Carbon steel offers superior strength and durability for roofing, making it ideal for long-lasting, load-bearing structures, while zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance and self-healing properties, enhancing roof longevity in harsh weather conditions. Choosing between carbon steel and zinc depends on priorities like structural integrity versus maintenance and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
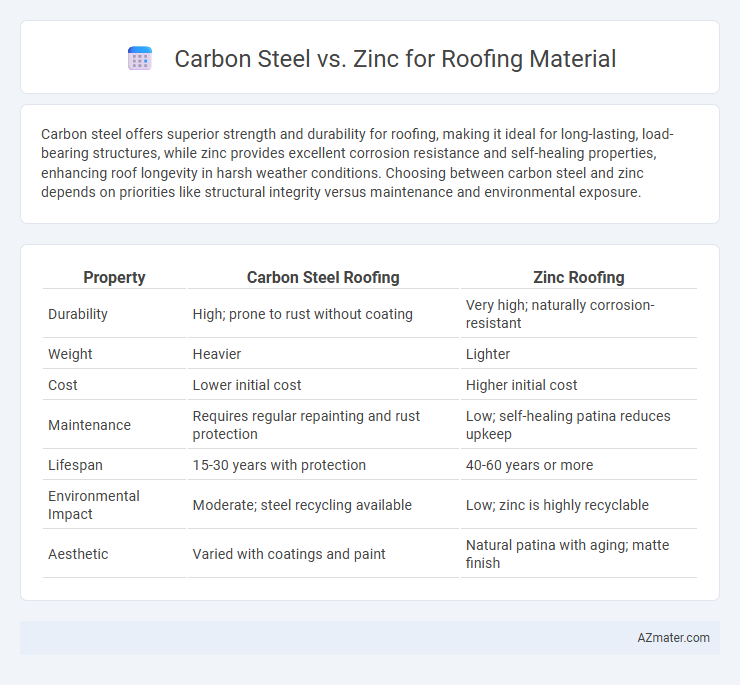
| Property | Carbon Steel Roofing | Zinc Roofing |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High; prone to rust without coating | Very high; naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires regular repainting and rust protection | Low; self-healing patina reduces upkeep |
| Lifespan | 15-30 years with protection | 40-60 years or more |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate; steel recycling available | Low; zinc is highly recyclable |
| Aesthetic | Varied with coatings and paint | Natural patina with aging; matte finish |
Introduction to Carbon Steel and Zinc Roofing
Carbon steel roofing offers exceptional strength and durability, making it a popular choice for residential and commercial buildings due to its resistance to impact and ability to support heavy loads. Zinc roofing is valued for its natural corrosion resistance, self-healing properties, and aesthetic appeal, often used in historical renovations and modern architectural designs. Both materials provide long-lasting protection but differ in maintenance requirements, lifespan, and initial cost, influencing their suitability depending on environmental conditions and project needs.
Material Composition and Properties
Carbon steel roofing consists primarily of iron with a carbon content between 0.05% and 0.25%, offering high tensile strength and durability with a moderate resistance to corrosion. Zinc roofing, composed mainly of zinc with trace amounts of titanium and copper, exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance due to the formation of a protective patina, enhancing longevity in harsh environments. While carbon steel provides superior mechanical strength, zinc's self-healing surface and low maintenance requirements make it ideal for long-term weather resistance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Carbon steel roofing offers exceptional durability with high tensile strength and resistance to impact, making it suitable for extreme weather conditions. Zinc roofing excels in longevity due to its natural corrosion resistance and self-healing patina, often lasting over 80 years with minimal maintenance. While carbon steel may require protective coatings to prevent rust, zinc's maintenance-free properties make it a superior choice for long-term roofing solutions.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Carbon steel roofing is prone to rust and corrosion when exposed to moisture and oxygen unless it is coated or galvanized for protection. Zinc roofing naturally forms a passive oxide layer that provides superior corrosion resistance, making it more durable in harsh weather conditions and coastal environments. The self-healing properties of zinc also extend its lifespan significantly compared to untreated or even galvanized carbon steel.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Carbon steel roofing offers a sleek, industrial aesthetic with versatile finishes that can mimic traditional materials like slate or wood, appealing to modern design trends. Zinc roofs provide a natural, matte patina that evolves over time, enhancing architectural character with a unique blend of durability and timeless charm. Both materials support custom shapes and profiles, but zinc's malleability allows for more intricate design options, making it favored in high-end architectural projects.
Installation Process and Requirements
Carbon steel roofing requires precise cutting and welding with specific tools to prevent rust and ensure structural integrity, demanding experienced installers and protective coatings. Zinc roofing offers easier installation due to its malleability, allowing seamless fitting and fewer fasteners, which reduces labor time and potential leak points. Both materials benefit from corrosion-resistant treatments, but zinc's natural patina reduces maintenance needs compared to carbon steel's frequent protective paint applications.
Maintenance Needs and Costs
Carbon steel roofing requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, often involving protective coatings and periodic inspections, resulting in moderate upkeep costs. Zinc roofing is highly resistant to corrosion and self-healing, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and long-term expenses. The initial cost of zinc is higher, but its low maintenance needs offer better cost efficiency over time compared to carbon steel.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel roofing consumes substantial energy during production, resulting in higher carbon emissions compared to zinc, which requires less energy and has a lower environmental footprint. Zinc is highly recyclable and can last over 80 years with minimal maintenance, contributing to its sustainability credentials, while carbon steel, although durable, often requires protective coatings that may contain harmful chemicals. The recyclability and longevity of zinc roofing support sustainable building practices by reducing waste and the need for frequent replacements.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Carbon steel roofing is generally more affordable upfront, with prices ranging from $4 to $7 per square foot, compared to zinc, which costs between $10 and $15 per square foot. Long-term costs favor zinc due to its superior corrosion resistance and longevity, often lasting over 80 years with minimal maintenance, whereas carbon steel may require additional protective coatings and more frequent repairs, increasing lifetime expenses. The total cost of ownership for zinc can be lower despite higher initial investment, making it a cost-effective choice for durable roofing solutions.
Choosing the Right Roofing Material for Your Project
Carbon steel roofing offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for areas prone to harsh weather conditions, while zinc roofing excels in corrosion resistance and self-healing properties, extending its lifespan to over 80 years. Cost considerations also influence the choice, as carbon steel is generally more affordable but requires protective coatings to prevent rust, whereas zinc's natural patina reduces maintenance needs. Selecting between carbon steel and zinc roofing depends on project budget, environmental exposure, and desired longevity for optimal performance.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Zinc for Roofing material
 azmater.com
azmater.com