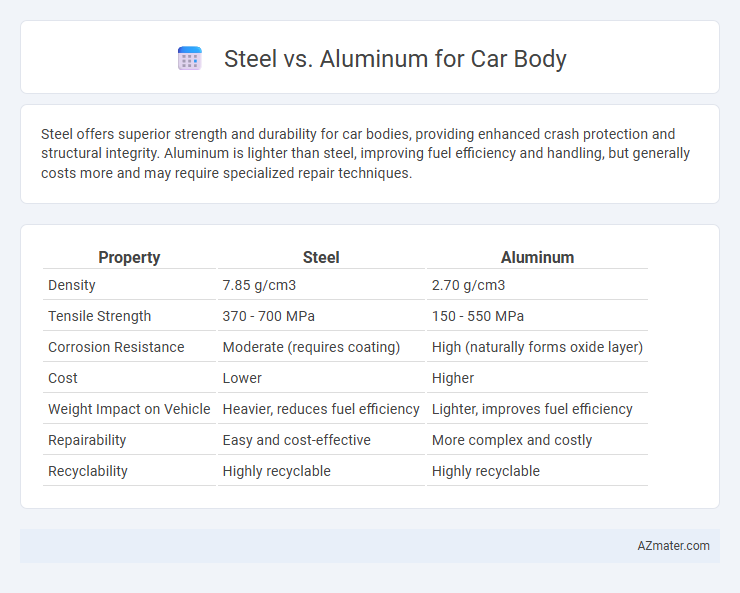
Steel offers superior strength and durability for car bodies, providing enhanced crash protection and structural integrity. Aluminum is lighter than steel, improving fuel efficiency and handling, but generally costs more and may require specialized repair techniques.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.85 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 370 - 700 MPa | 150 - 550 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (requires coating) | High (naturally forms oxide layer) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Weight Impact on Vehicle | Heavier, reduces fuel efficiency | Lighter, improves fuel efficiency |
| Repairability | Easy and cost-effective | More complex and costly |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Highly recyclable |
Introduction to Car Body Materials: Steel vs Aluminum
Steel and aluminum are the primary materials used in modern car bodies, each offering distinct advantages in strength, weight, and cost. Steel provides superior durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for structural components, while aluminum's lightweight nature enhances fuel efficiency and handling performance. Advances in alloy technology and manufacturing processes continue to influence the choice between steel and aluminum in automotive design for optimized safety and efficiency.
Historical Evolution of Steel and Aluminum in Automobiles
Steel dominated early automobile manufacturing due to its strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, enabling mass production of robust car bodies in the 20th century. Aluminum gained prominence in the late 20th and early 21st centuries as manufacturers sought lighter materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, leading to aluminum alloys being used increasingly in high-performance and luxury vehicles. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing processes have continually refined the use of both metals, balancing strength, weight, and cost in modern automotive design.
Material Properties: Strength, Weight, and Durability
Steel offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for vehicle safety and structural integrity, while aluminum boasts a significantly lighter weight that improves fuel efficiency and handling. Aluminum's corrosion resistance enhances long-term durability, although steel generally provides better fatigue strength and is more cost-effective for large-scale production. The choice between steel and aluminum for car bodies hinges on balancing strength requirements with the benefits of reduced weight and corrosion resistance.
Cost Comparison: Steel versus Aluminum Manufacturing
Steel offers a lower material cost and is widely used in car body manufacturing due to its affordability and ease of fabrication. Aluminum, while more expensive upfront, provides benefits in weight reduction and fuel efficiency that can offset initial costs over the vehicle's lifespan. The manufacturing process for aluminum involves higher energy consumption and specialized techniques, leading to increased production expenses compared to steel.
Fuel Efficiency and Performance Impacts
Steel offers higher strength and durability for car bodies, enhancing crash safety but adding significant weight, which can reduce fuel efficiency compared to aluminum. Aluminum's lighter weight improves fuel economy by reducing the vehicle's overall mass, leading to better acceleration and handling performance. However, aluminum may require more complex manufacturing processes and can have different impact resistance characteristics, influencing long-term performance and repair costs.
Crash Safety and Structural Integrity
Steel offers superior crash safety and structural integrity for car bodies due to its higher tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities, which effectively protect passengers during collisions. Advanced high-strength steel (AHSS) enhances rigidity while maintaining impact resistance, enabling better crash energy management compared to aluminum. Although aluminum is lighter and resists corrosion, steel's durability and ability to maintain shape under impact make it the preferred choice for maximizing occupant protection in automotive safety design.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to steel due to its natural oxide layer that protects against rust and environmental damage. Steel, while stronger and more impact-resistant, requires protective coatings such as galvanization to prevent corrosion and extend vehicle longevity. Advances in high-strength, coated steel improve durability, but aluminum remains the preferred material for long-term corrosion resistance in automotive body panels.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Steel car bodies offer high recyclability with a recycling rate of over 90%, significantly reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient production technologies and widespread steel recycling infrastructure. Aluminum offers a lightweight alternative, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions during vehicle use, but its production requires substantially more energy, leading to higher initial carbon footprints. Sustainable automotive design balances aluminum's efficiency benefits with steel's recyclability to optimize environmental performance over a vehicle's lifecycle.
Repair, Maintenance, and Insurance Considerations
Steel car bodies generally offer easier and less expensive repair options due to widespread availability of compatible parts and established repair techniques, whereas aluminum bodies often require specialized tools and trained technicians, increasing repair costs. Maintenance for steel vehicles may involve more frequent rust prevention measures, while aluminum resists corrosion but can suffer from fatigue and requires careful inspection for cracks. Insurance premiums may be higher for aluminum-bodied cars because of costlier repairs and parts, impacting overall ownership expenses.
Future Trends in Automotive Body Materials
Advancements in automotive body materials show a growing preference for aluminum due to its lightweight properties, which improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, aligning with stricter environmental regulations. Steel continues to evolve with high-strength alloys and advanced manufacturing techniques, maintaining its dominance through cost-effectiveness and structural integrity. Emerging trends highlight hybrid materials combining steel and aluminum, maximizing strength-to-weight ratios and facilitating the production of safer, more energy-efficient vehicles.
Infographic: Steel vs Aluminum for Car Body
 azmater.com
azmater.com