Tool steel offers excellent toughness and wear resistance for cutting tools, while tungsten provides superior hardness and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-speed cutting applications. Choosing between tool steel and tungsten depends on the specific cutting conditions, such as material hardness and operating temperature.
Table of Comparison
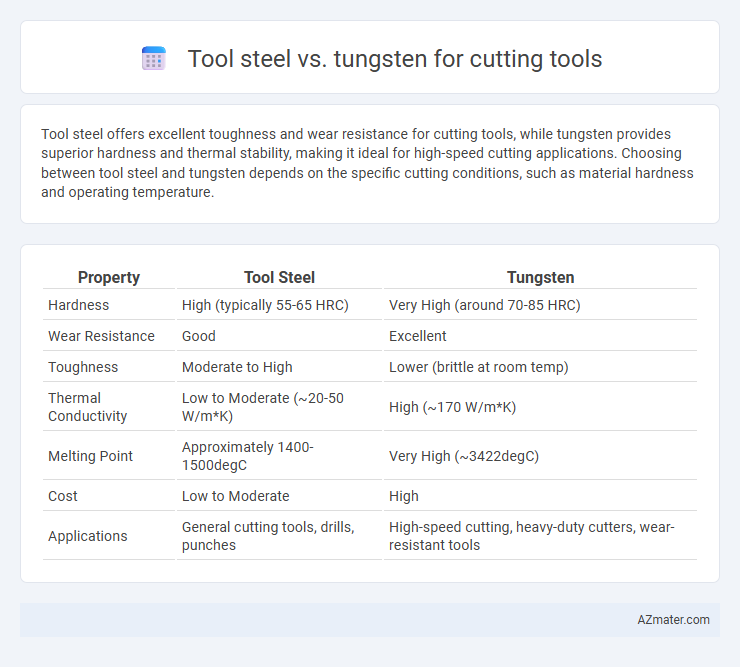
| Property | Tool Steel | Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (typically 55-65 HRC) | Very High (around 70-85 HRC) |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Toughness | Moderate to High | Lower (brittle at room temp) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to Moderate (~20-50 W/m*K) | High (~170 W/m*K) |
| Melting Point | Approximately 1400-1500degC | Very High (~3422degC) |
| Cost | Low to Moderate | High |
| Applications | General cutting tools, drills, punches | High-speed cutting, heavy-duty cutters, wear-resistant tools |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Tungsten
Tool steel, characterized by its high hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain a sharp edge, is widely used in the manufacturing of cutting tools for metalworking and machining applications. Tungsten, often alloyed in high-speed steel or used in carbide form, provides exceptional hardness and heat resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools that require durability at high temperatures. Both materials are essential in cutting tool production, with tool steel offering toughness and tungsten enhancing performance under extreme conditions.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Tool steel primarily consists of iron with carbon content ranging from 0.5% to 1.5%, along with alloying elements such as chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, and manganese to enhance hardness and wear resistance. Tungsten, often used in cemented carbide cutting tools, contains 70-95% tungsten carbide (WC) combined with cobalt as a binder, providing exceptional hardness and thermal stability. The high tungsten content allows cutting tools to maintain sharpness and resist deformation at elevated temperatures, outperforming traditional tool steels in high-speed machining applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Toughness
Tool steel exhibits high tensile strength and excellent toughness, making it ideal for cutting tools that require resistance to deformation and impact. Tungsten, especially in carbide form, offers superior hardness and wear resistance but generally has lower toughness compared to tool steel, leading to brittleness under high shock loads. The balance between strength and toughness in tool steels provides enhanced durability in applications involving intermittent cutting, while tungsten excels in high-speed and abrasive conditions due to its hardness.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Tool steel offers high hardness and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for general cutting applications, but tungsten outperforms tool steel with superior hardness, often exceeding 70 HRC, and exceptional wear resistance due to its high melting point and carbide formation. Tungsten carbide cutting tools maintain edge retention and cutting performance under extreme conditions, surpassing most tool steels in durability and longevity. The enhanced hardness and wear resistance of tungsten materials result in longer tool life and improved efficiency in high-speed and precision machining processes.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Tool steel exhibits moderate heat resistance with a typical maximum operating temperature around 500degC, making it suitable for general cutting applications. Tungsten, with a melting point near 3422degC and exceptional thermal stability, resists deformation and wear under high-temperature cutting conditions. Its superior heat resistance ensures longer tool life and consistent performance in demanding machining processes involving elevated temperatures.
Machinability and Fabrication
Tool steel offers excellent machinability due to its balanced hardness and toughness, making it easier to shape and fabricate with conventional cutting tools. Tungsten, while extremely hard and wear-resistant, presents challenges in machinability because of its high melting point and brittleness, often requiring specialized equipment and processes such as powder metallurgy for fabrication. The choice between tool steel and tungsten for cutting tools depends on balancing ease of machining and fabrication cost with the desired tool life and cutting performance.
Cost and Availability
Tool steel offers a cost-effective and widely available solution for cutting tools, making it a popular choice in general manufacturing due to its balance of hardness and toughness. Tungsten, although significantly more expensive and less abundant, provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature stability, ideal for premium cutting applications. The higher price and limited supply of tungsten alloys often restrict their use to specialized or high-performance cutting tools where durability justifies the investment.
Typical Applications in Cutting Tools
Tool steel, known for its high hardness and wear resistance, is typically used in cutting tools such as drills, milling cutters, and dies for machining softer materials like aluminum and mild steel. Tungsten, particularly in the form of tungsten carbide, excels in high-speed cutting applications and is preferred for cutting hard materials including stainless steel and cast iron due to its superior toughness and resistance to heat. The choice between tool steel and tungsten-based cutting tools depends on the material being machined and the required cutting speed, with tungsten providing longer tool life and efficiency in demanding industrial applications.
Performance in Different Cutting Environments
Tool steel offers excellent toughness and wear resistance, making it suitable for cutting softer materials and operations involving intermittent cuts. Tungsten, especially in carbide form, provides superior hardness and heat resistance, excelling in high-speed, high-temperature cutting environments such as machining hardened metals. Performance comparison reveals tool steel excels in durability under shock loads, while tungsten carbide outperforms in sustained cutting applications requiring precision and thermal stability.
Choosing Between Tool Steel and Tungsten
Tool steel offers excellent toughness, wear resistance, and is easier to machine, making it ideal for general-purpose cutting tools in moderate conditions. Tungsten, particularly tungsten carbide, provides superior hardness and heat resistance, ensuring exceptional performance in high-speed, heavy-duty cutting applications. Selecting between tool steel and tungsten depends on the required cutting speed, durability, and material hardness to optimize tool life and machining efficiency.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Tungsten for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com