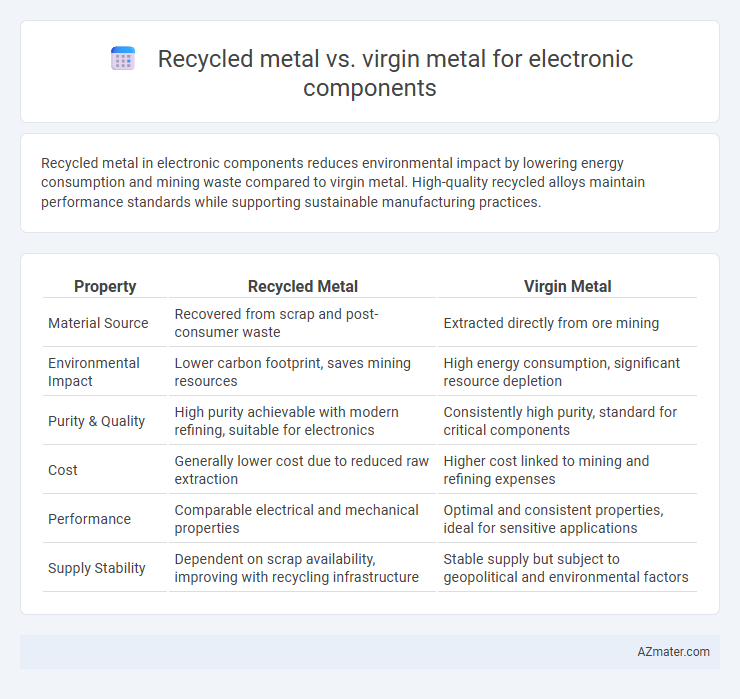
Recycled metal in electronic components reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and mining waste compared to virgin metal. High-quality recycled alloys maintain performance standards while supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Metal | Virgin Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Recovered from scrap and post-consumer waste | Extracted directly from ore mining |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, saves mining resources | High energy consumption, significant resource depletion |
| Purity & Quality | High purity achievable with modern refining, suitable for electronics | Consistently high purity, standard for critical components |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to reduced raw extraction | Higher cost linked to mining and refining expenses |
| Performance | Comparable electrical and mechanical properties | Optimal and consistent properties, ideal for sensitive applications |
| Supply Stability | Dependent on scrap availability, improving with recycling infrastructure | Stable supply but subject to geopolitical and environmental factors |
Introduction to Metal Sourcing in Electronics
Recycled metal in electronic components offers a sustainable alternative to virgin metal, reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. Virgin metals, extracted directly from ores, provide high purity and consistent quality essential for reliable electronic performance. The choice between recycled and virgin metals significantly influences supply chain sustainability, cost efficiency, and material availability in electronics manufacturing.
Defining Recycled vs Virgin Metals
Recycled metal in electronic components originates from previously used materials that are reprocessed to meet industry standards, reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. Virgin metal is extracted directly from ores through mining and refining, ensuring high purity and performance reliability critical for sensitive electronic applications. The distinct sourcing and processing methods influence the material properties, cost, and sustainability profile of electronic components.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Metals
Recycled metals in electronic components significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and minimizing mining-related habitat destruction compared to virgin metals. Producing recycled metals generates up to 90% less greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to reduced carbon footprints in electronics manufacturing. Utilizing recycled metals also decreases landfill waste and conserves finite natural resources, promoting sustainable material cycles in the electronics industry.
Cost Comparison: Economic Benefits and Challenges
Recycled metal for electronic components significantly reduces raw material costs, offering economic benefits through lower extraction and processing expenses compared to virgin metal. However, recycled metals may require additional refining and quality assurance processes, increasing operational costs and potentially impacting overall cost-efficiency. Balancing these factors, recycled metals provide a cost-effective alternative but face challenges in maintaining consistent purity and performance standards essential for high-precision electronic components.
Quality and Performance in Electronic Components
Recycled metal in electronic components can offer comparable conductivity and mechanical strength to virgin metal when properly processed, although impurities may slightly affect consistency. Virgin metal typically provides higher purity and uniformity, ensuring optimal electrical performance and enhanced reliability in precision applications. Advances in metallurgical refining techniques are narrowing the quality gap, making recycled metal increasingly viable without significant compromise on performance.
Supply Chain and Availability Issues
Recycled metal in electronic components helps alleviate supply chain disruptions by reducing dependency on finite virgin metal sources, which are often subject to geopolitical tensions and mining restrictions. The availability of recycled metals fluctuates based on collection and processing infrastructure, leading to potential inconsistencies in supply volume and purity levels. Leveraging advanced recycling technologies and improving scrap metal recovery can enhance the stability and sustainability of metal supply chains in the electronics industry.
Energy Consumption and Emissions
Recycled metal in electronic components significantly reduces energy consumption, requiring up to 95% less energy compared to extracting and processing virgin metal. Emissions associated with recycled metals are substantially lower, contributing to a decrease in greenhouse gases by approximately 40-60% across the supply chain. Utilizing recycled metals promotes sustainable manufacturing by minimizing environmental impact while maintaining material quality essential for electronic components.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Recycled metal used in electronic components must meet stringent regulatory standards such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives to ensure safety and environmental compliance. Virgin metal often has a more consistent chemical composition, simplifying compliance verification with standards like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals). Manufacturers increasingly favor recycled metals that comply with environmental regulations while reducing resource depletion and minimizing hazardous waste in electronic production.
Innovation and Advancements in Metal Recycling
Innovations in metal recycling have significantly enhanced the quality and purity of recycled metals, making them increasingly viable for high-performance electronic components compared to virgin metals. Advanced processes such as hydrometallurgy and electrochemical refining enable efficient recovery of rare and precious metals like gold, silver, and palladium, essential in semiconductors and circuit boards. These technological advancements not only reduce environmental impact but also lower production costs, driving sustainability and innovation in the electronics industry.
Future Outlook: Sustainable Electronics Manufacturing
Recycled metal in electronic components significantly reduces environmental impact by conserving natural resources and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin metal extraction. Advancements in recycling technologies and stringent regulatory policies are driving the shift towards sustainable electronics manufacturing, promoting circular economy principles. The future outlook emphasizes increased investment in recycled metal supply chains to meet growing demand for eco-friendly and cost-effective electronic materials.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Virgin metal for Electronic component
 azmater.com
azmater.com