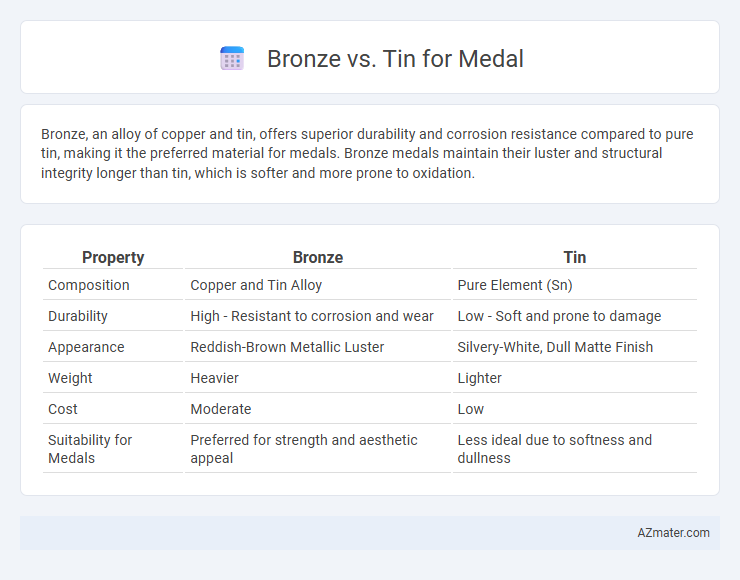
Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to pure tin, making it the preferred material for medals. Bronze medals maintain their luster and structural integrity longer than tin, which is softer and more prone to oxidation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Tin Alloy | Pure Element (Sn) |
| Durability | High - Resistant to corrosion and wear | Low - Soft and prone to damage |
| Appearance | Reddish-Brown Metallic Luster | Silvery-White, Dull Matte Finish |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Suitability for Medals | Preferred for strength and aesthetic appeal | Less ideal due to softness and dullness |
Introduction: Bronze vs Tin for Medals
Bronze, an alloy primarily consisting of copper and tin, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to pure tin, making it a preferred material for medals. Tin, while sweeter in luster and more affordable, lacks the mechanical strength bronze provides, resulting in medals that are more prone to deformation and wear over time. The combination of copper and tin in bronze enhances the aesthetic appeal and longevity of medals, solidifying its dominance in award manufacturing.
Historical Use of Bronze and Tin in Medals
Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, has been historically favored for medals due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and pleasing patina, with roots tracing back to ancient civilizations such as Greece and Rome where it symbolized strength and honor. Tin, while less common as a standalone metal for medals, plays a crucial role in bronze alloys by enhancing hardness and flexibility, which improves the medal's longevity and detail retention. The combined use of bronze and tin in medal production reflects centuries of metallurgical advancements that balance aesthetic appeal with functional resilience.
Composition and Properties: Bronze vs Tin
Bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, features enhanced strength, corrosion resistance, and durability compared to pure tin, which is softer and more malleable but prone to oxidation and wear. The typical bronze alloy contains about 12-12.5% tin, providing hardness suitable for medal crafting, while tin's lower melting point and brittleness limit its use in durable awards. Bronze's superior tensile strength and resistance to deformation make it the preferred choice for medals requiring longevity and detailed engraving.
Aesthetic Differences in Medal Appearance
Bronze medals exhibit a warm, rich brown tone with subtle reddish undertones, creating a classic and timeless appearance, while tin medals tend to have a cooler, silver-gray hue that appears more muted and industrial. The natural oxidation process enhances bronze's patina, adding depth and character over time, whereas tin maintains a relatively uniform finish that can appear less vibrant. These distinct aesthetic qualities influence the perceived prestige and historic value of the medals in competitive and commemorative contexts.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Bronze medals, composed mainly of copper and tin, offer superior durability and resistance to corrosion compared to pure tin medals, making them ideal for long-term display and preservation. Tin medals, while lighter and softer, are more prone to scratching, denting, and oxidation, which can diminish their aesthetic appeal over time. The alloy properties of bronze contribute to enhanced structural integrity and longevity, ensuring that bronze medals maintain their condition better under physical stress and environmental exposure.
Cost and Availability of Bronze and Tin
Bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, generally costs more than pure tin due to the higher price of copper and the manufacturing process involved. Tin is more readily available as a raw metal, but the demand for bronze in various industries can affect its overall cost and availability. The fluctuating prices of copper and tin on global markets significantly influence the cost-effectiveness and supply stability of bronze medals compared to those made solely from tin.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, generally has a lower environmental impact compared to pure tin due to its longer lifecycle and durability in medals, reducing the need for frequent replacements. The extraction of copper and tin both pose ecological challenges, but recycling bronze medals significantly lowers carbon emissions and conserves natural resources, enhancing sustainability. Tin's mining process can be more environmentally damaging due to habitat disruption and toxic waste, making bronze a more sustainable choice when sourced and recycled responsibly.
Cultural Significance in Medal Crafting
Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, holds profound cultural significance in medal crafting due to its historical association with durability and achievement since ancient civilizations. Tin's addition to copper enhances bronze's strength and corrosion resistance, symbolizing resilience and prestige in commemorative medals. The enduring use of bronze medals in competitions and awards signifies honor and valor, reflecting societal values rooted in tradition and craftsmanship.
Modern Trends in Medal Materials
Modern trends in medal materials highlight a shift from traditional bronze to advanced bronze-tin alloys that enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. Bronze, typically composed of copper with varying tin percentages, is favored for its strength and corrosion resistance, while tin addition improves the medal's luster and reduces brittleness. Innovations in alloy composition and surface treatments have optimized the balance between historic bronze attributes and contemporary demands for lightweight, long-lasting, and visually striking medals.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metal for Medals
Bronze offers superior durability and a rich, traditional appearance, making it ideal for long-lasting medals that symbolize prestige. Tin provides a cost-effective and lightweight alternative, suitable for casual or temporary awards where budget and ease of production are priorities. Selecting the right metal depends on balancing factors like longevity, aesthetic appeal, and budget requirements specific to the awarding event.
Infographic: Bronze vs Tin for Medal
 azmater.com
azmater.com