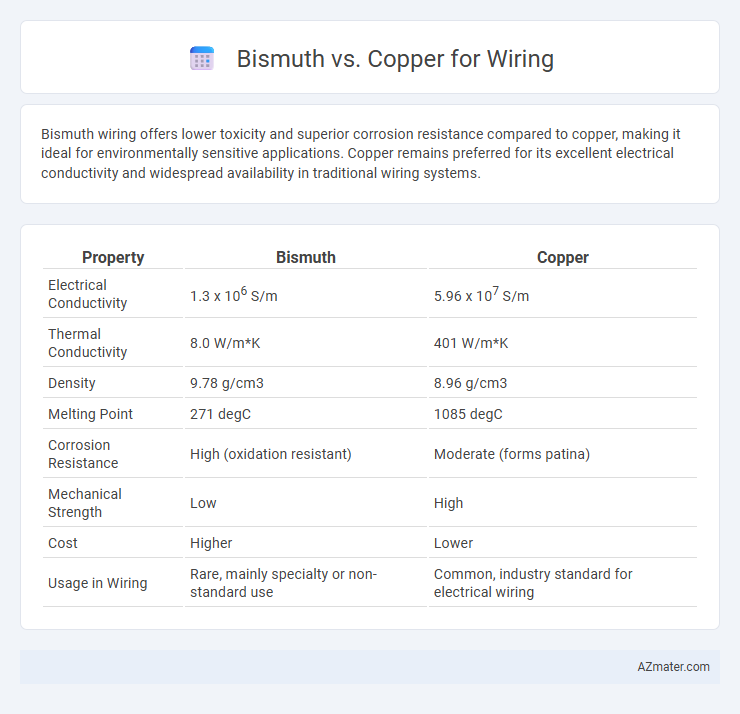
Bismuth wiring offers lower toxicity and superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for environmentally sensitive applications. Copper remains preferred for its excellent electrical conductivity and widespread availability in traditional wiring systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.3 x 106 S/m | 5.96 x 107 S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.0 W/m*K | 401 W/m*K |
| Density | 9.78 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 271 degC | 1085 degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (oxidation resistant) | Moderate (forms patina) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low | High |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Usage in Wiring | Rare, mainly specialty or non-standard use | Common, industry standard for electrical wiring |
Introduction to Bismuth and Copper Wiring
Bismuth and copper are two metals considered for electrical wiring, each with distinct properties affecting conductivity and durability. Copper, a traditional choice, offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it highly reliable for residential and industrial applications. Bismuth, though less common, provides lower thermal conductivity and is non-toxic, which can be advantageous in specialized wiring environments where biocompatibility and reduced heat transfer are critical.
Electrical Conductivity: Bismuth vs Copper
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than bismuth, making it the preferred material for electrical wiring due to its efficient current flow and minimal energy loss. Bismuth's conductivity is approximately 1.5% that of copper, resulting in greater resistance and heat generation when used as a conductor. Consequently, copper remains the industry standard for wiring applications requiring optimal electrical performance and durability.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Bismuth exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to copper, making it less suitable for high-stress wiring applications. Copper's superior tensile strength and ductility provide excellent flexibility and durability, ideal for electrical wiring subjected to frequent bending. The enhanced mechanical properties of copper ensure reliable performance and longer lifespan in wiring systems.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Bismuth wiring offers enhanced corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it suitable for environments with high humidity or chemical exposure. Its durability stems from a naturally forming protective oxide layer that prevents further degradation, whereas copper tends to oxidize and develop patina over time. Bismuth's unique anti-corrosive properties extend the lifespan of wiring systems in harsh conditions, outperforming traditional copper wiring in long-term reliability.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Bismuth exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity than copper, with values around 7.97 W/m*K compared to copper's approximately 400 W/m*K, making copper a superior choice for efficient heat dissipation in wiring applications. Copper's high thermal conductivity enhances its ability to transfer and dissipate heat, reducing the risk of overheating in electrical circuits. Bismuth, while less conductive thermally, is sometimes used for its non-toxic and liquid metal alloy properties rather than for thermal management in wiring systems.
Cost and Availability Factors
Bismuth is significantly less common and more expensive than copper, making it a cost-prohibitive choice for wiring applications. Copper remains the industry standard due to its abundant availability and relatively low price, ensuring cost-efficiency in electrical installations. The widespread mining and established supply chains for copper guarantee consistent material access, unlike bismuth, which has limited production and higher market volatility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bismuth, a non-toxic element, offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to copper in wiring due to its low toxicity and biodegradability, reducing soil and water contamination risks during disposal. Copper mining and refining processes generate significant environmental pollution, including heavy metal contamination and high energy consumption, which bismuth production mitigates with lower ecological footprints. Although copper remains highly conductive, bismuth's sustainability benefits make it a promising material for green electrical wiring solutions.
Safety and Health Considerations
Bismuth wiring offers enhanced safety due to its non-toxic and environmentally friendly properties compared to copper, which can pose health risks through long-term exposure to copper dust or corrosive copper compounds. Bismuth's lower electrical conductivity requires careful application to maintain efficiency, but its resistance to corrosion minimizes potential exposure to harmful substances over time. Copper remains widely used for its superior conductivity, though adequate insulation and handling protocols are essential to mitigate health risks associated with copper wiring.
Applications in Electrical Engineering
Bismuth is rarely used in wiring due to its brittleness and lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which remains the preferred material for electrical engineering applications because of its excellent conductivity, ductility, and thermal stability. Copper wiring is essential in power distribution, telecommunications, and electronic circuits, providing minimal resistance and superior durability under varying environmental conditions. Specialized applications may incorporate bismuth alloys as low-melting-point solders or fusible links, but copper dominates in mainstream electrical wiring infrastructure.
Summary: Choosing Between Bismuth and Copper
Bismuth wiring offers superior corrosion resistance and non-toxicity compared to traditional copper wiring, making it ideal for specialized environments where safety and environmental impact are critical. Copper remains the preferred choice for general electrical applications due to its excellent electrical conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and widespread availability. Selecting between bismuth and copper depends on balancing factors such as conductivity requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Copper for Wiring
 azmater.com
azmater.com