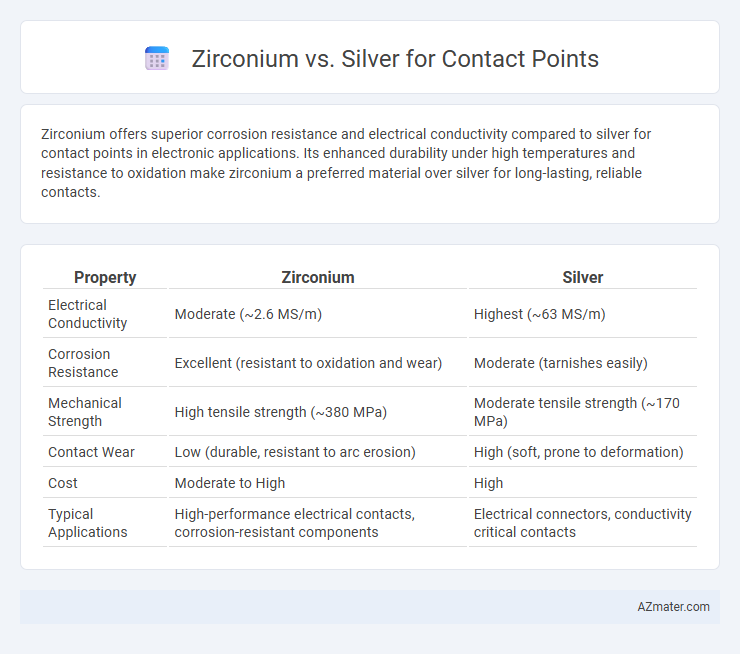
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to silver for contact points in electronic applications. Its enhanced durability under high temperatures and resistance to oxidation make zirconium a preferred material over silver for long-lasting, reliable contacts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate (~2.6 MS/m) | Highest (~63 MS/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (resistant to oxidation and wear) | Moderate (tarnishes easily) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength (~380 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (~170 MPa) |
| Contact Wear | Low (durable, resistant to arc erosion) | High (soft, prone to deformation) |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High |
| Typical Applications | High-performance electrical contacts, corrosion-resistant components | Electrical connectors, conductivity critical contacts |
Introduction to Contact Points: Zirconium vs Silver
Contact points in electrical systems require materials with excellent conductivity and durability to ensure efficient current flow and minimal wear. Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and lower contact resistance compared to silver, making it ideal for high-reliability applications. Silver, known for its exceptional electrical conductivity and thermal performance, remains a popular choice despite its tendency to oxidize and wear faster under heavy loads.
Material Properties Overview: Zirconium and Silver
Zirconium offers high corrosion resistance, excellent strength, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for durable contact points in harsh environments. Silver exhibits superior electrical conductivity and thermal properties, but its softness and susceptibility to tarnish limit long-term performance. Choosing between zirconium and silver depends on prioritizing conductivity versus mechanical robustness and environmental stability.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Zirconium exhibits significantly lower electrical conductivity than silver, with zirconium's conductivity around 2.7 million S/m compared to silver's exceptional 63 million S/m, making silver the superior choice for contact points requiring minimal resistance. Silver's high conductivity ensures better current flow and reduced energy loss, critical in high-performance electrical connectors and switches. Despite zirconium's corrosion resistance, silver remains the preferred material where optimal electrical conductivity is essential.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Zirconium contact points exhibit superior durability and wear resistance compared to silver, making them ideal for high-performance electrical applications requiring long-term stability. The hardness of zirconium reduces abrasion and deformation under mechanical stress, ensuring consistent conductivity over extended use. Silver, while highly conductive, is softer and more prone to wear, which can lead to increased contact resistance and reduced lifespan in demanding environments.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Zirconium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to silver, making it ideal for contact points exposed to harsh environments and moisture. Its stable oxide layer prevents degradation and ensures consistent electrical conductivity over time. Silver, while an excellent conductor, tarnishes and corrodes faster, reducing its longevity in contact applications.
Cost and Availability Factors
Zirconium contact points are generally more expensive than silver due to higher raw material and manufacturing costs, but they offer superior durability and corrosion resistance, reducing long-term replacement expenses. Silver is widely available and more cost-effective upfront, favored in applications requiring excellent electrical conductivity despite its susceptibility to oxidation and wear. Industry demand and supply chain stability make silver easier to source globally, whereas zirconium's availability can be constrained by specialized production facilities.
Applications in Industry and Electronics
Zirconium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to silver, making it ideal for demanding industrial and electronic contact points where durability is critical. Silver, known for its exceptional electrical conductivity, is widely used in low-resistance electrical contacts and connectors but tends to tarnish, reducing long-term reliability in harsh environments. Industries such as aerospace and chemical processing favor zirconium for contact points due to its robustness, while consumer electronics and telecommunications rely heavily on silver for optimal electrical performance.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility compared to silver, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and metal ion leaching in contact point applications. Silver, while an excellent conductor, poses concerns due to its potential antimicrobial toxicity and environmental accumulation during disposal. Choosing zirconium enhances safety for users and minimizes ecological impact through lower bioavailability and safer recycling processes.
Maintenance and Performance Over Time
Zirconium contact points offer superior corrosion resistance and maintain consistent electrical conductivity over extended periods, reducing the frequency of maintenance compared to silver. Silver contact points, while excellent conductors initially, tend to oxidize and wear faster, leading to increased contact resistance and more frequent cleaning or replacement. Over time, zirconium's durability enhances performance reliability, making it a preferred choice in applications demanding long-term stability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Contact Points
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and longer durability compared to silver, making it ideal for high-performance and long-lasting contact points in electrical applications. Silver provides exceptional electrical conductivity but is prone to tarnishing and wear, which can reduce reliability over time. Selecting the right material depends on balancing conductivity needs with maintenance requirements and operational environment conditions.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Silver for Contact Point
 azmater.com
azmater.com