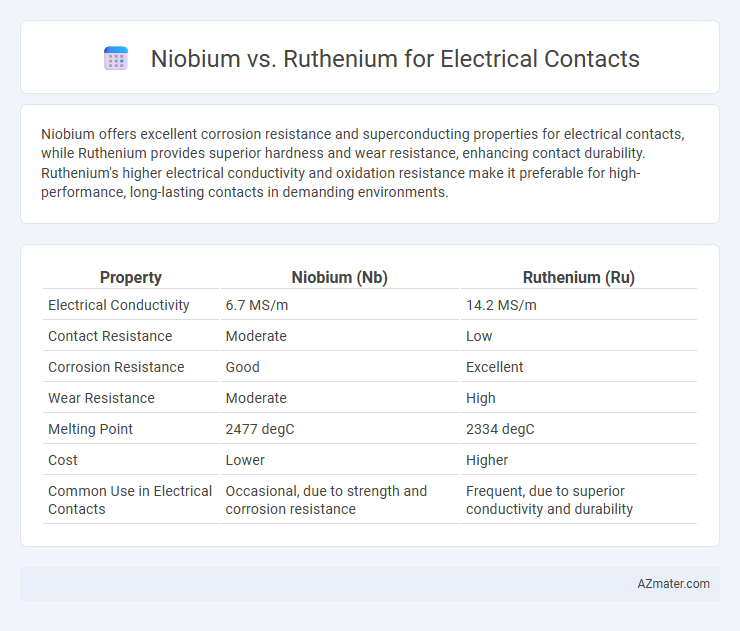
Niobium offers excellent corrosion resistance and superconducting properties for electrical contacts, while Ruthenium provides superior hardness and wear resistance, enhancing contact durability. Ruthenium's higher electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance make it preferable for high-performance, long-lasting contacts in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Ruthenium (Ru) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 6.7 MS/m | 14.2 MS/m |
| Contact Resistance | Moderate | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Melting Point | 2477 degC | 2334 degC |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Electrical Contacts | Occasional, due to strength and corrosion resistance | Frequent, due to superior conductivity and durability |
Introduction to Electrical Contact Materials
Niobium and ruthenium are critical electrical contact materials valued for their exceptional conductivity and corrosion resistance. Niobium offers high ductility and oxidation resistance, enhancing durability under varying environmental conditions, while ruthenium provides superior hardness and excellent wear resistance, ensuring stable electrical performance. The choice between niobium and ruthenium significantly impacts contact efficiency, longevity, and reliability in electrical applications.
Overview of Niobium and Ruthenium
Niobium and Ruthenium, both transition metals, are critical in electrical contact applications due to their unique properties. Niobium offers excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point (2477degC), and good superconducting capabilities, making it ideal for durable, high-performance contacts. Ruthenium is prized for its exceptional hardness, high electrical conductivity, and resistance to oxidation, which enhances the reliability and longevity of electrical connectors in demanding environments.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Niobium exhibits electrical conductivity around 6.7 million S/m, making it a moderately conductive metal suitable for electrical contacts requiring corrosion resistance and strength. Ruthenium offers higher conductivity, approximately 7.1 million S/m, coupled with excellent wear resistance and oxidation stability, enhancing contact performance under harsh conditions. While Ruthenium's superior conductivity and durability favor its use in high-performance switches and connectors, Niobium's unique properties excel in applications demanding lower conductivity but greater mechanical resilience.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Niobium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance in acidic and oxidizing environments due to its stable oxide layer, making it suitable for electrical contacts exposed to harsh conditions. Ruthenium offers superior oxidation resistance, forming a robust and conductive oxide film that enhances contact durability and performance in high-temperature applications. When comparing Niobium and Ruthenium, Ruthenium generally provides better long-term stability against oxidation, while Niobium excels in resisting chemical corrosion.
Wear and Durability Performance
Niobium excels in electrical contacts due to its high corrosion resistance and excellent wear performance under moderate current loads, providing stable conductivity over extended use. Ruthenium offers superior durability and wear resistance in harsh electrical environments, maintaining low contact resistance and preventing material degradation even at high cyclic operations. While Niobium is favored for applications requiring moderate mechanical stress, Ruthenium is preferred for heavy-duty electrical contacts demanding enhanced longevity and reliable wear performance.
Cost and Availability Factors
Niobium offers a cost-effective option for electrical contacts with moderate availability, primarily sourced from Brazil and Canada, making it more economical compared to ruthenium. Ruthenium, a rare platinum-group metal, is significantly more expensive due to limited global reserves concentrated in South Africa and Russia, impacting its cost-effectiveness for large-scale electrical contacts. The choice between niobium and ruthenium hinges on balancing the higher price and scarcity of ruthenium against the relatively abundant supply and lower cost of niobium in electrical contact applications.
Solderability and Workability
Niobium offers excellent solderability due to its strong oxide layer, which can be effectively managed with proper surface treatments, ensuring reliable electrical contacts. Ruthenium exhibits superior workability with its high corrosion resistance and excellent hardness, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and wear-resistant electrical contacts. While niobium provides better flexibility in soldering, ruthenium excels in mechanical stability and lifespan under harsh environmental conditions.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Niobium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and superconducting properties, making it highly suitable for electrical contacts in aerospace and medical device industries where reliability under extreme conditions is critical. Ruthenium, a member of the platinum group metals, offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and stable conductivity, ideal for automotive electronics and high-performance connectors in telecommunications. Both metals' unique characteristics influence their application, with niobium favored in environments requiring high temperature stability and ruthenium in durability-focused, high-cycle electrical contacts.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Niobium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and low toxicity, making it an environmentally safer option for electrical contacts compared to Ruthenium, which can pose risks due to its potential to release harmful ruthenium tetroxide vapors during manufacturing or disposal. Ruthenium's rare and costly nature also raises sustainability concerns, while niobium's relative abundance contributes to lower environmental impact throughout the material lifecycle. Both metals require careful handling and recycling processes to minimize ecological footprint and ensure workplace safety.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material
Niobium offers excellent corrosion resistance and high ductility, making it suitable for electrical contacts in harsh environments requiring durability and flexibility. Ruthenium provides superior wear resistance and maintains stable electrical conductivity under high current densities, ideal for applications demanding long-lasting contact performance. Selecting between niobium and ruthenium depends on specific requirements such as environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and conductivity stability for optimal electrical contact performance.
Infographic: Niobium vs Ruthenium for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com