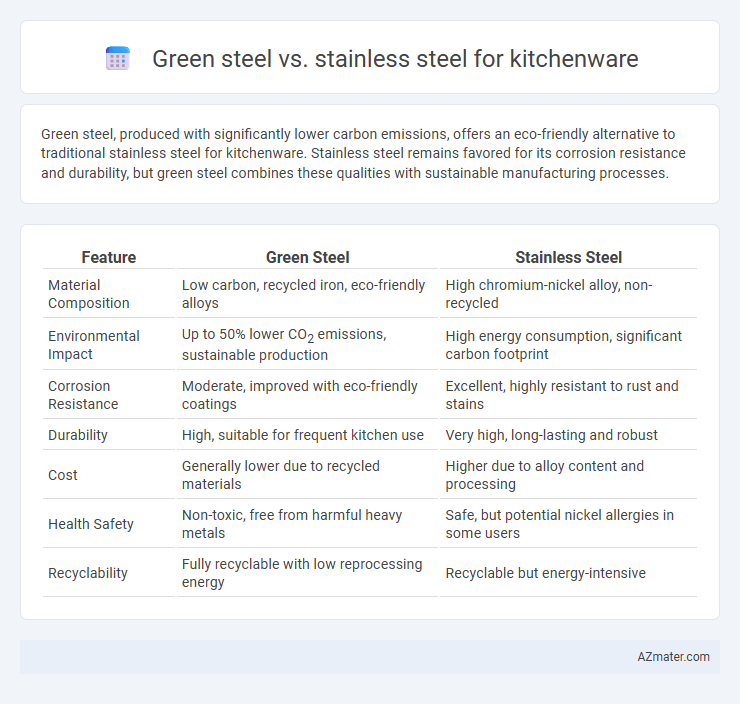
Green steel, produced with significantly lower carbon emissions, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional stainless steel for kitchenware. Stainless steel remains favored for its corrosion resistance and durability, but green steel combines these qualities with sustainable manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Low carbon, recycled iron, eco-friendly alloys | High chromium-nickel alloy, non-recycled |
| Environmental Impact | Up to 50% lower CO2 emissions, sustainable production | High energy consumption, significant carbon footprint |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, improved with eco-friendly coatings | Excellent, highly resistant to rust and stains |
| Durability | High, suitable for frequent kitchen use | Very high, long-lasting and robust |
| Cost | Generally lower due to recycled materials | Higher due to alloy content and processing |
| Health Safety | Non-toxic, free from harmful heavy metals | Safe, but potential nickel allergies in some users |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable with low reprocessing energy | Recyclable but energy-intensive |
Understanding Green Steel and Stainless Steel
Green steel, produced using environmentally friendly methods such as hydrogen reduction or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional stainless steel, which commonly relies on carbon-intensive blast furnaces. Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance, durability, and food safety, typically contains a mix of iron, chromium, and nickel, while green steel emphasizes reducing carbon emissions throughout the production process without compromising material quality. Understanding these differences helps consumers and manufacturers make informed decisions about kitchenware that balances sustainability with performance.
Environmental Impact: Green Steel vs Stainless Steel
Green steel significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing renewable energy and hydrogen-based reduction processes, unlike traditional stainless steel production which relies heavily on fossil fuels and produces substantial CO2 emissions. The use of recycled materials in green steel further lowers its environmental footprint, supporting circular economy principles in kitchenware manufacturing. Stainless steel, while durable and corrosion-resistant, remains energy-intensive to produce, making green steel a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Green steel manufacturing reduces carbon emissions by using hydrogen-based direct reduction or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, contrasting with stainless steel's traditional reliance on carbon-intensive blast furnaces. The production of green steel often involves recycled scrap steel and minimizes the use of harmful chemicals, promoting environmental sustainability in kitchenware. Stainless steel manufacturing includes alloying with chromium and nickel, which requires complex smelting and refining processes that contribute to higher energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Durability and Strength in Kitchenware
Green steel, produced using environmentally sustainable methods, offers impressive durability and corrosion resistance ideal for kitchenware, often matching or surpassing traditional stainless steel in strength. Stainless steel, especially grades like 304 and 316, remains highly favored for its excellent resistance to rust, staining, and mechanical wear under high temperatures and frequent use. Both metals provide robust performance, but green steel's reduced carbon footprint makes it an increasingly attractive option for eco-conscious consumers seeking long-lasting kitchen tools.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Green steel offers a unique matte finish and customizable color options that enhance modern kitchenware aesthetics and provide greater design flexibility compared to traditional stainless steel. Stainless steel maintains its timeless luster and smooth texture, delivering a classic, polished look favored in professional kitchens. Both materials afford durability, but green steel's eco-friendly production allows for innovative shapes and textures that appeal to sustainable and stylish kitchen designs.
Cost Analysis: Green Steel vs Stainless Steel
Green steel kitchenware generally offers a competitive cost advantage due to lower energy consumption and reduced carbon footprint during production, potentially qualifying for eco-friendly subsidies and incentives. Stainless steel kitchenware incurs higher raw material and manufacturing expenses because of its chromium and nickel content, leading to greater initial investments. Over time, maintenance and durability costs may offset initial prices, with stainless steel often providing longer lifespan benefits, while green steel aims to minimize environmental impact and associated long-term expenses.
Health and Food Safety Considerations
Green steel offers a lower carbon footprint and reduces exposure to toxic substances during production, making it an increasingly popular choice for sustainable kitchenware. Stainless steel remains the industry standard for health and food safety due to its excellent corrosion resistance, non-reactivity with acidic or alkaline foods, and durability that prevents leaching of harmful metals. Choosing kitchenware made from stainless steel or certified green steel ensures minimal risk of contaminating food while supporting environmental health.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Green steel kitchenware typically requires less intensive maintenance due to its corrosion-resistant coatings and environmentally friendly production processes that reduce surface degradation. Stainless steel is highly durable, offering excellent resistance to rust and staining, but it often demands regular polishing and careful drying to maintain its luster and prevent water spots. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, though green steel combines sustainability with lower upkeep, while stainless steel offers proven durability with traditional maintenance routines.
Market Availability and Consumer Choices
Green steel kitchenware is gaining traction in the market due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products, though its availability remains limited compared to the widespread presence of stainless steel. Stainless steel dominates the market with extensive options, proven durability, and established consumer trust, making it the preferred choice for most buyers. Market data indicates a gradual shift as manufacturers introduce green steel alternatives, but stainless steel maintains a strong lead in both retail presence and consumer preference.
Future Trends in Sustainable Kitchenware Materials
Green steel, produced with significantly lower carbon emissions using hydrogen or renewable energy, is gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional stainless steel in kitchenware manufacturing. Future trends emphasize the integration of green steel with recycled stainless steel to reduce environmental impact while maintaining durability and corrosion resistance essential for kitchen tools. Advancements in material science aim to enhance the recyclability and energy efficiency of these alloys, promoting eco-friendly kitchenware that aligns with increasing consumer demand for sustainability.
Infographic: Green steel vs Stainless steel for Kitchenware
 azmater.com
azmater.com