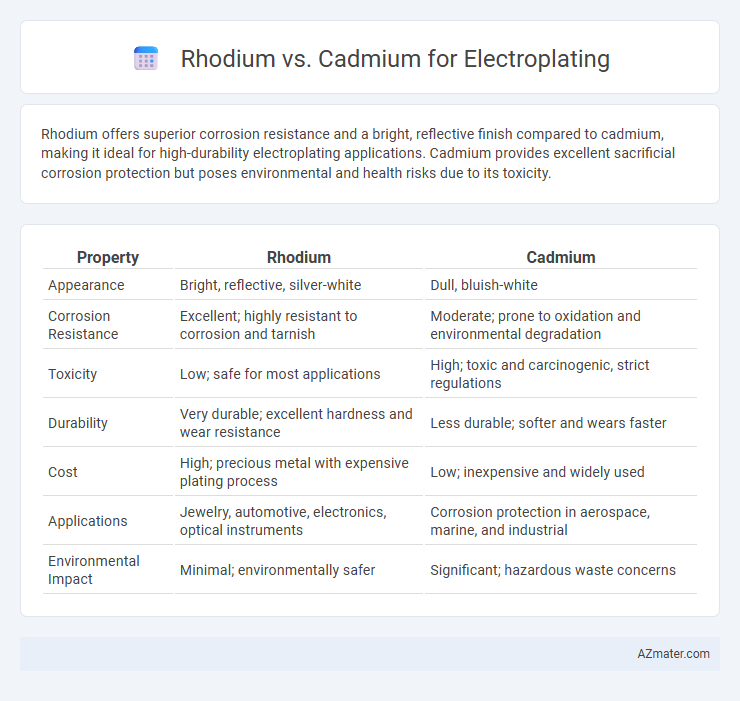
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and a bright, reflective finish compared to cadmium, making it ideal for high-durability electroplating applications. Cadmium provides excellent sacrificial corrosion protection but poses environmental and health risks due to its toxicity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium | Cadmium |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Bright, reflective, silver-white | Dull, bluish-white |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent; highly resistant to corrosion and tarnish | Moderate; prone to oxidation and environmental degradation |
| Toxicity | Low; safe for most applications | High; toxic and carcinogenic, strict regulations |
| Durability | Very durable; excellent hardness and wear resistance | Less durable; softer and wears faster |
| Cost | High; precious metal with expensive plating process | Low; inexpensive and widely used |
| Applications | Jewelry, automotive, electronics, optical instruments | Corrosion protection in aerospace, marine, and industrial |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal; environmentally safer | Significant; hazardous waste concerns |
Introduction to Electroplating: Rhodium vs Cadmium
Rhodium and cadmium serve distinct roles in electroplating, each offering unique properties suited for specific applications. Rhodium provides exceptional corrosion resistance, a brilliant silver-white finish, and superior hardness, making it ideal for jewelry and high-precision electronic components. Cadmium electroplating offers excellent sacrificial corrosion protection and lubricity, frequently used in aerospace and military hardware to prevent rust and wear under harsh conditions.
Overview of Rhodium and Cadmium Properties
Rhodium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, high hardness, and superior reflectivity, making it ideal for decorative and protective electroplating applications. Cadmium offers excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments, combined with good ductility and solderability, often used for aerospace and automotive parts. While rhodium provides a bright, tarnish-resistant finish with outstanding wear resistance, cadmium plating is favored for its sacrificial corrosion protection and ease of application.
Electroplating Process: Rhodium vs Cadmium
Rhodium electroplating involves using a plating solution containing rhodium salt and an acidic medium, typically under controlled temperature and current density to achieve a bright, corrosion-resistant finish. Cadmium electroplating utilizes a cyanide-based bath with cadmium ions, offering excellent sacrificial protection but requiring stringent environmental controls due to toxicity concerns. The rhodium process delivers superior hardness and tarnish resistance, while cadmium excels in resistance to corrosion in marine environments.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Rhodium provides superior corrosion resistance compared to cadmium, making it more suitable for applications requiring long-term durability in harsh environments. Cadmium coatings offer good corrosion protection, particularly in marine and industrial atmospheres, but tend to tarnish and degrade faster than rhodium. The higher chemical inertness and hardness of rhodium contribute to its enhanced resistance against oxidation, acids, and wear during electroplating.
Aesthetic and Finish Differences
Rhodium provides a bright, reflective, and highly lustrous finish often used in fine jewelry for its brilliant white shine and superior scratch resistance. Cadmium plating results in a duller, matte finish with a slightly yellowish tint, commonly applied in industrial settings for corrosion protection rather than aesthetic appeal. The aesthetic superiority of rhodium makes it the preferred choice for decorative electroplating where visual brilliance and durability are paramount.
Durability and Wear Performance
Rhodium electroplating offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to cadmium, making it ideal for high-wear applications such as jewelry and electrical contacts. Rhodium's hardness and corrosion resistance significantly reduce surface degradation, extending the lifespan of plated components. Cadmium, while providing good corrosion resistance, tends to wear faster under mechanical stress, limiting its effectiveness in demanding environments.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Rhodium electroplating offers a safer environmental profile with low toxicity and minimal hazardous waste compared to cadmium, which is highly toxic and poses significant health risks including carcinogenicity and respiratory issues during plating processes. Cadmium plating requires stringent handling protocols and specialized waste management due to its bioaccumulative nature and potential to contaminate soil and water. Transitioning to rhodium plating aligns with regulatory efforts to reduce heavy metal pollution and protect worker safety in industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: Rhodium vs Cadmium Plating
Rhodium plating commands a significantly higher cost due to its rarity and superior corrosion resistance, often ranging from $500 to $1,000 per ounce, whereas cadmium plating is more affordable, typically priced between $20 to $60 per pound. The long-term financial implications favor rhodium for high-value applications because of its durability, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses despite the upfront premium. Cadmium plating remains cost-effective for industrial uses where budget constraints outweigh longevity and environmental concerns, with additional costs arising from regulatory compliance due to cadmium's toxicity.
Common Applications in Industry
Rhodium electroplating is widely used in the automotive and jewelry industries for its superior corrosion resistance and brilliant, reflective finish, making it ideal for decorative coatings and electrical contacts. Cadmium plating finds common applications in aerospace, military, and marine industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance in harsh environments and ability to provide sacrificial protection to steel components. Both metals serve critical roles in enhancing durability and performance, with rhodium favored for high-end aesthetic finishes and cadmium chosen for robust, protective coatings.
Choosing the Right Metal for Electroplating
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance, high reflectivity, and excellent hardness, making it ideal for jewelry and automotive trim electroplating, though it comes at a higher cost. Cadmium provides good corrosion protection and ductility, commonly used in aerospace and electronics, but presents environmental and health hazards due to its toxicity. Selecting the right metal depends on application requirements, balancing performance, cost, and regulatory compliance for safety and durability.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Cadmium for Electroplating
 azmater.com
azmater.com