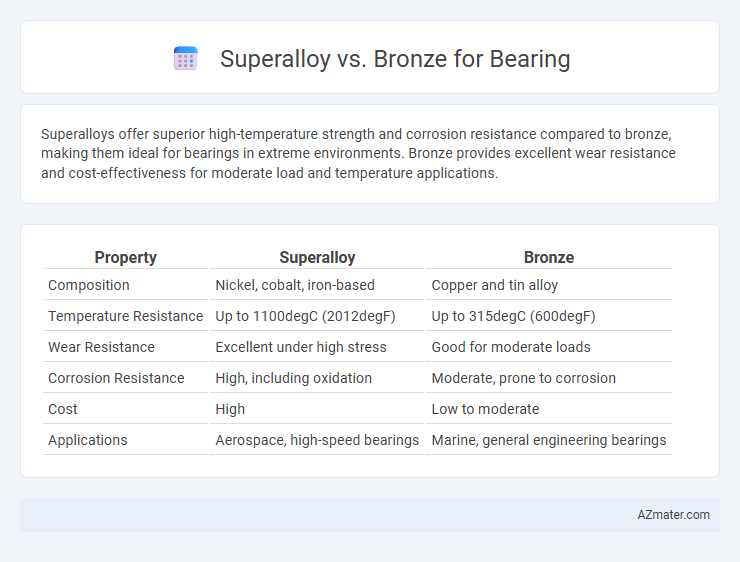
Superalloys offer superior high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance compared to bronze, making them ideal for bearings in extreme environments. Bronze provides excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness for moderate load and temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superalloy | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nickel, cobalt, iron-based | Copper and tin alloy |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1100degC (2012degF) | Up to 315degC (600degF) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent under high stress | Good for moderate loads |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, including oxidation | Moderate, prone to corrosion |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Applications | Aerospace, high-speed bearings | Marine, general engineering bearings |
Introduction to Bearing Materials
Superalloys exhibit exceptional high-temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and wear endurance, making them ideal for demanding bearing applications in aerospace and industrial machinery. Bronze, a traditional bearing material, offers excellent frictional properties, good machinability, and cost-effectiveness for moderate-load environments. Selecting between superalloy and bronze bearings depends on operational conditions such as temperature, load, and corrosion exposure, as these factors directly influence material performance and lifespan.
Overview of Superalloys
Superalloys are advanced high-performance materials primarily composed of nickel, cobalt, or iron, engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, mechanical stress, and corrosion in demanding bearing applications. Their superior creep resistance and oxidation stability make them ideal for high-load, high-speed environments where bronze bearings would degrade faster. The microstructure of superalloys offers enhanced strength retention at elevated temperatures, outperforming bronze in terms of durability and longevity for critical industrial bearings.
Properties of Bronze as a Bearing Material
Bronze as a bearing material offers exceptional corrosion resistance, excellent wear properties, and low friction coefficients, making it ideal for high-load, low-speed applications. Its inherent ability to embed small particles minimizes shaft damage, while its thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat dissipation during operation. The alloy's toughness and fatigue resistance contribute to longer bearing life in marine, industrial, and automotive environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Superalloys exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to bronze, making them ideal for high-stress bearing applications requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation. The tensile strength of superalloys can exceed 1,200 MPa, whereas bronze typically ranges between 200 to 400 MPa, highlighting a significant difference in performance under extreme mechanical loads. Enhanced fatigue resistance and elevated temperature stability further position superalloys as the preferred choice for demanding bearing environments over bronze alloys.
Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Superalloys exhibit superior wear resistance compared to bronze due to their enhanced hardness and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-stress bearing applications. Corrosion resistance in superalloys is significantly higher, attributed to their alloying elements like chromium and nickel, which form protective oxide layers, whereas bronze may suffer from dezincification and corrosion in harsh environments. This makes superalloys more suitable for bearings subjected to extreme temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Superalloy bearings exhibit superior performance in high-temperature environments due to their exceptional thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and mechanical strength, maintaining integrity beyond 600degC. Bronze bearings, while effective in moderate temperatures up to approximately 300degC, tend to experience reduced load capacity and increased wear under extreme heat. The advanced metallurgy of superalloys enables prolonged service life and reliable operation in aerospace, turbine, and industrial applications where elevated temperatures compromise bronze bearing performance.
Lubrication Requirements and Maintenance
Superalloy bearings require specialized high-temperature lubricants such as synthetic oils or solid lubricants like molybdenum disulfide to maintain performance under extreme conditions, reducing wear and oxidation. Bronze bearings, typically used with conventional mineral oils or greases, demand regular lubrication intervals to prevent metal-to-metal contact and corrosion. Maintenance for superalloy bearings involves monitoring lubricant degradation and replacing it with high-performance fluids, whereas bronze bearings require more frequent manual lubrication and inspection to ensure longevity and prevent contamination.
Cost and Availability of Superalloys vs Bronze
Superalloys typically have higher costs than bronze due to their complex manufacturing processes and premium raw materials like nickel, cobalt, and chromium, making them less accessible for budget-sensitive applications. Bronze bearings benefit from widespread availability and cost-effectiveness, as copper and tin--primary components--are more abundant and less expensive than elements used in superalloys. While superalloys offer superior performance in extreme conditions, bronze remains the preferred choice for many industries requiring affordable, readily obtainable bearing materials without sacrificing durability.
Typical Applications in Industry
Superalloy bearings are commonly used in aerospace and gas turbine engines due to their exceptional high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for extreme operating conditions. Bronze bearings find extensive application in marine, automotive, and heavy machinery industries because of their excellent wear resistance, low friction, and cost-effectiveness in moderate load environments. The choice between superalloy and bronze depends on the operational temperature, load demands, and environmental exposure specific to industrial uses.
Choosing the Optimal Material for Your Bearing
Superalloys provide superior high-temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and wear durability, making them ideal for demanding bearing applications in aerospace or industrial turbines. Bronze bearings offer excellent machinability, good load-carrying capacity, and cost-effectiveness for moderate stress and temperature conditions. Selecting the optimal bearing material depends on operational temperature, load requirements, and environmental factors to ensure longevity and performance.
Infographic: Superalloy vs Bronze for Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com