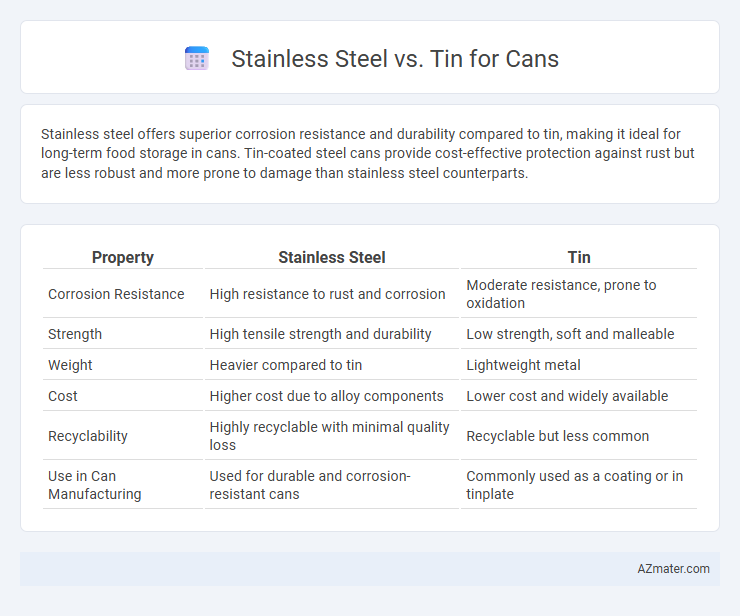
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to tin, making it ideal for long-term food storage in cans. Tin-coated steel cans provide cost-effective protection against rust but are less robust and more prone to damage than stainless steel counterparts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to rust and corrosion | Moderate resistance, prone to oxidation |
| Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Low strength, soft and malleable |
| Weight | Heavier compared to tin | Lightweight metal |
| Cost | Higher cost due to alloy components | Lower cost and widely available |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable with minimal quality loss | Recyclable but less common |
| Use in Can Manufacturing | Used for durable and corrosion-resistant cans | Commonly used as a coating or in tinplate |
Introduction to Can Materials: Stainless Steel vs Tin
Stainless steel and tin serve as primary materials for can manufacturing, each offering unique properties tailored to specific applications. Stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance, durability, and strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty and long-term food or chemical storage. Tin, often used as a coating on steel cans, prevents rust and extends shelf life while maintaining cost-effectiveness and suitability for lightweight packaging.
Historical Usage of Stainless Steel and Tin in Cans
Tin has been used for can manufacturing since the early 19th century due to its corrosion-resistant properties and malleability, making it ideal for preserving food. Stainless steel emerged in the 20th century as a durable alternative, offering superior strength, resistance to corrosion, and longer shelf-life for canned goods. Historical usage shows tin cans dominated early food preservation, while stainless steel cans gained prominence for industrial and high-quality packaging applications.
Material Composition: Stainless Steel vs Tin
Stainless steel cans are primarily composed of iron alloyed with chromium, nickel, and sometimes molybdenum, providing enhanced corrosion resistance and structural strength. Tin, often used as a coating rather than the base material, protects steel cans by preventing rust and food contamination through its non-reactive properties. The combination of steel with tin coatings balances durability and food safety, while pure stainless steel offers superior longevity and resistance to acidic contents without additional coatings.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Stainless steel cans offer superior durability and strength due to their high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for long-term storage and transportation. Tin cans, while providing adequate protection for lighter products, are more prone to denting and corrosion over time, especially when exposed to moisture. The enhanced structural integrity of stainless steel ensures better product preservation and reduces the risk of contamination compared to tin.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Stainless steel cans exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer preventing rust and degradation in various environments. Tin cans, typically coated with a thin layer of tin on steel, offer moderate corrosion protection but are more prone to corrosion over time, especially when exposed to acidic or salty substances. Consequently, stainless steel cans provide enhanced longevity, ensuring durable food storage solutions with minimal risk of contamination or structural failure.
Food Safety and Chemical Reactivity
Stainless steel cans offer superior food safety due to their highly inert surface that resists corrosion and prevents chemical leaching, ensuring food remains uncontaminated. Tin, commonly used as a coating on steel cans, provides a protective barrier but can degrade over time, potentially leading to trace metal migration when exposed to acidic or salty foods. The corrosion resistance and non-reactive properties of stainless steel make it a preferred choice for packaging a broad range of food products without compromising safety or flavor integrity.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Stainless steel cans offer superior recyclability with a global recycling rate exceeding 85%, and their durability reduces the need for frequent replacement, minimizing waste. Tin cans, often made from steel coated with tin, have a lower environmental impact during production but face challenges in recycling due to tin coatings that require specialized processing. The lifecycle assessment indicates stainless steel is more environmentally sustainable in the long term, supported by efficient recycling infrastructures that conserve raw materials and reduce carbon emissions.
Cost Analysis: Stainless Steel Cans vs Tin Cans
Stainless steel cans typically incur higher production costs due to expensive raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, while tin cans benefit from lower material costs and widespread availability, making them more economical for mass production. The durability and corrosion resistance of stainless steel justify its premium price in specialized applications, but tin remains the preferred choice for cost-sensitive packaging markets. Long-term cost analysis shows tin cans offer better affordability, whereas stainless steel cans provide enhanced longevity and recyclability, influencing overall lifecycle expenses.
Applications and Common Uses in Packaging
Stainless steel is widely used in packaging for beverages, food cans, and aerosol containers due to its corrosion resistance, strength, and ability to maintain product integrity under various conditions. Tin, often used as a coating on steel cans, provides a protective layer against rust and contamination in packaging applications such as food preservation and household products. In packaging, stainless steel suits long-term storage and high-end products, while tin-coated steel is preferred for cost-effective, high-volume food cans and preservation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Cans
Stainless steel offers superior durability, corrosion resistance, and recyclability, making it ideal for long-term food storage and industrial applications. Tin provides excellent corrosion protection with a lightweight and cost-effective option, suitable for short-term or single-use packaging. Selecting the best material depends on specific requirements such as product shelf life, budget constraints, and environmental impact goals.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Tin for Can
 azmater.com
azmater.com