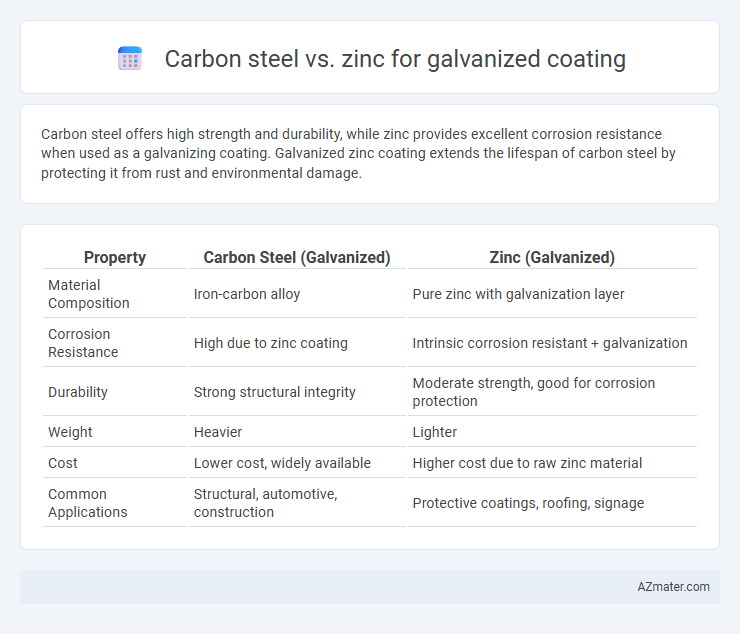
Carbon steel offers high strength and durability, while zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance when used as a galvanizing coating. Galvanized zinc coating extends the lifespan of carbon steel by protecting it from rust and environmental damage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel (Galvanized) | Zinc (Galvanized) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Iron-carbon alloy | Pure zinc with galvanization layer |
| Corrosion Resistance | High due to zinc coating | Intrinsic corrosion resistant + galvanization |
| Durability | Strong structural integrity | Moderate strength, good for corrosion protection |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to raw zinc material |
| Common Applications | Structural, automotive, construction | Protective coatings, roofing, signage |
Introduction to Galvanized Coatings
Galvanized coatings primarily involve applying a protective zinc layer to carbon steel to prevent corrosion and extend the metal's lifespan. Carbon steel's reactive surface bonds effectively with molten zinc during the galvanization process, forming a durable, corrosion-resistant barrier. Zinc's sacrificial properties ensure that even if the coating is scratched, the underlying steel remains protected against rust through electrochemical corrosion prevention.
Understanding Carbon Steel Properties
Carbon steel exhibits high tensile strength and durability, making it an ideal substrate for galvanized coatings. Its composition, primarily iron with a small percentage of carbon, provides structural integrity but requires protective layers like zinc to prevent corrosion. Zinc coating on carbon steel forms a sacrificial layer, enhancing corrosion resistance and extending the lifespan of steel components in various industrial applications.
Key Characteristics of Zinc Coating
Zinc coating on carbon steel provides excellent corrosion resistance due to its ability to act as a sacrificial anode, protecting the underlying steel from rust. The coating typically forms a tightly bonded layer that offers durability and long-term protection in various environments, including outdoor and marine conditions. Zinc coatings also exhibit self-healing properties where exposed areas can re-bond with oxygen and moisture to prevent further corrosion.
Galvanization Process Overview
The galvanization process involves coating carbon steel with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion through a metallurgical reaction where zinc bonds to the steel surface. Zinc serves as a sacrificial anode, offering superior corrosion resistance by preventing rust formation on the underlying carbon steel substrate. Hot-dip galvanizing is the most common method, where cleaned carbon steel is immersed in molten zinc, creating a durable, corrosion-resistant coating that extends the steel's service life in harsh environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Carbon Steel vs Zinc
Zinc provides superior corrosion resistance when used as a galvanized coating on carbon steel by forming a protective barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the steel surface. Carbon steel alone is prone to rust and oxidation in humid or wet environments, whereas zinc's sacrificial anode properties allow it to corrode preferentially, protecting the underlying steel. The galvanization process significantly extends the lifespan of carbon steel structures by reducing corrosion rates.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Carbon steel coated with zinc through galvanization exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to the sacrificial protection zinc offers, significantly enhancing durability in harsh environments. Zinc's ability to form a protective oxide layer prevents rust formation on carbon steel, extending the lifespan by decades under normal atmospheric conditions. The longevity of galvanized carbon steel typically ranges from 20 to 50 years, depending on thickness and environmental exposure, outperforming untreated carbon steel and many other coatings.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Carbon steel coated with zinc through galvanization exhibits superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments due to zinc's sacrificial properties, which protect the steel substrate from rust and degradation. Zinc coatings also provide a durable barrier against moisture, salt, and chemical exposure, significantly extending the lifespan of carbon steel structures in marine and industrial settings. The combination of carbon steel's mechanical strength and zinc's protective layer ensures optimal performance in environments characterized by extreme weather, high humidity, and corrosive agents.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Carbon steel offers a lower base material cost compared to zinc, making it economically attractive for large-scale projects requiring structural strength. Zinc, used in galvanized coatings, significantly enhances corrosion resistance but adds to the overall expense due to material and application costs. Evaluating lifecycle cost savings from reduced maintenance and extended asset longevity is essential when comparing carbon steel alone versus zinc-coated alternatives.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Carbon steel with galvanized zinc coating is widely used in construction, automotive, and infrastructure industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Zinc coating provides a protective barrier against rust, making galvanized carbon steel ideal for outdoor structures, roofing, and pipelines exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Industries such as agriculture, telecommunications, and HVAC rely on galvanized carbon steel components for durability and long service life in both structural and mechanical applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Galvanized Coating
Carbon steel offers excellent strength and durability but requires a high-quality zinc coating for corrosion resistance in galvanized applications. Zinc provides a sacrificial layer that protects carbon steel from rust by corroding first, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial environments. Selecting the best material involves balancing the mechanical properties of carbon steel with the protective benefits of a thick, uniform zinc coating to maximize longevity and performance.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Zinc for Galvanized coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com