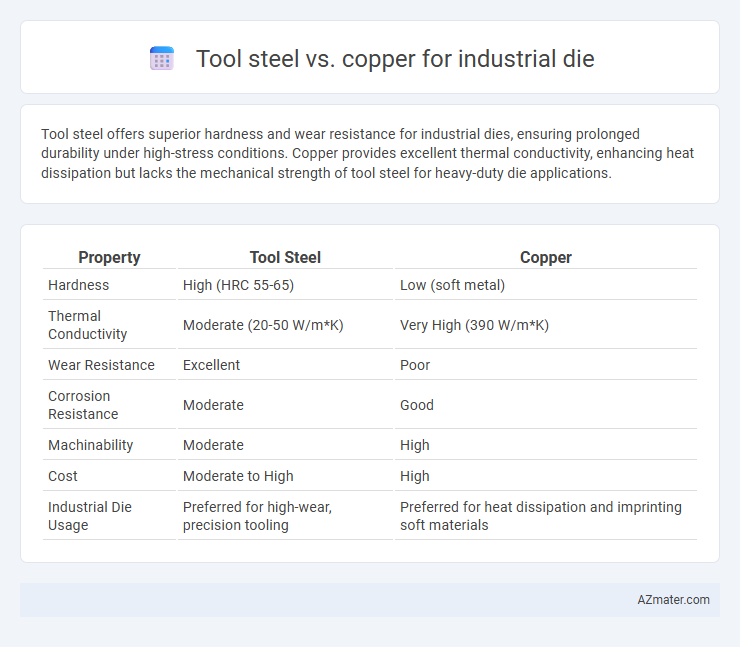
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance for industrial dies, ensuring prolonged durability under high-stress conditions. Copper provides excellent thermal conductivity, enhancing heat dissipation but lacks the mechanical strength of tool steel for heavy-duty die applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (HRC 55-65) | Low (soft metal) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (20-50 W/m*K) | Very High (390 W/m*K) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Good |
| Machinability | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High |
| Industrial Die Usage | Preferred for high-wear, precision tooling | Preferred for heat dissipation and imprinting soft materials |
Introduction: Tool Steel vs Copper in Industrial Die Applications
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for demanding industrial die applications requiring precision and durability. Copper excels in thermal conductivity, enabling rapid heat dissipation, which reduces cycle times and minimizes thermal deformation in dies. Selecting between tool steel and copper depends on balancing strength and heat management to optimize die performance and lifespan.
Key Properties of Tool Steel for Die Manufacturing
Tool steel is preferred over copper for industrial die manufacturing due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge at high temperatures. The high carbon and alloy content in tool steel enhances toughness and thermal stability, making it ideal for repeated impact and machining operations. Its superior dimensional stability under thermal stress ensures precision and longevity in die applications compared to copper.
Key Properties of Copper for Industrial Dies
Copper offers excellent thermal conductivity, enabling rapid heat dissipation critical in industrial die applications to prevent overheating and ensure dimensional stability. Its superior electrical conductivity also supports processes involving electrical discharge machining (EDM), enhancing precision and tool life. High corrosion resistance and good machinability make copper an ideal choice for dies requiring frequent modifications and prolonged durability in harsh industrial environments.
Performance Comparison: Tool Steel vs Copper
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-load industrial die applications, while copper excels in thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, enabling rapid heat dissipation and reduced cycle times. Tool steel's strength ensures longer die life in abrasive or high-pressure environments, whereas copper's excellent heat transfer properties prevent overheating and maintain dimensional accuracy during cutting or stamping. The choice between tool steel and copper depends on balancing durability requirements with thermal management needs in specific industrial die processes.
Wear Resistance and Durability Factors
Tool steel surpasses copper in wear resistance due to its high hardness and ability to retain strength at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for industrial die applications exposed to abrasive conditions. Copper offers excellent thermal conductivity but lacks the durability required for long-term wear resistance, leading to faster degradation under mechanical stress. Selecting tool steel enhances die lifespan, reduces downtime, and maintains precision in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Thermal Conductivity: Tool Steel vs Copper
Copper exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity, approximately 401 W/m*K, compared to tool steel's average of 20-50 W/m*K, enabling faster heat dissipation in industrial dies. This superior thermal conductivity of copper minimizes thermal fatigue and reduces cycle times in manufacturing processes. Tool steel, while less conductive, offers greater hardness and wear resistance, but copper's thermal performance is unmatched for efficient temperature control in die applications.
Machinability and Ease of Fabrication
Tool steel offers superior machinability and ease of fabrication for industrial dies due to its hardness and wear resistance, allowing precise cutting and shaping with standard machining equipment. Copper, while softer and more malleable, provides excellent thermal conductivity but poses challenges during machining because of its tendency to work-harden and stick to cutting tools. Selecting tool steel generally results in longer tool life and higher dimensional stability in die fabrication compared to copper, which requires specialized tooling and techniques to achieve comparable precision.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Copper Dies
Tool steel dies exhibit higher initial costs due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes, yet their superior hardness and wear resistance ensure longer tool life and reduced maintenance expenses. Copper dies offer lower upfront costs and excellent thermal conductivity, enhancing cooling efficiency and cycle times in certain industrial applications. When analyzing total cost of ownership, tool steel's durability often results in lower long-term expenses, whereas copper dies may be more cost-effective for short production runs or applications requiring rapid heat dissipation.
Best Use Cases for Tool Steel Dies
Tool steel dies excel in high-wear industrial applications requiring exceptional hardness, thermal resistance, and durability, such as metal stamping, extrusion, and cutting operations. Copper dies, by contrast, offer superior thermal conductivity and are ideal for processes involving heat dissipation and rapid cooling, like injection molding or plastic shaping. The best use cases for tool steel dies involve heavy-duty manufacturing with repeated mechanical stress and precision, ensuring longevity and consistent performance under high pressure and temperature.
Ideal Applications for Copper Dies
Copper dies excel in high-thermal-conductivity applications, making them ideal for industries requiring rapid heat dissipation such as plastic injection molding and extrusion. Their superior thermal properties reduce cycle times and minimize the risk of thermal fatigue compared to tool steel dies. Copper dies are preferred for production scenarios involving short runs or delicate materials where precise temperature control enhances product quality.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Copper for Industrial die
 azmater.com
azmater.com