Tungsten offers exceptional wear resistance and high melting point, making it ideal for electrical relay contacts exposed to arcing. Rhodium provides superior corrosion resistance and lower contact resistance, enhancing relay performance and longevity in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
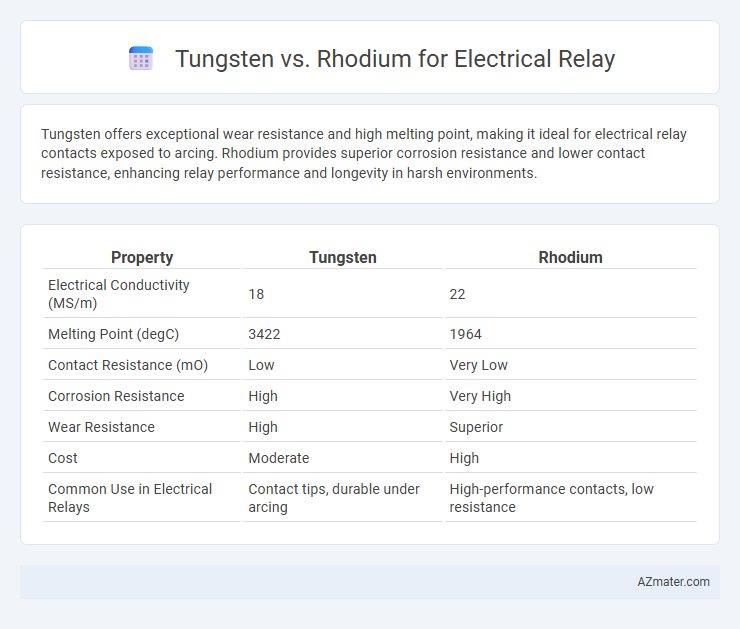
| Property | Tungsten | Rhodium |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity (MS/m) | 18 | 22 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 3422 | 1964 |
| Contact Resistance (mO) | Low | Very Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Very High |
| Wear Resistance | High | Superior |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Common Use in Electrical Relays | Contact tips, durable under arcing | High-performance contacts, low resistance |
Introduction: Tungsten vs Rhodium in Electrical Relays
Tungsten and rhodium are critical materials used in electrical relays due to their unique electrical and physical properties. Tungsten offers exceptional wear resistance and high melting point, making it ideal for handling high currents with minimal degradation. Rhodium provides superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, enhancing relay performance in demanding and harsh environments.
Key Properties of Tungsten for Electrical Contacts
Tungsten exhibits exceptional hardness and high melting point of 3,422degC, making it ideal for electrical relay contacts subjected to intense arcing and wear. Its excellent electrical conductivity combined with strong resistance to arc erosion ensures reliable performance and longevity in switching applications. Tungsten's low thermal expansion coefficient minimizes contact distortion under thermal cycling, enhancing stability and durability in harsh operating environments.
Key Properties of Rhodium for Electrical Contacts
Rhodium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and superior hardness, making it highly durable for electrical relay contacts exposed to harsh environments. Its excellent electrical conductivity combined with a low contact resistance ensures efficient current flow and minimal signal loss. Moreover, rhodium's high melting point and resistance to oxidation significantly extend the lifespan of electrical contacts in relays, outperforming tungsten in reliability and maintenance requirements.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Tungsten and rhodium differ significantly in electrical conductivity, with rhodium exhibiting higher conductivity at approximately 21.0 x 10^6 S/m compared to tungsten's 18.2 x 10^6 S/m, enhancing contact performance in electrical relays. Tungsten offers superior arc resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-current switching applications despite its slightly lower conductivity. Rhodium's excellent corrosion resistance and low contact resistance ensure reliable signal integrity in precision relay contacts.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Tungsten exhibits exceptional mechanical strength and resistance to wear, making it highly durable under the repetitive mechanical stresses found in electrical relays. Rhodium, although possessing good corrosion resistance, offers lower mechanical strength compared to tungsten, which can limit its performance in high-wear relay contacts. For relay applications requiring robust durability and long-term mechanical reliability, tungsten is generally preferred over rhodium.
Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance
Tungsten exhibits high oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for electrical relays operating in harsh environments, but it is prone to surface corrosion when exposed to moisture. Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and oxidation stability due to its noble metal properties, ensuring prolonged relay contact durability and minimal resistance increase over time. The choice between tungsten and rhodium for relay contacts depends on the operating conditions, with rhodium preferred for enhanced long-term oxidation and corrosion protection.
Cost and Availability of Tungsten and Rhodium
Tungsten offers a cost-effective solution for electrical relays due to its abundance and lower market price compared to rhodium, which remains scarce and significantly more expensive. The high demand and limited supply of rhodium result in price volatility and procurement challenges, impacting production costs. Tungsten's widespread availability ensures steadier supply chains and budget-friendly manufacturing in relay applications.
Performance in High-Voltage Applications
Tungsten electrical relays offer exceptional durability and high melting point, making them ideal for high-voltage applications where arc resistance is critical. Rhodium relays provide superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, ensuring stable contact resistance and longevity under frequent switching at elevated voltages. Comparing performance, tungsten excels in thermal stability and arc suppression, while rhodium delivers enhanced reliability in maintaining low contact resistance during rapid cycling.
Suitability for Specific Relay Types
Tungsten's high melting point and excellent arc resistance make it ideal for high-current electrical relays such as contactors and power relays used in industrial settings. Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and low contact resistance, making it suitable for low-voltage signal relays and precision applications requiring stable conductivity. Selecting between tungsten and rhodium depends largely on relay operating conditions, with tungsten favored for heavy-duty applications and rhodium preferred for reliability in low-current, high-precision environments.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Material for Electrical Relays
Tungsten offers superior durability and high melting point, making it ideal for relays exposed to extreme electrical and thermal stress. Rhodium provides excellent corrosion resistance and low electrical contact resistance, ensuring reliable performance in precision applications. Selecting between tungsten and rhodium depends on balancing the need for mechanical robustness with conductivity and corrosion resistance in the specific relay environment.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Rhodium for Electrical Relay
 azmater.com
azmater.com