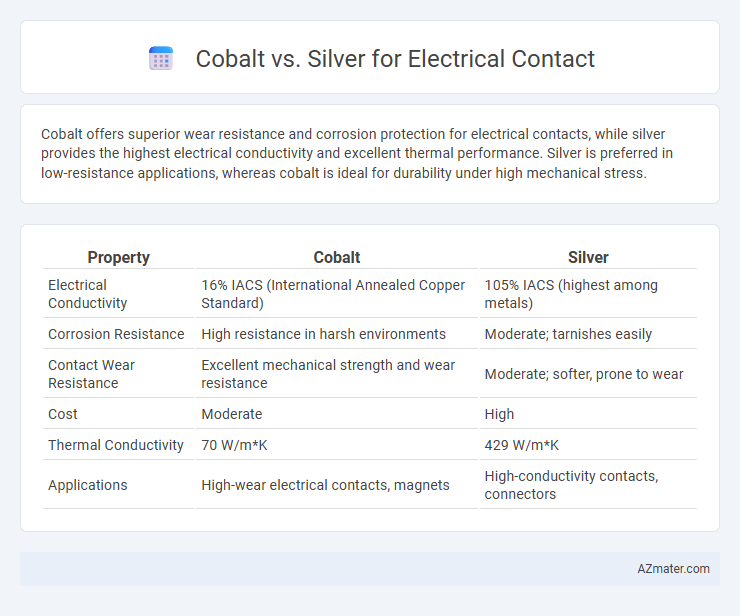
Cobalt offers superior wear resistance and corrosion protection for electrical contacts, while silver provides the highest electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance. Silver is preferred in low-resistance applications, whereas cobalt is ideal for durability under high mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cobalt | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 16% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) | 105% IACS (highest among metals) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance in harsh environments | Moderate; tarnishes easily |
| Contact Wear Resistance | Excellent mechanical strength and wear resistance | Moderate; softer, prone to wear |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Conductivity | 70 W/m*K | 429 W/m*K |
| Applications | High-wear electrical contacts, magnets | High-conductivity contacts, connectors |
Introduction: Importance of Electrical Contacts
Electrical contacts play a crucial role in ensuring reliable conductivity and minimal resistance in electrical circuits. Cobalt is valued for its high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding contact applications. Silver offers exceptional electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, which enhances overall circuit performance and efficiency.
Overview of Cobalt and Silver Properties
Cobalt offers high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and good conductivity, making it suitable for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Silver boasts the highest electrical and thermal conductivity among metals, along with excellent corrosion resistance and low contact resistance. While silver provides superior conductivity, cobalt's durability and resistance to deformation make it ideal for contacts requiring mechanical strength and longevity.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Silver exhibits superior electrical conductivity of approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it the highest among all metals for electrical contacts. Cobalt, in contrast, has a significantly lower conductivity around 17 x 10^6 S/m, which limits its efficiency in electrical contact applications. Silver's excellent conductivity ensures lower contact resistance and better performance in high-current and sensitive electronic components compared to cobalt.
Thermal Conductivity: Cobalt vs Silver
Silver exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity than cobalt, making it the preferred choice for electrical contacts requiring efficient heat dissipation. Silver's thermal conductivity is approximately 429 W/m*K, whereas cobalt's is around 100 W/m*K, highlighting silver's superior ability to conduct heat rapidly. This difference enhances silver's performance in applications where thermal management is critical to maintain contact reliability and prevent overheating.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Cobalt exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to silver in electrical contacts, making it more durable in harsh environments. Silver offers excellent electrical conductivity but is prone to tarnishing and corrosion, which can degrade performance over time. Cobalt's enhanced longevity and stability under oxidative stress provide a reliable choice for long-term electrical contact applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cobalt offers superior mechanical strength and resistance to wear compared to silver, making it ideal for electrical contacts subjected to heavy mechanical stress. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity but tends to deform and wear faster under repeated mechanical cycles, reducing durability. Combining cobalt with silver alloys enhances both durability and conductivity for demanding electrical contact applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Cobalt offers a cost-effective alternative to silver for electrical contacts due to its lower raw material price and greater abundance, reducing supply chain risks. Silver remains more expensive and less abundant, impacting large-scale applications despite its superior electrical conductivity. Manufacturers often balance cobalt's affordability and availability against silver's performance benefits when selecting materials for reliable electrical contacts.
Common Applications in Electrical Contacts
Cobalt alloys are commonly used in electrical contacts for applications requiring high wear resistance and excellent thermal stability, such as in aerospace connectors and industrial switches. Silver, known for its superior electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, is frequently used in high-performance electrical contacts, including circuit breakers, relays, and automotive electrical systems. Blended alloys combining silver with cobalt improve contact durability while maintaining optimal conductivity, making them ideal for heavy-duty electrical switching and power distribution equipment.
Environmental and Health Impacts
Cobalt in electrical contacts poses significant environmental and health risks due to its toxicity and potential to cause respiratory issues and skin sensitization. Silver is generally considered safer, with lower toxicity and minimal environmental impact, though excessive mining still affects ecosystems. Choosing silver contacts reduces hazardous waste and occupational health hazards compared to cobalt-based materials.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Cobalt and Silver
Cobalt offers superior wear resistance and durability for electrical contacts in high-load or harsh environment applications, while silver excels in electrical conductivity and thermal management, making it ideal for low-resistance, high-current circuits. Selecting between cobalt and silver depends largely on the specific operational demands, with cobalt favored for mechanical stability and silver preferred for optimal electrical performance. Balancing these properties ensures reliable contact performance and extended service life tailored to the device's functional requirements.
Infographic: Cobalt vs Silver for Electrical contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com