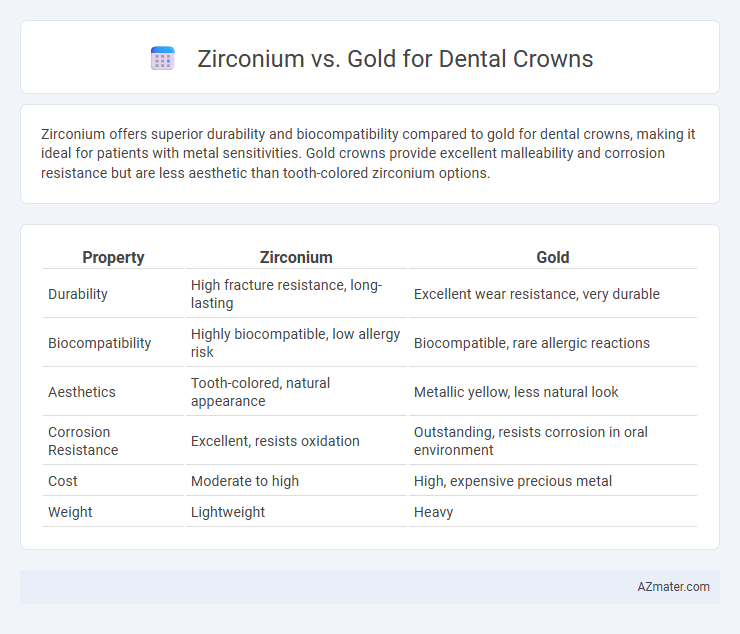
Zirconium offers superior durability and biocompatibility compared to gold for dental crowns, making it ideal for patients with metal sensitivities. Gold crowns provide excellent malleability and corrosion resistance but are less aesthetic than tooth-colored zirconium options.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High fracture resistance, long-lasting | Excellent wear resistance, very durable |
| Biocompatibility | Highly biocompatible, low allergy risk | Biocompatible, rare allergic reactions |
| Aesthetics | Tooth-colored, natural appearance | Metallic yellow, less natural look |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists oxidation | Outstanding, resists corrosion in oral environment |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High, expensive precious metal |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
Introduction: Zirconium vs Gold Dental Crowns
Zirconium and gold are two popular materials used in dental crowns, each offering distinct advantages. Zirconium crowns provide exceptional strength, durability, and a natural tooth-like appearance, making them ideal for aesthetic restoration. Gold crowns excel in longevity, biocompatibility, and resistance to wear, often preferred for their superior fit and minimal tooth reduction requirements.
Material Composition and Properties
Zirconium crowns consist of zirconium dioxide, a biocompatible ceramic known for its exceptional strength, fracture resistance, and natural tooth color, making it highly aesthetic and durable. Gold crowns are composed of a gold alloy combining gold with metals like copper and silver, offering excellent malleability, corrosion resistance, and long-lasting durability due to their ability to withstand heavy chewing forces. Zirconium crowns provide superior aesthetics and biocompatibility, while gold crowns excel in longevity and adaptability to tooth structure.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Zirconium crowns offer exceptional durability and high fracture resistance, making them ideal for withstanding heavy chewing forces and reducing the risk of chipping. Gold crowns are renowned for their superior malleability and long-lasting strength, allowing them to endure significant wear without compromising their integrity. Both materials provide excellent longevity, but zirconium's hardness offers enhanced resistance to cracking, while gold crowns exhibit unrivaled flexibility under stress.
Aesthetic Appeal: Zirconium vs Gold
Zirconium crowns offer superior aesthetic appeal due to their natural tooth-like translucency and color, closely mimicking real enamel without metal visibility. Gold crowns, while highly durable, lack the natural appearance and are typically noticeable due to their metallic yellow hue. Patients seeking a discreet, lifelike dental restoration often prefer zirconium for its ability to blend seamlessly with surrounding teeth.
Biocompatibility and Allergy Concerns
Zirconium crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to gold, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions and adverse tissue responses due to their inert ceramic composition. Gold crowns, although historically favored for their durability and malleability, can trigger allergic reactions in a minority of patients sensitive to metal alloys. Zirconium's hypoallergenic properties and resistance to corrosion make it a preferred choice for patients with metal sensitivities or concerns about long-term oral health compatibility.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Zirconium crowns offer superior longevity and wear resistance compared to gold crowns, lasting up to 15 years or more with excellent durability against chipping and fractures. Gold crowns, while highly biocompatible and gentle on opposing teeth, typically exhibit less resistance to abrasive wear over time and may require replacement sooner, averaging around 10-15 years. The high compressive strength of zirconium makes it ideal for patients seeking long-term restorative solutions with minimal degradation under daily oral stresses.
Cost Analysis: Zirconium vs Gold Crowns
Zirconium crowns typically cost between $800 to $2,500 per tooth, offering a more affordable option compared to gold crowns, which range from $1,000 to $2,800 depending on gold purity and market prices. The durability of gold crowns often justifies their higher initial investment due to their resistance to wear and corrosion, potentially reducing future dental expenses. Zirconium crowns provide a cost-effective, aesthetically pleasing solution but may require more frequent replacement, impacting long-term cost efficiency.
Clinical Indications and Suitability
Zirconium crowns offer high strength, biocompatibility, and excellent aesthetics, making them ideal for both anterior and posterior restorations, especially in patients with metal allergies or high aesthetic demands. Gold crowns provide superior durability and wear resistance, making them suitable for posterior teeth where occlusal forces are greatest, with a long history of clinical success in restorations requiring minimal tooth reduction. Clinical indications favor zirconium for visible areas due to its tooth-like appearance and gold for posterior crowns where function and longevity outweigh aesthetic considerations.
Maintenance and Oral Hygiene
Zirconium crowns offer superior resistance to plaque accumulation and staining, making them easier to maintain with regular brushing and flossing. Gold crowns, while highly durable and biocompatible, require meticulous oral hygiene to prevent gum irritation and buildup around the margins. Both materials benefit from routine dental check-ups to ensure longevity and optimal oral health.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Zirconium crowns offer superior biocompatibility, durability, and aesthetic appeal with their tooth-like translucency, making them ideal for visible front teeth restorations. Gold crowns provide exceptional strength and longevity, especially for molars subjected to heavy chewing forces, but lack the natural appearance of zirconium. Selecting the right material depends on balancing aesthetics, functional demands, and patient preferences for long-term dental crown performance.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Gold for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com