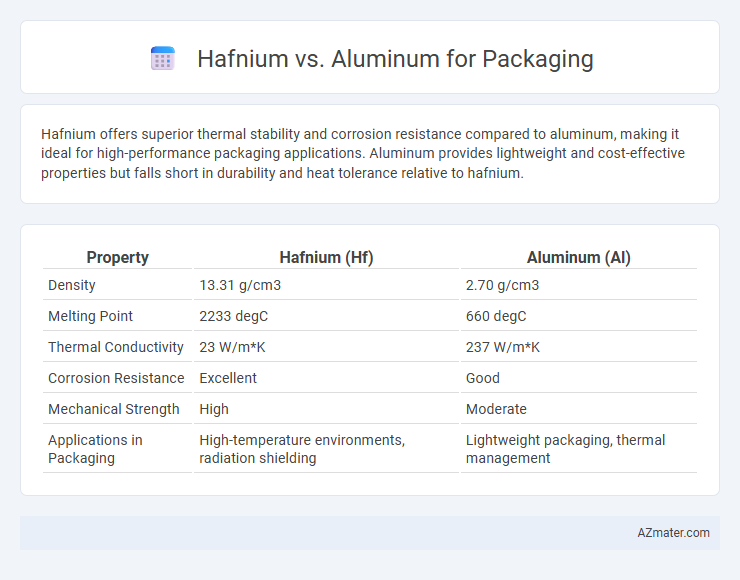
Hafnium offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications. Aluminum provides lightweight and cost-effective properties but falls short in durability and heat tolerance relative to hafnium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Aluminum (Al) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 13.31 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2233 degC | 660 degC |
| Thermal Conductivity | 23 W/m*K | 237 W/m*K |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Applications in Packaging | High-temperature environments, radiation shielding | Lightweight packaging, thermal management |
Introduction to Hafnium and Aluminum in Packaging
Hafnium and aluminum serve distinct roles in packaging, with aluminum widely favored for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for food and beverage containers. Hafnium, although less common, is valued in specialized packaging applications due to its exceptional resistance to high temperatures and strong oxidation resistance. The choice between hafnium and aluminum hinges on the packaging requirements, where aluminum dominates in mass applications while hafnium excels in high-performance, niche environments.
Material Properties Comparison: Hafnium vs Aluminum
Hafnium exhibits significantly higher melting point (2233degC) and superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, which melts at 660degC, making hafnium suitable for high-temperature packaging applications. Hafnium's density (13.31 g/cm3) is much greater than aluminum's (2.70 g/cm3), impacting weight-sensitive packaging design. Additionally, aluminum offers excellent thermal conductivity (237 W/m*K) and is lightweight and cost-effective, whereas hafnium provides enhanced mechanical strength and radiation resistance ideal for specialized packaging environments.
Barrier Performance: Protecting Products
Hafnium exhibits superior barrier performance compared to aluminum, effectively protecting products from moisture, oxygen, and chemical contaminants. Its dense atomic structure and high corrosion resistance reduce permeation, ensuring longer shelf life and maintaining product integrity. Hafnium's enhanced protective qualities make it ideal for sensitive packaging applications demanding exceptional durability.
Weight and Durability Considerations
Hafnium offers superior durability compared to aluminum due to its high melting point and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for packaging that demands long-term protection. Although hafnium is denser than aluminum, its strength-to-weight ratio allows for thinner, lighter packaging materials without compromising structural integrity. Aluminum remains the preferred choice when minimizing weight is critical, but hafnium excels in applications where enhanced durability outweighs the slight weight increase.
Cost Analysis: Hafnium vs Aluminum Packaging
Hafnium packaging is significantly more expensive than aluminum due to the rarity and complex extraction process of hafnium, which drives up raw material costs. Aluminum's abundance and well-established manufacturing infrastructure result in lower production and material expenses, making it the preferred choice for cost-sensitive packaging applications. Despite hafnium's superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability, aluminum offers a cost-effective solution with a favorable price-to-performance ratio in the packaging industry.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability compared to aluminum, reducing environmental degradation over time in packaging applications. Aluminum is highly recyclable with a well-established global recycling infrastructure, significantly lowering its carbon footprint and energy consumption during production. The sustainability of packaging materials hinges on the balance between hafnium's durability and aluminum's recyclability, with aluminum currently favored for large-scale sustainable packaging due to its circular economy benefits.
Application Suitability in Packaging Industries
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-temperature and harsh chemical packaging environments. Aluminum's lightweight, malleability, and cost-effectiveness remain advantageous for large-scale consumer packaging applications requiring easy shaping and recyclability. Selecting between hafnium and aluminum depends on balancing durability needs with economic and manufacturing efficiency in packaging industries.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Hafnium offers superior safety and regulatory compliance in packaging due to its excellent corrosion resistance and non-toxic nature, reducing contamination risks in sensitive products. Aluminum, while widely used for packaging, requires strict adherence to coating and recycling standards to prevent metal leaching and environmental impact. Regulatory bodies like FDA and EU emphasize material purity and recyclability, where hafnium's stable properties provide a compliance advantage over aluminum in specialized applications.
Innovation and Future Trends in Packaging Materials
Hafnium's emerging role in packaging materials signals a shift towards superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional aluminum, enabling advanced applications in high-performance and flexible packaging. Innovations leveraging hafnium alloys and coatings aim to enhance barrier properties, extend shelf life, and support sustainable packaging solutions by reducing material thickness and weight. Future trends indicate a growing integration of hafnium-based composites in smart packaging technology, driving improvements in product protection and environmental impact reduction.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Takeaways
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting points compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-temperature packaging applications requiring exceptional durability. Aluminum excels in lightweight, cost-effective packaging with excellent thermal conductivity and ease of fabrication, suitable for everyday consumer products. Selecting the right material hinges on balancing performance needs such as thermal stability and corrosion resistance with budget constraints and specific use-case requirements.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Aluminum for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com