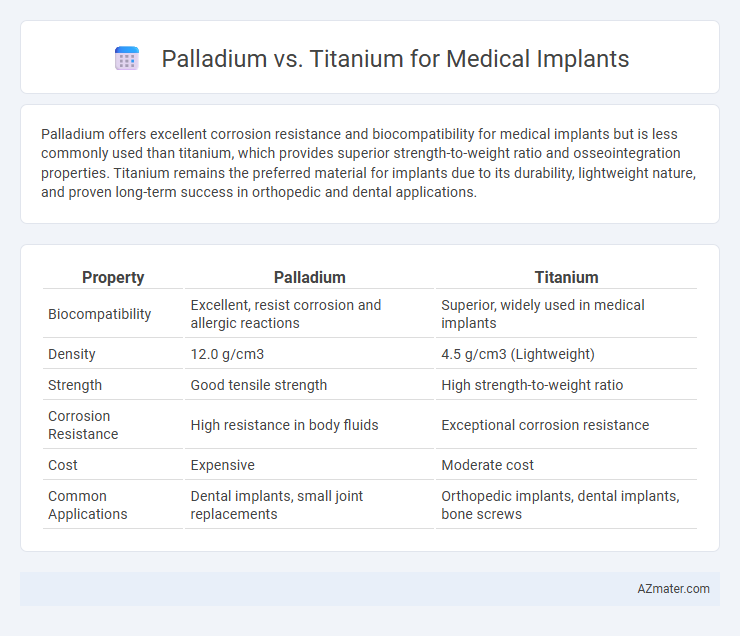
Palladium offers excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility for medical implants but is less commonly used than titanium, which provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration properties. Titanium remains the preferred material for implants due to its durability, lightweight nature, and proven long-term success in orthopedic and dental applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Palladium | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, resist corrosion and allergic reactions | Superior, widely used in medical implants |
| Density | 12.0 g/cm3 | 4.5 g/cm3 (Lightweight) |
| Strength | Good tensile strength | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance in body fluids | Exceptional corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Expensive | Moderate cost |
| Common Applications | Dental implants, small joint replacements | Orthopedic implants, dental implants, bone screws |
Introduction to Medical Implant Materials
Palladium and titanium are prominent materials in medical implant manufacturing due to their biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Titanium, widely used for orthopedic and dental implants, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration properties. Palladium, often utilized in dental alloys and certain implant coatings, provides superior malleability and resistance to tarnish, enhancing long-term durability in biological environments.
Overview of Palladium in Medical Implants
Palladium is valued in medical implants for its excellent biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and ability to integrate well with human tissues, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or implant rejection. Its high density and malleability allow for durable and precisely engineered components, particularly in dental and orthopedic applications where longevity and strength are crucial. Palladium's resistance to wear and tarnish contributes to the longevity of implants, making it a reliable choice for long-term medical device performance.
Overview of Titanium in Medical Implants
Titanium is widely used in medical implants due to its exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio. Its ability to osseointegrate with bone tissue makes it ideal for dental implants, orthopedic devices, and cardiovascular components. Medical-grade titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-4V, provide enhanced mechanical properties while minimizing allergic reactions and tissue rejection.
Biocompatibility: Palladium vs Titanium
Titanium exhibits superior biocompatibility due to its stable oxide layer that resists corrosion and integrates well with bone tissue, making it the preferred choice for medical implants. Palladium, while biocompatible and often used in dental alloys, has a higher risk of allergic reactions and metal ion release compared to titanium. Studies indicate titanium's bioinert properties promote better osseointegration and long-term implant success rates over palladium-based materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium exhibits superior mechanical strength and fatigue resistance compared to palladium, making it the preferred choice for load-bearing medical implants. Palladium, while biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, has lower tensile strength and is less durable under repetitive stress conditions. Titanium alloys provide enhanced longevity and structural integrity critical for long-term implant success in orthopedic and dental applications.
Corrosion Resistance in Biological Environments
Palladium and titanium exhibit distinct corrosion resistance properties in biological environments critical for medical implants. Titanium forms a stable and highly protective titanium dioxide (TiO2) passive layer that offers excellent resistance to corrosion, ensuring long-term biocompatibility and minimal ion release. Palladium, while corrosion-resistant due to its noble metal status, may not form as robust a passive layer as titanium, potentially affecting its durability and performance in the aggressive ionic conditions of physiological fluids.
Allergic Reactions and Patient Safety
Palladium and titanium both serve as materials for medical implants, with titanium being highly favored due to its exceptional biocompatibility and minimal allergic reactions in patients. While palladium exhibits good corrosion resistance, it carries a higher risk of metal hypersensitivity, leading to allergic responses in some patients. Titanium's low allergenic profile and strong osseointegration make it the preferred choice for ensuring patient safety and implant longevity.
Cost and Availability of Palladium and Titanium
Palladium is generally more expensive and less abundant than titanium, which contributes to higher costs in medical implant applications. Titanium's wide availability, biocompatibility, and relatively low price make it the preferred material for most implants, supporting large-scale manufacturing and accessibility. The limited global reserves and extraction complexity of palladium often restrict its use to specialized implants where its unique properties justify the higher cost.
Common Applications of Palladium and Titanium Implants
Palladium is commonly used in dental alloys and cardiovascular implants due to its excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Titanium implants dominate orthopedic applications such as joint replacements and bone fixation because of their high strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration properties. Both metals are favored in medical implants for their durability and minimal adverse reactions in the human body.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Medical Implants
Titanium offers superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio, making it the preferred material for most medical implants. Palladium's excellent corrosion resistance and hypoallergenic properties are beneficial, but its higher cost and lower mechanical strength limit its use primarily to specific dental and orthopedic applications. For long-term durability and patient safety, titanium remains the optimal choice in medical implant materials.
Infographic: Palladium vs Titanium for Medical Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com