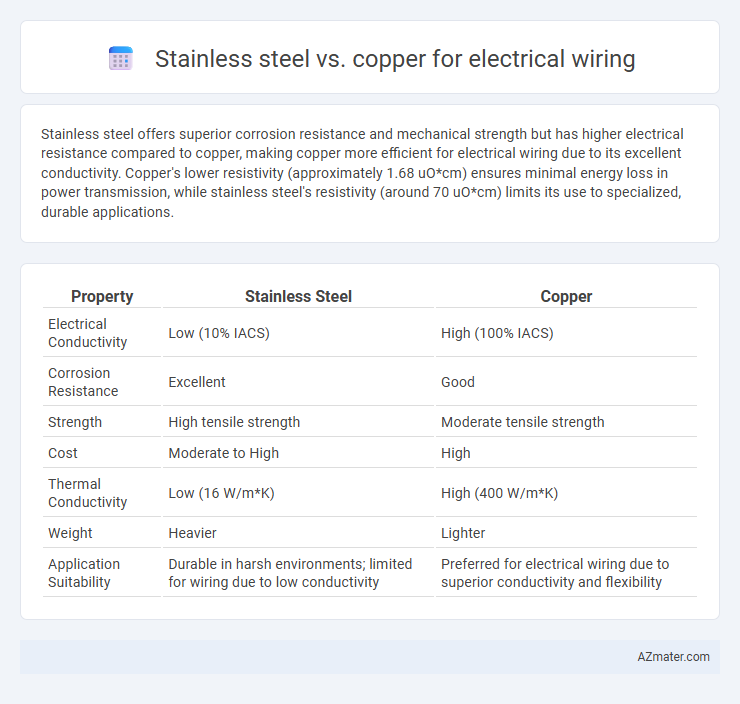
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength but has higher electrical resistance compared to copper, making copper more efficient for electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity. Copper's lower resistivity (approximately 1.68 uO*cm) ensures minimal energy loss in power transmission, while stainless steel's resistivity (around 70 uO*cm) limits its use to specialized, durable applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (10% IACS) | High (100% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (16 W/m*K) | High (400 W/m*K) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Application Suitability | Durable in harsh environments; limited for wiring due to low conductivity | Preferred for electrical wiring due to superior conductivity and flexibility |
Introduction to Electrical Wiring Materials
Stainless steel and copper are two prominent materials used in electrical wiring, each offering distinct electrical conductivity and durability characteristics. Copper is highly favored for its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for efficient current flow and long-term use. Stainless steel, while less conductive, provides superior strength and resistance to mechanical damage, suitable for specialized applications requiring enhanced structural integrity.
Overview of Stainless Steel and Copper
Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance, durability, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for environments requiring robust, long-lasting wiring solutions. Copper provides excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, making it the preferred choice for standard electrical wiring with efficient current flow and minimal energy loss. Both metals serve critical roles in electrical applications, with copper dominating for conductivity and stainless steel favored for structural resilience and environmental resistance.
Conductivity Comparison: Stainless Steel vs Copper
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity, with a value of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, compared to stainless steel's much lower conductivity, generally around 1.4 x 10^6 S/m. This stark difference means copper allows electric current to flow more efficiently, reducing energy losses and heat generation in wiring applications. While stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, copper remains the preferred material for electrical wiring due to its exceptional conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for harsh environments where oxidation and chemical exposure are concerns. Its durability and mechanical strength exceed copper, providing long-lasting performance in structural and high-stress applications. Copper, while highly conductive, tends to corrode over time, particularly in moist or acidic conditions, which can degrade electrical connections and overall system reliability.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Stainless steel offers superior mechanical strength compared to copper, making it highly resistant to physical damage and suitable for applications requiring durability and structural support. Copper excels in flexibility, allowing easier bending and installation in tight spaces without compromising electrical conductivity. While copper remains the preferred choice for most electrical wiring due to its balance of flexibility and conductivity, stainless steel is advantageous in environments demanding higher mechanical robustness.
Cost Analysis: Stainless Steel vs Copper
Copper electrical wiring generally costs more upfront due to higher raw material prices but offers superior conductivity and durability, which can reduce long-term energy losses and maintenance expenses. Stainless steel wiring, while cheaper initially, has higher resistance leading to increased energy consumption and potential overheating issues, raising operational costs over time. Evaluating total lifecycle cost shows copper as more cost-effective for high-performance and long-term electrical applications despite its initial price premium.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Stainless steel electrical wiring offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, reducing maintenance frequency compared to copper, which is softer and more prone to oxidation requiring regular inspections. Installation of copper wiring is typically easier due to its higher ductility and excellent electrical conductivity, allowing for simpler bending and connection processes. However, stainless steel's rigidity demands specialized tools and techniques for installation, increasing initial labor efforts but resulting in longer-term maintenance savings.
Safety Considerations in Electrical Wiring
Stainless steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance and higher mechanical strength, reducing the risk of damage and electrical faults in wiring applications. Copper provides superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance, minimizing overheating and fire hazards. Proper insulation and grounding are critical for both materials to ensure safe and reliable electrical installations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper is highly conductive, reducing energy losses and improving efficiency in electrical wiring, which supports sustainability by lowering overall power consumption. Stainless steel, while less conductive, offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing resource extraction impact. Copper mining, however, poses significant environmental challenges including habitat destruction and pollution, whereas stainless steel's alloy composition relies on recycled materials, enhancing its environmental profile in sustainable wiring applications.
Applications and Industry Recommendations
Stainless steel wiring is preferred in harsh industrial environments due to its high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, often used in aerospace and marine applications where durability is critical. Copper remains the industry standard for electrical wiring in residential and commercial buildings because of its excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness. Industry recommendations emphasize using copper for most electrical circuits, reserving stainless steel for niche applications requiring enhanced mechanical protection and corrosion resistance.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Copper for Electrical wiring
 azmater.com
azmater.com