideal for non-corrosive environments and disposable applications. Platinum excels in high-temperature stability, corrosion resistance, and catalytic properties, suited for demanding experiments and long-term use. Selecting between bismuth and platinum depends on the lab's specific temperature, chemical exposure, and budget requirements.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Platinum for Laboratory equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com