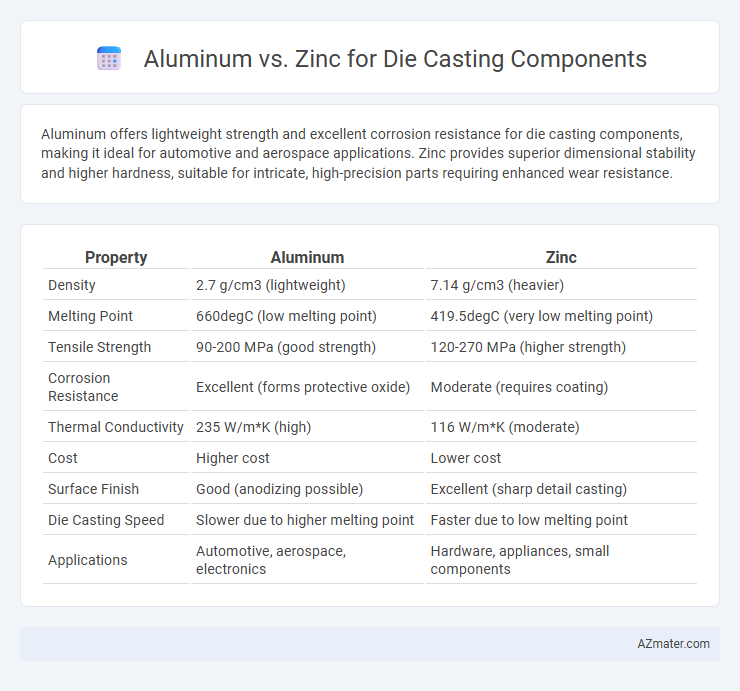
Aluminum offers lightweight strength and excellent corrosion resistance for die casting components, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Zinc provides superior dimensional stability and higher hardness, suitable for intricate, high-precision parts requiring enhanced wear resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.7 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 7.14 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Melting Point | 660degC (low melting point) | 419.5degC (very low melting point) |
| Tensile Strength | 90-200 MPa (good strength) | 120-270 MPa (higher strength) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (forms protective oxide) | Moderate (requires coating) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 235 W/m*K (high) | 116 W/m*K (moderate) |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Surface Finish | Good (anodizing possible) | Excellent (sharp detail casting) |
| Die Casting Speed | Slower due to higher melting point | Faster due to low melting point |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, electronics | Hardware, appliances, small components |
Introduction to Die Casting: Aluminum vs Zinc
Die casting commonly uses aluminum and zinc due to their unique material properties optimal for precision components. Aluminum offers lightweight strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace parts. Zinc provides superior fluidity for intricate molds, higher ductility, and cost-effectiveness, well-suited for complex small components in electronics and hardware.
Material Properties: Aluminum and Zinc Explained
Aluminum offers a superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for lightweight die casting components requiring durability. Zinc provides high dimensional accuracy and superior surface finish due to its low melting point and excellent fluidity, which allows for intricate designs. Both metals have distinct thermal conductivity levels, with aluminum featuring high thermal dissipation useful in heat-sensitive applications, while zinc's lower melting temperature ensures faster cycle times in manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminum die casting components exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet robust materials. Zinc offers higher tensile strength and excellent wear resistance, contributing to enhanced durability in high-stress environments. The choice between aluminum and zinc depends on specific durability requirements, with aluminum favored for corrosion resistance and zinc preferred for abrasion resistance.
Weight and Density Differences
Aluminum die casting components offer a significant weight advantage due to aluminum's lower density of approximately 2.7 g/cm3 compared to zinc's density of around 7.1 g/cm3. This density difference makes aluminum parts substantially lighter, ideal for applications requiring weight reduction without sacrificing strength. The lighter weight of aluminum also contributes to enhanced fuel efficiency and better overall performance in automotive and aerospace industries.
Corrosion Resistance in Aluminum vs Zinc
Aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc in die casting components due to its natural oxide layer that protects against environmental degradation. Zinc alloys tend to corrode faster, especially in humid or acidic environments, compromising the longevity of the component. Selecting aluminum for die casting improves durability and reduces maintenance costs in applications prone to corrosion.
Manufacturing Process and Efficiency
Aluminum die casting offers faster cycle times due to its lower melting point of about 660degC compared to zinc's 420degC, enabling quicker mold filling and solidification. The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces wear on tooling and injection systems, enhancing equipment longevity and reducing downtime. Zinc's higher fluidity allows for more intricate designs and thinner walls, but aluminum components typically provide better strength-to-weight ratios, improving overall manufacturing efficiency for structural applications.
Cost Analysis: Aluminum vs Zinc Die Casting
Aluminum die casting typically incurs higher raw material costs compared to zinc, but offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Zinc die casting benefits from lower melting temperatures, resulting in faster production cycles and decreased energy consumption, translating to reduced manufacturing costs. Overall, zinc is more cost-effective for high-volume, complex parts requiring tight tolerances, while aluminum is preferred for lightweight, structurally demanding components despite its higher initial cost.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Aluminum offers superior design flexibility and complexity for die casting components due to its lighter weight and excellent fluidity, enabling intricate shapes and thinner walls. Zinc's lower melting point allows for faster cycle times but limits the achievable detail and thinness compared to aluminum. Both metals support precise component design, but aluminum excels in applications demanding high complexity and structural performance.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Aluminum die casting offers a smooth, bright surface finish with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for aesthetically demanding applications. Zinc die casting provides superior detail reproduction and a shiny, attractive appearance but may require additional surface treatments to enhance durability. Both metals support a range of finishes, but aluminum's natural luster and resistance to oxidation often result in longer-lasting, high-quality aesthetics.
Best Applications for Aluminum and Zinc Die Casting
Aluminum die casting excels in applications requiring lightweight, high-strength components such as automotive parts, aerospace components, and consumer electronics housings due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Zinc die casting is ideal for intricate, high-precision parts with thin walls found in electrical connectors, hardware fittings, and toys, benefiting from its superior castability and dimensional stability. Both materials offer distinct advantages that align with specific industry needs, optimizing performance and production efficiency.
Infographic: Aluminum vs Zinc for Die casting component
 azmater.com
azmater.com