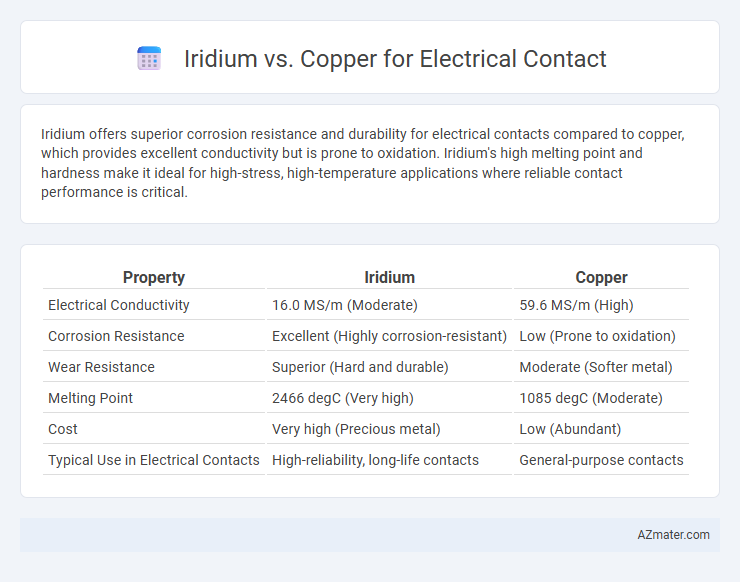
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability for electrical contacts compared to copper, which provides excellent conductivity but is prone to oxidation. Iridium's high melting point and hardness make it ideal for high-stress, high-temperature applications where reliable contact performance is critical.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Iridium | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 16.0 MS/m (Moderate) | 59.6 MS/m (High) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Highly corrosion-resistant) | Low (Prone to oxidation) |
| Wear Resistance | Superior (Hard and durable) | Moderate (Softer metal) |
| Melting Point | 2466 degC (Very high) | 1085 degC (Moderate) |
| Cost | Very high (Precious metal) | Low (Abundant) |
| Typical Use in Electrical Contacts | High-reliability, long-life contacts | General-purpose contacts |
Introduction to Electrical Contacts
Electrical contacts rely heavily on the material's conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion to ensure reliable performance in circuits. Iridium, a rare and dense metal, offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced wear properties compared to copper, which provides excellent electrical conductivity but is more prone to oxidation and surface degradation over time. The choice between iridium and copper for electrical contacts depends on the application's demand for longevity, electrical efficiency, and environmental conditions.
Material Properties of Iridium and Copper
Iridium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, high melting point (2446degC), and superior hardness, making it ideal for long-lasting electrical contacts in harsh environments. Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity (approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m) and thermal conductivity but is softer and more prone to oxidation compared to iridium. Combining these materials leverages iridium's durability with copper's conductivity to enhance contact performance and reliability.
Conductivity Comparison: Iridium vs Copper
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity with a value of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, significantly higher than iridium's conductivity of about 1.0 x 10^7 S/m. While copper's high conductivity enables efficient current flow in most electrical contacts, iridium offers enhanced corrosion resistance and durability under harsh conditions. The trade-off between copper's excellent conductivity and iridium's robustness is critical in applications demanding both electrical performance and long-term reliability.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Iridium exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to copper in electrical contacts due to its high melting point of 2446degC and exceptional hardness, making it ideal for high-load and high-temperature applications. Copper, while known for excellent electrical conductivity (approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m), suffers from softer mechanical properties leading to faster wear and degradation under repeated mechanical stress. Iridium's ability to maintain stable contact under harsh conditions significantly extends the lifespan of electrical connectors in demanding environments.
Corrosion Resistance in Electrical Applications
Iridium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper in electrical contact applications, enduring harsh environments without significant degradation. Copper, while highly conductive, is prone to oxidation and tarnishing, leading to increased contact resistance and potential failure over time. Iridium's exceptional durability and chemical stability make it ideal for high-reliability electronics and aerospace components where long-term corrosion resistance is critical.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Copper is widely favored for electrical contacts due to its excellent conductivity and abundant availability, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. Iridium, although offering superior corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments, comes with high material costs and limited availability, primarily sourced as a rare platinum-group metal. The cost disparity and scarcity of iridium restrict its use to specialized applications requiring enhanced performance and longevity despite copper's dominance in general electrical contacts.
Common Uses in Electrical Engineering
Iridium contacts excel in high-reliability applications such as aerospace, medical devices, and high-frequency switches due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and ability to withstand arcing and high temperatures. Copper contacts, valued for their superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, are widely used in power distribution systems, circuit breakers, and electrical connectors where lower resistance and efficient current flow are critical. The choice between iridium and copper typically depends on the balance between durability in harsh environments versus high conductivity and affordability for large-scale electrical engineering projects.
Performance Under High Current Loads
Iridium offers superior performance under high current loads due to its exceptional resistance to arc erosion and high melting point, ensuring greater durability and reliability in electrical contacts. Copper provides excellent electrical conductivity but tends to degrade faster under intense arcing conditions, leading to increased maintenance and replacement costs. The combination of iridium's hardness and copper's conductivity often results in hybrid contacts that optimize both longevity and electrical efficiency in high current applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Iridium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, minimizing environmental contamination risks compared to copper, which is prone to oxidation and can release toxic copper ions into the environment. Iridium's non-toxic nature and low reactivity enhance safety in electrical contacts, reducing hazards associated with copper's potential to cause allergic reactions and environmental toxicity. The long lifespan of iridium contacts also decreases the frequency of replacement, leading to lower environmental impact and improved sustainability in electrical applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Iridium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and wear durability, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh environments. Copper provides superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but may suffer from oxidation and wear over time. Selecting between iridium and copper depends on balancing conductivity, longevity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal contact performance.
Infographic: Iridium vs Copper for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com