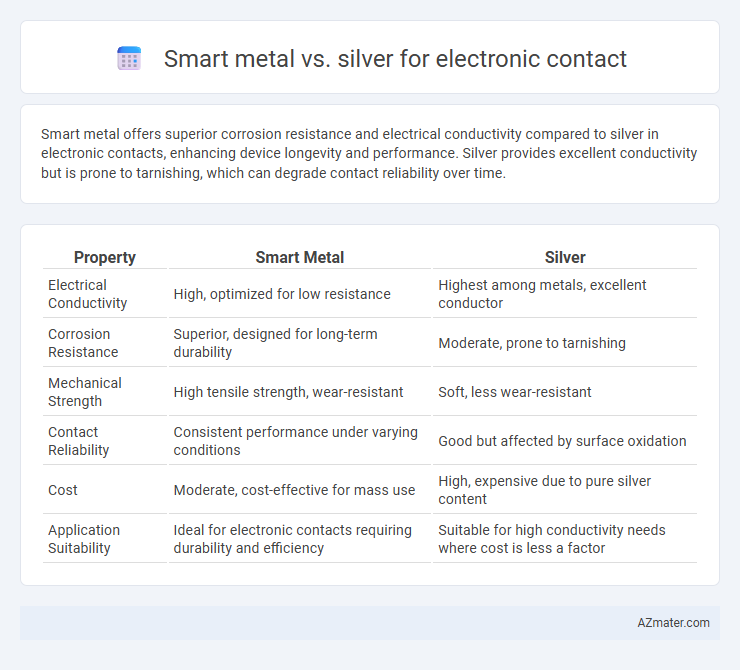
Smart metal offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to silver in electronic contacts, enhancing device longevity and performance. Silver provides excellent conductivity but is prone to tarnishing, which can degrade contact reliability over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Metal | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, optimized for low resistance | Highest among metals, excellent conductor |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior, designed for long-term durability | Moderate, prone to tarnishing |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, wear-resistant | Soft, less wear-resistant |
| Contact Reliability | Consistent performance under varying conditions | Good but affected by surface oxidation |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for mass use | High, expensive due to pure silver content |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for electronic contacts requiring durability and efficiency | Suitable for high conductivity needs where cost is less a factor |
Understanding Smart Metal and Silver in Electronics
Smart metal alloys, engineered for superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, outperform traditional silver in demanding electronic contact applications by reducing contact resistance and enhancing durability. Silver, despite its highest electrical conductivity among metals, suffers from tarnishing and wear, limiting long-term reliability in high-cycle switching environments. Advances in smart metal compositions optimize mechanical strength and electrical stability, making these materials increasingly preferred in precision connectors and high-frequency electronic components.
Key Properties of Smart Metal vs Silver
Smart metal for electronic contacts offers superior corrosion resistance, enhanced durability, and excellent conductivity tailored for long-term reliability, surpassing traditional silver in high-stress environments. Silver boasts the highest electrical conductivity among metals but suffers from tarnishing and reduced lifespan due to oxidation. Smart metal alloys incorporate elements that improve hardness and wear resistance while maintaining conductivity levels close to silver, making them more effective in rugged electronic applications.
Conductivity Comparison: Smart Metal vs Silver
Smart metal alloys designed for electronic contacts offer enhanced durability and corrosion resistance but typically exhibit lower electrical conductivity compared to pure silver, which remains the benchmark with a conductivity of about 63 MS/m at room temperature. Silver's superior conductivity ensures minimal contact resistance and efficient current flow, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications where signal integrity is critical. Despite silver's expense and susceptibility to tarnishing, its unmatched electrical properties often outweigh these drawbacks when conductivity is the primary concern over the mechanical advantages of smart metals.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Smart metals like copper alloys and conductive polymers offer superior cost efficiency compared to silver due to lower raw material expenses and enhanced durability, reducing long-term maintenance costs. Silver's excellent electrical conductivity is offset by its high price volatility and limited availability, making it less economically viable for large-scale electronic contact applications. Choosing smart metals improves supply chain stability and overall affordability while maintaining reliable electrical performance.
Durability and Longevity in Electronic Contacts
Smart metal alloys, often composed of silver-cadmium oxide or silver-nickel, offer superior durability and resistance to arc erosion compared to pure silver, making them ideal for high-load electronic contacts. Silver provides excellent conductivity but tends to wear faster and tarnish, reducing longevity in demanding electrical applications. The enhanced mechanical strength and reduced oxidation of smart metals extend service life and maintain consistent performance in electronic contacts.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Material Performs Better?
Smart metal alloys, engineered with enhanced corrosion-resistant properties, generally outperform pure silver in electronic contacts by maintaining conductivity and preventing oxidation over time. Silver, despite its excellent electrical conductivity, is prone to tarnishing and sulfur corrosion, which can degrade contact performance in harsh environments. Advanced smart metals such as gold-plated copper or specialized alloys provide superior protection against environmental factors, ensuring longer-lasting and more reliable electronic connections.
Application Areas: Where Each Material Excels
Smart metal alloys excel in high-frequency and high-precision electronic contacts due to their superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for advanced telecommunications and aerospace applications. Silver stands out in power distribution systems and automotive electronics because of its unmatched electrical conductivity and thermal management capabilities. Both materials are critical in electronic manufacturing, but smart metals are preferred for durability in harsh environments, while silver is favored for efficient current transmission in high-load circuits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart metal alloys used in electronic contacts often contain environmentally friendlier elements like copper and nickel, reducing reliance on precious metals such as silver, which has a higher environmental extraction cost and greater ecological footprint. Silver mining involves significant water use and toxic chemical byproducts, contributing to habitat degradation and pollution, whereas smart metals typically offer better recyclability and lower resource depletion. Sustainable electronic contact materials prioritize reduced environmental impact through efficient resource use, longer lifecycle, and minimal toxic waste generation, areas where smart metals demonstrate advantages over conventional silver contacts.
Industry Trends in Electronic Contact Materials
Smart metal alloys demonstrate increasing adoption in electronic contact applications due to their superior conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical durability compared to traditional silver contacts. Industry trends emphasize the shift towards smart metals containing elements like copper, tin, and rare earth metals to enhance performance while reducing reliance on expensive and tarnish-prone silver. Market analysis forecasts continuous growth in smart metal usage driven by higher demand for reliable, long-lasting components in automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics sectors.
Selecting the Right Material for Electronic Contacts
Smart metal alloys offer superior wear resistance and lower contact resistance compared to traditional silver contacts, enhancing device reliability in high-frequency applications. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance but may suffer from surface degradation and higher cost in demanding environments. Selecting the right material depends on factors like electrical load, environmental conditions, and cost-efficiency to ensure optimal performance and longevity of electronic contacts.
Infographic: Smart metal vs Silver for Electronic contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com