Recycled metal containers reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to tin containers. Tin offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability but has a higher carbon footprint due to mining and refining processes.
Table of Comparison
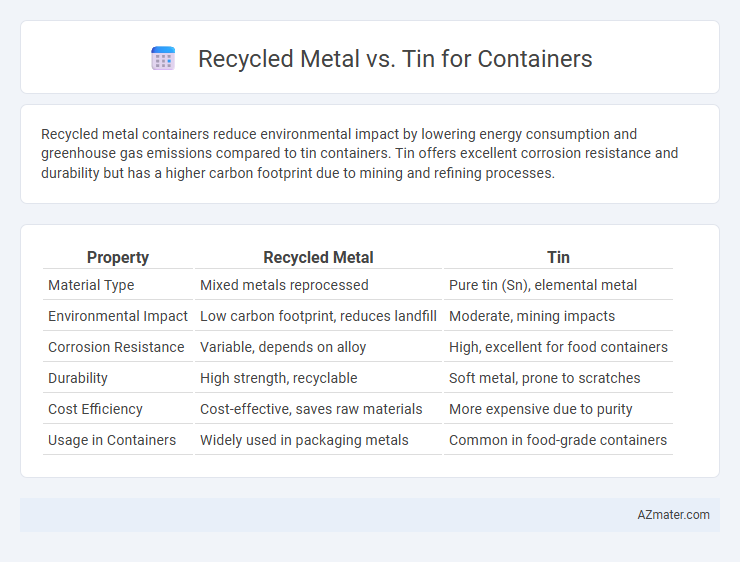
| Property | Recycled Metal | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Mixed metals reprocessed | Pure tin (Sn), elemental metal |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, reduces landfill | Moderate, mining impacts |
| Corrosion Resistance | Variable, depends on alloy | High, excellent for food containers |
| Durability | High strength, recyclable | Soft metal, prone to scratches |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective, saves raw materials | More expensive due to purity |
| Usage in Containers | Widely used in packaging metals | Common in food-grade containers |
Introduction to Sustainable Containers
Sustainable containers are increasingly vital in reducing environmental impact, with recycled metal offering significant benefits compared to traditional tin. Recycled metal containers require less energy to produce, significantly lowering carbon emissions and conserving natural resources. Choosing recycled metals supports circular economy practices by minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency in packaging solutions.
What is Recycled Metal?
Recycled metal is material reclaimed from discarded products, refined, and repurposed for new manufacturing processes, reducing the need for virgin ores and lowering environmental impact. It offers durability and sustainability benefits for containers compared to tin, which is a soft, malleable metal traditionally used for food packaging but less eco-friendly due to mining and production practices. Using recycled metal in container production supports resource conservation and energy savings by minimizing waste and carbon emissions.
Understanding Tin as a Container Material
Tin, often used as a coating rather than the main material, provides excellent corrosion resistance for containers, ensuring food safety and extending shelf life. Unlike recycled metals, tin's non-reactive properties make it ideal for preserving taste and preventing contamination in canned goods. Its lightweight nature combined with durability enhances container performance while supporting sustainable packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Metal vs Tin
Recycled metal containers significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to tin, which requires intensive mining and refining processes. Utilizing recycled metals minimizes landfill waste and decreases greenhouse gas emissions, making them a more sustainable choice for packaging. In contrast, tin production often contributes to habitat destruction and contamination, highlighting recycled metal as the eco-friendlier alternative.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Recycled metal containers exhibit superior durability and strength compared to tin due to their enhanced alloy composition and processing techniques, which increase resistance to corrosion and impact. Tin, while lightweight and easy to mold, tends to be softer and more prone to denting or deformation under stress. Industrial-grade recycled metals, particularly aluminum and steel blends, offer longer lifespan and structural integrity, making them ideal for heavy-duty and reusable container applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Recycled metal offers significant cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption in production compared to tin, making it a budget-friendly option for container manufacturing. Tin remains more expensive due to limited natural reserves and complex extraction processes, though it provides superior corrosion resistance and appearance. Availability of recycled metal is higher and more sustainable, as it relies on established recycling streams, whereas tin supply is constrained by geographic concentration and mining rates.
Health and Food Safety Considerations
Recycled metal containers require stringent testing for contaminants like lead and cadmium to ensure food safety, while tin containers, often made from tinplate, provide a corrosion-resistant and non-toxic barrier ideal for preserving food quality. The presence of safe coatings in both recycled metals and tin reduces the risk of chemical leaching into food, maintaining consumer health standards. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EFSA enforce strict guidelines on metal migration limits to guarantee the safety of food packaging materials.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Recycled metal offers superior aesthetic versatility for containers, enabling designers to incorporate a variety of finishes such as matte, gloss, and textured surfaces, which enhance visual appeal and tactile experience. Tin, while traditional and corrosion-resistant, provides limited design flexibility due to its uniform surface and thinner gauge, restricting creative embossing or intricate detailing. The durability and malleability of recycled metals allow for innovative shapes and customization, making them ideal for modern, eco-conscious packaging solutions.
Industrial and Consumer Applications
Recycled metal offers superior environmental benefits and cost efficiency compared to tin in industrial and consumer container applications due to its reduced energy consumption and lower carbon footprint. Tin, traditionally used for corrosion resistance and food safety in cans, remains valuable for specific uses but is less sustainable and more resource-intensive to produce. The shift toward recycled metals supports circular economy goals, enhancing supply chain resilience and meeting increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Needs
Recycled metal containers offer superior sustainability benefits by reducing environmental impact through resource reuse and lower energy consumption compared to tin. Tin containers provide excellent corrosion resistance and a lightweight solution ideal for food preservation but involve higher environmental costs in extraction and processing. Selecting the best option depends on prioritizing sustainability and durability versus cost-effectiveness and specific usage requirements.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Tin for Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com