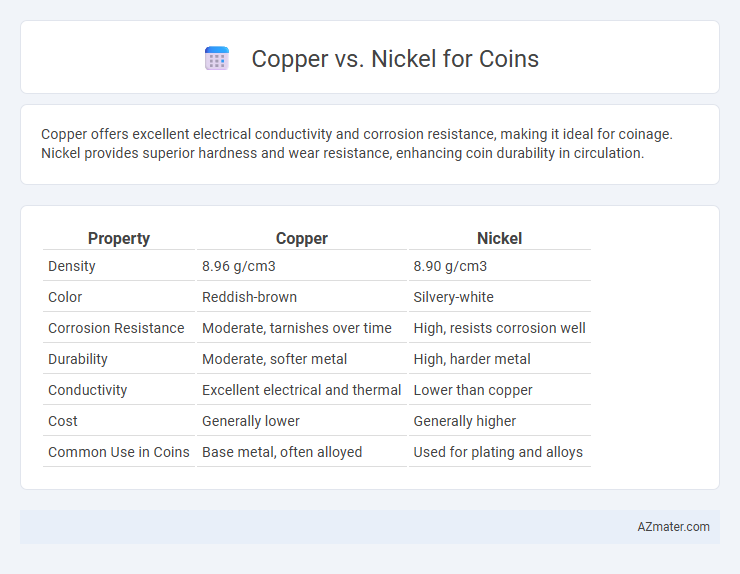
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for coinage. Nickel provides superior hardness and wear resistance, enhancing coin durability in circulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Copper | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.96 g/cm3 | 8.90 g/cm3 |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Silvery-white |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, tarnishes over time | High, resists corrosion well |
| Durability | Moderate, softer metal | High, harder metal |
| Conductivity | Excellent electrical and thermal | Lower than copper |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Common Use in Coins | Base metal, often alloyed | Used for plating and alloys |
Overview of Copper and Nickel in Coinage
Copper and nickel are essential metals in coinage due to their durability and corrosion resistance. Copper offers excellent conductivity and a distinctive reddish hue, making it popular for lower denomination coins, while nickel provides a silver-like appearance and increased hardness. The combination of copper-nickel alloys balances cost-effectiveness with longevity, ensuring coins withstand extensive circulation and maintain visual appeal.
Historical Use of Copper and Nickel in Coins
Copper and nickel have played pivotal roles in coinage due to their durability and corrosion resistance. Historically, copper was used extensively in ancient and medieval coins because of its abundance and ease of minting, while nickel gained popularity in the 19th century as an alloy component to enhance hardness and wear resistance. Modern coin production often combines copper and nickel, such as in cupronickel alloys, to balance cost-efficiency with longevity and maintain distinct metallic properties essential for circulation coins.
Physical Properties: Copper vs Nickel
Copper exhibits excellent electrical conductivity, malleability, and a reddish-brown color, making it easy to mint and aesthetically distinct in coins. Nickel is harder, more corrosion-resistant, and silvery-white, providing durability and wear resistance essential for long-lasting coinage. The density of copper (8.96 g/cm3) and nickel (8.90 g/cm3) are similar, but copper's softer nature contrasts with nickel's higher tensile strength, influencing coin longevity and feel.
Visual Appearance and Tactile Differences
Copper coins exhibit a warm, reddish-brown hue that deepens with age and handling, creating a distinctive vintage appeal. Nickel coins feature a cooler, silvery-gray tone with a smooth, metallic sheen that resists tarnishing and maintains a consistent shine. In tactile terms, copper coins often feel heavier and develop a unique patina over time, while nickel coins are lighter with a harder surface that provides a crisp, firm grip.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Copper exhibits excellent durability for coins due to its inherent hardness and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-lasting circulation without significant degradation. Nickel offers superior wear resistance compared to copper, maintaining coin detail and surface integrity even under frequent handling and friction. The blend of copper and nickel in coin alloys optimizes both durability and wear resistance, providing a balanced solution for high-traffic currency use.
Cost Comparison: Copper vs Nickel
Copper coins generally have a lower production cost compared to nickel coins due to the lower market price of copper per ton. Nickel's higher durability and resistance to corrosion come at a premium, increasing the overall expense for minting. Cost-efficiency analysis favors copper for large-scale coin production, especially when budget constraints are critical.
Anti-Counterfeiting Qualities
Copper exhibits distinct electromagnetic signatures and color properties that enhance coin authentication through advanced detection technologies. Nickel's resistance to corrosion and its specific magnetic permeability provide reliable anti-counterfeiting features when integrated into coin alloys. Combining copper and nickel optimizes security measures by leveraging their complementary metallurgical and physical properties in modern currency production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper coins have a lower environmental footprint due to their higher recyclability and lower energy consumption during extraction compared to nickel. Nickel mining contributes significantly to soil and water pollution, raising concerns about ecosystem damage and biodiversity loss. Sustainable coin production increasingly favors copper alloys for their reduced environmental impact and greater circular economy benefits.
Allergenic and Health Considerations
Copper is generally considered hypoallergenic and rarely causes skin reactions, making it a safer choice for coins handled frequently. Nickel is a known allergen and can induce contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals, raising health concerns for coins with high nickel content. Choosing copper or copper alloys minimizes the risk of allergic reactions and supports better long-term skin health in coin handling.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Coin Metal
Copper offers excellent corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for durability and hygiene in coins. Nickel provides superior hardness and wear resistance, ensuring longevity and maintaining coin detail over time. Selecting the ideal coin metal depends on balancing copper's antimicrobial benefits with nickel's strength to meet specific circulation and usage requirements.
Infographic: Copper vs Nickel for Coin
 azmater.com
azmater.com