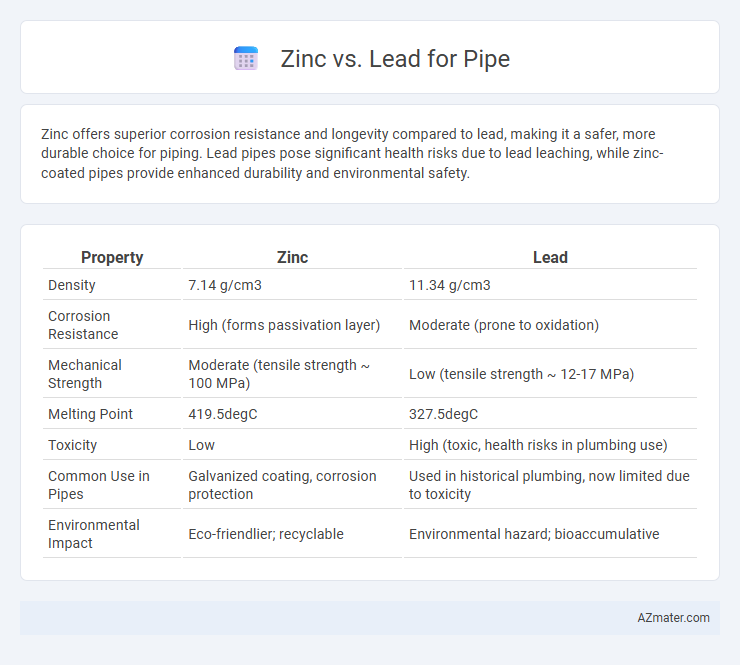
Zinc offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity compared to lead, making it a safer, more durable choice for piping. Lead pipes pose significant health risks due to lead leaching, while zinc-coated pipes provide enhanced durability and environmental safety.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zinc | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.14 g/cm3 | 11.34 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (forms passivation layer) | Moderate (prone to oxidation) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate (tensile strength ~ 100 MPa) | Low (tensile strength ~ 12-17 MPa) |
| Melting Point | 419.5degC | 327.5degC |
| Toxicity | Low | High (toxic, health risks in plumbing use) |
| Common Use in Pipes | Galvanized coating, corrosion protection | Used in historical plumbing, now limited due to toxicity |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendlier; recyclable | Environmental hazard; bioaccumulative |
Introduction: Zinc vs Lead Pipes
Zinc and lead pipes differ significantly in terms of durability and health impact, with zinc offering enhanced corrosion resistance and safer water quality compared to lead. Lead pipes pose serious health risks due to lead leaching into drinking water, which can cause neurological damage and other health issues. Zinc pipes, often used in galvanized steel applications, provide a protective coating that minimizes corrosion while ensuring safer plumbing infrastructure.
Historical Use of Zinc and Lead in Plumbing
Zinc and lead have been historically utilized in plumbing due to their malleability and resistance to corrosion, with lead pipes commonly used in ancient Rome and up to the early 20th century despite health risks. Zinc gained popularity in the 19th and 20th centuries as a protective coating for iron and steel pipes, enhancing their durability and preventing rust. Modern plumbing favors zinc-coated or galvanized pipes over lead to ensure safe drinking water and reduce lead poisoning hazards.
Chemical Properties: Zinc vs Lead
Zinc exhibits high corrosion resistance due to its ability to form a stable oxide layer, making it suitable for protective coatings on pipes. Lead, possessing a denser atomic structure and lower melting point, is more prone to corrosion in acidic environments, limiting its use in potable water systems. The distinct electrochemical potentials of zinc (-0.76 V) and lead (-0.13 V) affect their galvanic behavior, with zinc acting as a sacrificial anode to prevent lead pipe degradation.
Health Impacts of Lead and Zinc Pipes
Lead pipes pose significant health risks, including lead poisoning that can result in cognitive impairments, developmental delays, and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases due to lead leaching into drinking water. Zinc pipes offer a safer alternative, as zinc is an essential trace mineral with low toxicity and minimal leaching, reducing the risk of contamination in potable water systems. Replacing lead pipes with zinc or other non-toxic materials is crucial for safeguarding public health, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children and pregnant women.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Zinc-coated pipes, also known as galvanized pipes, offer superior corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes due to the protective zinc layer that prevents rust formation and extends pipe lifespan. Lead pipes are prone to corrosion, which can lead to structural damage and contamination, making them less durable and unsafe for potable water systems. The enhanced durability and corrosion resistance of zinc pipes make them a preferred choice in modern plumbing and industrial applications.
Environmental Considerations
Zinc-coated pipes offer better resistance to corrosion, reducing the risk of leaching harmful metals into water systems compared to lead pipes, which are notorious for contaminating drinking water with toxic lead. Environmental regulations have increasingly restricted lead pipe use due to its detrimental health impacts and long-term soil and water pollution. The use of zinc as a protective coating in piping systems promotes safer water quality and lower environmental toxicity.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Zinc-coated (galvanized) pipes offer easier installation due to their corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements compared to lead pipes, which require careful handling and specialized joints to avoid lead contamination. Maintenance of galvanized pipes is generally less intensive, as the zinc layer protects against rust, whereas lead pipes often demand regular monitoring and potential replacement to mitigate health risks from lead leaching. The durability and safety benefits of zinc make it a preferred choice in modern plumbing systems, minimizing long-term maintenance costs and ensuring safer water delivery.
Cost Comparison: Zinc vs Lead Pipes
Zinc pipes generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to lead pipes, with zinc being less expensive to produce and purchase due to its abundant availability and lower processing requirements. Lead pipes, although historically common, are more costly because of increased regulatory measures and health-related disposal expenses. The overall installation and maintenance costs for zinc pipes are typically lower, making them a financially advantageous option in most plumbing applications.
Modern Regulations and Standards
Modern regulations and standards prioritize zinc-coated (galvanized) pipes for corrosion resistance and environmental safety, whereas lead pipes are banned or heavily restricted due to lead's toxicity and health risks. The Safe Drinking Water Act and NSF/ANSI standards mandate the use of lead-free materials in potable water systems, effectively phasing out lead-containing pipes in favor of zinc and other safer alternatives. Compliance with these regulations ensures safer water quality and aligns with global efforts to reduce lead exposure in residential and commercial plumbing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Zinc offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity compared to lead, making it a safer and more durable choice for plumbing pipes. Lead poses significant health risks due to its toxicity and is banned or heavily restricted in most building codes worldwide. Selecting zinc pipes ensures compliance with regulations and promotes safer drinking water systems.
Infographic: Zinc vs Lead for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com