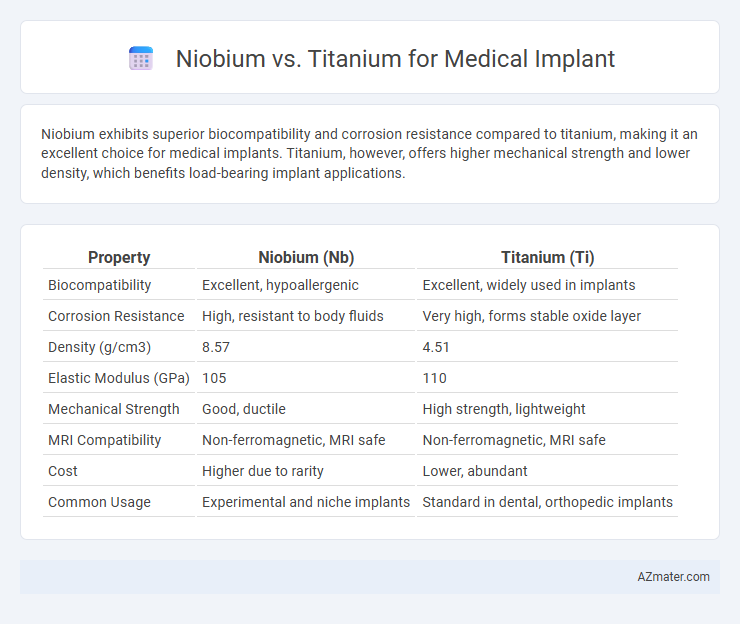
Niobium exhibits superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance compared to titanium, making it an excellent choice for medical implants. Titanium, however, offers higher mechanical strength and lower density, which benefits load-bearing implant applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Titanium (Ti) |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, hypoallergenic | Excellent, widely used in implants |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, resistant to body fluids | Very high, forms stable oxide layer |
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.57 | 4.51 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 105 | 110 |
| Mechanical Strength | Good, ductile | High strength, lightweight |
| MRI Compatibility | Non-ferromagnetic, MRI safe | Non-ferromagnetic, MRI safe |
| Cost | Higher due to rarity | Lower, abundant |
| Common Usage | Experimental and niche implants | Standard in dental, orthopedic implants |
Introduction: Niobium and Titanium in Medical Implants
Niobium and titanium are highly valued in medical implants due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Titanium's widespread use is attributed to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and proven integration with bone tissue, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. Niobium offers excellent biocompatibility and enhanced flexibility, often serving as an alloying element to improve implant performance and reduce allergic reactions.
Biocompatibility: Comparing Niobium and Titanium
Niobium and titanium both exhibit excellent biocompatibility, making them ideal for medical implants due to their resistance to corrosion and minimal immune response. Titanium is widely used in orthopedic and dental implants for its high strength-to-weight ratio and ability to osseointegrate with bone tissue. Niobium offers superior hemocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, which is beneficial in cardiovascular implants and devices requiring direct blood contact.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Niobium and titanium are widely used in medical implants due to their superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, but titanium exhibits higher mechanical strength with a tensile strength of approximately 900 MPa compared to niobium's 500 MPa. Titanium's exceptional fatigue resistance and modulus of elasticity closer to bone make it more suitable for load-bearing applications, enhancing implant durability and longevity. Niobium offers enhanced ductility and corrosion resistance, but its lower mechanical strength limits its use in high-stress implant environments.
Corrosion Resistance in Biological Environments
Niobium and titanium are both highly valued for their exceptional corrosion resistance in biological environments, making them ideal for medical implants. Niobium exhibits superior resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion due to its stable oxide layer, which enhances biocompatibility and longevity in saline and bodily fluids. Titanium, especially in its Ti-6Al-4V alloy form, provides excellent resistance to general corrosion and mechanical strength, but can be more susceptible to localized corrosion compared to niobium under aggressive physiological conditions.
Allergy and Hypersensitivity Risks
Niobium exhibits lower allergenic potential compared to titanium, making it a preferable option for patients with known metal hypersensitivities in medical implants. Titanium, while biocompatible and widely used, can occasionally trigger allergic reactions due to trace metal impurities or ion release over time. Studies highlight niobium's superior corrosion resistance and bioinert properties, reducing the risk of immune response and hypersensitivity in sensitive individuals.
Osseointegration Performance
Niobium exhibits superior osseointegration performance due to its excellent biocompatibility and ability to promote hydroxyapatite formation on the implant surface, which enhances bone bonding. Titanium, widely used in medical implants, offers high strength and corrosion resistance, but niobium's unique oxide layer provides better cellular response and faster bone growth. Studies reveal that niobium implants result in lower inflammation and improved long-term stability compared to titanium, making niobium a promising material for next-generation orthopedic and dental implants.
Imaging Compatibility (MRI & CT)
Niobium exhibits superior imaging compatibility compared to titanium due to its lower magnetic susceptibility, which significantly reduces artifacts in MRI scans. Its radiodensity is closer to that of human bone, enhancing CT image clarity and diagnostic accuracy. Titanium, while biocompatible and strong, often causes greater distortion in MRI and higher radiopacity in CT, potentially complicating post-surgical evaluations.
Surgical Handling and Fabrication
Niobium offers superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making it highly favored in surgical handling for medical implants due to its excellent formability and low elastic modulus that reduces stress shielding. Titanium, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration properties, provides robust fabrication options through advanced machining and additive manufacturing, ensuring precise implant customization. Surgical handling benefits from niobium's enhanced ductility and titanium's firm structural integrity, positioning both metals as critical materials in implant surgery.
Clinical Applications and Case Studies
Niobium and titanium are prominent materials in medical implants due to their biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, with titanium being extensively used in orthopedic and dental implants, supported by numerous clinical studies demonstrating its excellent osseointegration and long-term stability. Niobium, though less common, shows promising results in biomedical applications, particularly in vascular stents and dental implants, where case studies highlight its superior radiopacity and enhanced bioactivity compared to titanium. Comparative clinical data reveal that niobium alloys may reduce inflammatory responses and improve tissue compatibility, suggesting potential advantages in personalized implant solutions.
Cost and Availability in Healthcare
Niobium offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance but is generally more expensive and less abundant than titanium, affecting its widespread use in medical implants. Titanium is more cost-effective and readily available, making it the preferred choice in healthcare for implant manufacturing. The availability of titanium facilitates large-scale production and supply chain stability, while niobium remains specialized for niche applications due to higher material and processing costs.
Infographic: Niobium vs Titanium for Medical Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com