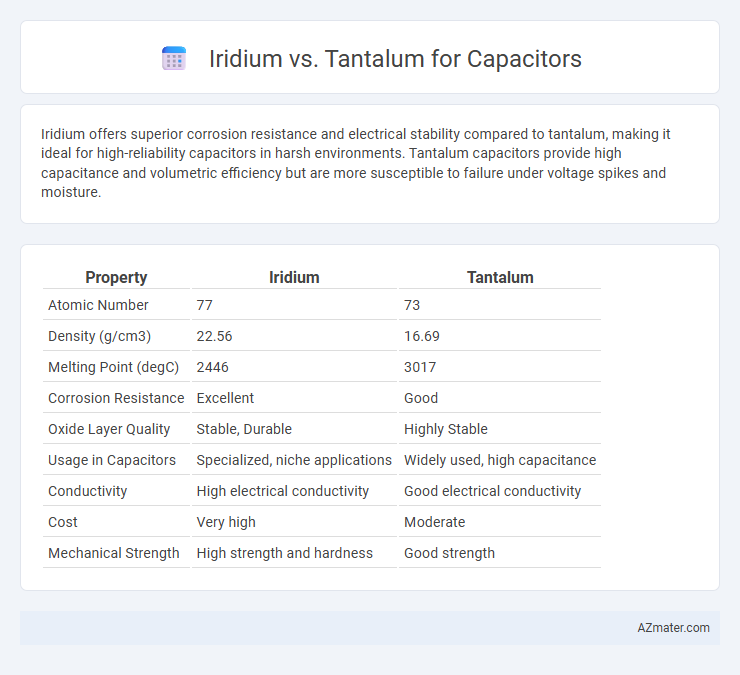
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical stability compared to tantalum, making it ideal for high-reliability capacitors in harsh environments. Tantalum capacitors provide high capacitance and volumetric efficiency but are more susceptible to failure under voltage spikes and moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Iridium | Tantalum |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 77 | 73 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 22.56 | 16.69 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2446 | 3017 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Oxide Layer Quality | Stable, Durable | Highly Stable |
| Usage in Capacitors | Specialized, niche applications | Widely used, high capacitance |
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity | Good electrical conductivity |
| Cost | Very high | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and hardness | Good strength |
Introduction: Iridium vs Tantalum Capacitors
Iridium and tantalum capacitors offer distinct advantages in high-performance electronic circuits, with iridium providing superior corrosion resistance and longevity in extreme environments. Tantalum capacitors are prized for their high capacitance-to-volume ratio and stable electrical characteristics across a wide temperature range. Comparing iridium's robust durability to tantalum's efficiency highlights critical design considerations for aerospace, medical, and military applications.
Material Properties: Iridium and Tantalum
Iridium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point, making it highly stable under extreme conditions, while tantalum provides excellent capacitance density and reliable performance in miniaturized capacitors due to its high dielectric constant. Tantalum's oxide layer forms a robust dielectric, resulting in low leakage currents and long-term durability, whereas iridium's rarity and conductivity are less commonly utilized in capacitor fabrication. The choice between iridium and tantalum hinges on balancing performance requirements such as stability, capacitance, and cost-effectiveness in capacitor design.
Capacitance Performance Comparison
Iridium capacitors exhibit lower capacitance values compared to tantalum capacitors but offer superior stability and reliability under high-temperature and high-frequency conditions. Tantalum capacitors provide higher capacitance per volume, making them ideal for compact designs requiring large capacitance. The capacitance performance of iridium capacitors is optimized for precision applications, whereas tantalum capacitors excel in bulk energy storage and general-purpose filtering.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Iridium exhibits lower electrical conductivity compared to tantalum, making tantalum the preferred material for capacitors requiring high efficiency and minimal energy loss. Tantalum has an electrical conductivity around 7.4 x 10^6 S/m, significantly higher than iridium's conductivity of approximately 2.3 x 10^6 S/m. This difference directly impacts capacitor performance, as materials with higher conductivity provide faster charge-discharge cycles and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR).
Stability and Reliability in Circuits
Iridium capacitors demonstrate superior stability and reliability in circuits due to their excellent corrosion resistance and consistent electrical conductivity under extreme conditions. Tantalum capacitors, while offering high capacitance per volume and low ESR, can be prone to failure from voltage spikes and thermal stress, impacting long-term reliability. Iridium's robust performance in harsh environments makes it a preferred choice for applications demanding stable capacitance and durability.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Iridium capacitors exhibit superior temperature tolerance, maintaining stable electrical performance in extreme thermal environments up to 200degC, compared to tantalum capacitors typically rated around 125degC to 150degC. The thermal stability of iridium allows for consistent capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR) over a wider temperature range, making it ideal for high-reliability applications such as aerospace and military electronics. In contrast, tantalum capacitors may suffer from increased leakage current and degradation at elevated temperatures, limiting their use in harsh thermal conditions.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Iridium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to tantalum, making it highly reliable for capacitor electrodes in harsh environments. Tantalum capacitors are prone to oxide layer degradation under high voltage and temperature, which can lead to failure, whereas iridium forms a more stable and resilient oxide film. This stability enhances the lifespan and performance consistency of capacitors using iridium electrodes in demanding applications.
Cost and Availability of Iridium and Tantalum
Iridium is significantly more expensive and less abundant than tantalum, making it rare and cost-prohibitive for widespread capacitor use. Tantalum enjoys broader availability and lower cost, supported by well-established mining and processing infrastructure. These factors make tantalum the preferred choice in capacitor manufacturing despite iridium's superior corrosion resistance.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Iridium and tantalum both serve crucial roles in capacitor technology, with tantalum widely favored for its high capacitance per volume, making it ideal for compact, high-performance electronics such as smartphones and laptops. Iridium's superior corrosion resistance and stability at high temperatures position it for specialized applications in harsh environments, including aerospace and military electronics. The choice between iridium and tantalum capacitors depends on specific performance requirements, balancing factors like energy density, reliability, and environmental stability in modern electronic devices.
Future Trends in Capacitor Materials
Iridium and tantalum exhibit distinct properties influencing their roles in next-generation capacitors, with iridium offering superior corrosion resistance and tantalum providing high capacitance and reliability. Emerging research emphasizes iridium-based nanostructures to enhance charge storage capacity and longevity, positioning it as a potential alternative in high-performance capacitors. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach integrating iridium's stability with tantalum's electrochemical efficiency, driving innovation in miniaturized, energy-dense capacitor technologies for electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Infographic: Iridium vs Tantalum for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com