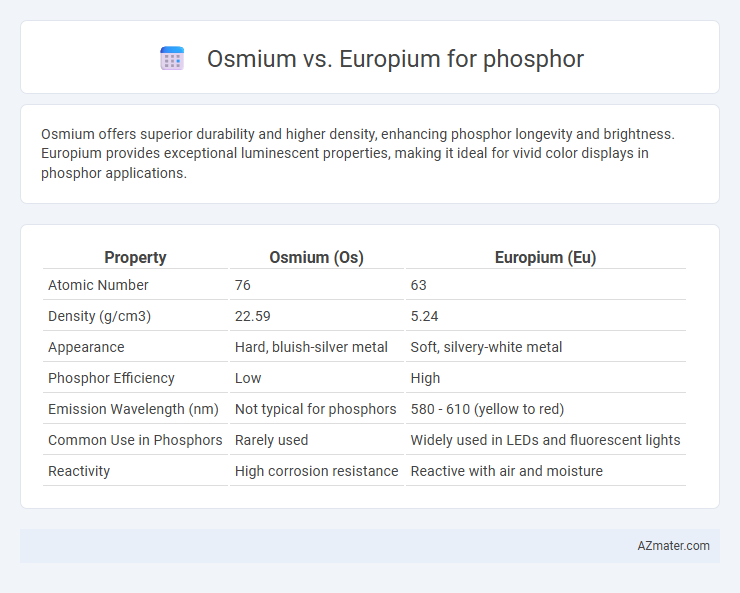
Osmium offers superior durability and higher density, enhancing phosphor longevity and brightness. Europium provides exceptional luminescent properties, making it ideal for vivid color displays in phosphor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Osmium (Os) | Europium (Eu) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 76 | 63 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 22.59 | 5.24 |
| Appearance | Hard, bluish-silver metal | Soft, silvery-white metal |
| Phosphor Efficiency | Low | High |
| Emission Wavelength (nm) | Not typical for phosphors | 580 - 610 (yellow to red) |
| Common Use in Phosphors | Rarely used | Widely used in LEDs and fluorescent lights |
| Reactivity | High corrosion resistance | Reactive with air and moisture |
Introduction to Osmium and Europium
Osmium, a dense transition metal known for its hardness and high melting point, is rarely used in phosphor applications due to its limited luminescent properties. Europium, a rare earth element, plays a crucial role in phosphor technology, particularly in red and blue phosphors used in LED displays and fluorescent lamps. The unique electronic configuration of europium allows efficient energy absorption and emission, making it essential for vibrant and long-lasting phosphorescence.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Osmium exhibits high density and a stable oxidation state mostly at +4 and +8, making it less reactive and suitable for applications requiring chemical durability. Europium, a lanthanide, displays variable oxidation states, primarily +2 and +3, enabling efficient electron transitions vital for phosphor luminescence. The distinct electron configurations and oxidation behavior of europium enhance its role in phosphors compared to osmium's limited luminescent properties.
Abundance and Sourcing
Osmium is an extremely rare platinum-group metal with a crustal abundance of about 0.001 parts per million, making its sourcing limited and primarily dependent on mining from platinum ores in regions like South Africa and Russia. Europium, a rare earth element, is more abundant with approximately 1.1 parts per million in the earth's crust and is typically extracted from minerals such as monazite and bastnasite found in China and the United States. Due to Europium's higher abundance and more established supply chain, it remains the preferred choice for phosphor applications over osmium, which is scarce and costly to procure.
Role in Phosphor Applications
Osmium's role in phosphor applications is limited due to its dense atomic structure and lower luminescent efficiency compared to europium. Europium is widely preferred in phosphor technology for its excellent red and blue emission characteristics, essential for high-performance display and lighting devices. The unique electronic configuration of europium ions enables superior luminescence, making them critical activators in phosphor materials for LED and fluorescent applications.
Efficiency and Performance in Lighting
Osmium exhibits limited efficiency in phosphor applications due to its lower luminescent properties compared to Europium, which is renowned for its superior emission intensity and color purity in lighting technologies. Europium-doped phosphors demonstrate high luminous efficiency and excellent stability, making them preferred in LED and fluorescent lighting for enhanced brightness and color rendering. The performance of Europium in activating phosphors significantly surpasses that of Osmium, resulting in more energy-efficient and long-lasting lighting solutions.
Color Emission Characteristics
Osmium and Europium differ significantly in their color emission characteristics when used as phosphors. Europium exhibits intense red and blue luminescence due to its efficient f-f electronic transitions, making it highly valuable in display and lighting technologies. Osmium, in contrast, shows weak and broad emission spectra with limited practical applications in phosphor-based color emission.
Stability and Longevity
Osmium-based phosphors exhibit exceptional chemical stability and resistance to oxidation, ensuring longer operational lifespans compared to europium-based counterparts. Europium phosphors, while known for their vibrant luminescence, often suffer from gradual degradation under prolonged exposure to moisture and heat, reducing their effective longevity. The superior stability of osmium compounds makes them more suitable for applications demanding consistent phosphor performance over extended periods.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Osmium, a dense and rare transition metal, poses significant environmental and safety risks due to its toxic osmium tetroxide byproduct, which can cause severe respiratory damage and requires stringent handling protocols. Europium, commonly used in phosphors for its efficient red and blue luminescence, exhibits lower toxicity and environmental impact, making it safer for manufacturing and disposal processes. Selecting europium-based phosphors reduces hazardous waste generation and enhances occupational safety compared to osmium-based alternatives.
Cost and Economic Factors
Osmium is significantly more expensive than europium due to its rarity and complex extraction processes, making europium the more cost-effective choice for phosphor applications. Europium's relative abundance and established supply chain contribute to its widespread use in LED and display phosphors, balancing performance with affordability. The higher market price of osmium limits its practical application despite potential unique properties.
Future Prospects in Phosphor Technology
Osmium's exceptional electron density and durability offer potential in enhancing phosphor stability and longevity for next-generation display technologies. Europium, renowned for its strong red and blue luminescence, remains integral in current phosphor applications but faces challenges in brightness efficiency and environmental sustainability. Emerging research explores osmium-doped phosphors aiming to overcome these limitations, suggesting a future where osmium could complement or even surpass europium in high-performance, eco-friendly phosphor materials.
Infographic: Osmium vs Europium for Phosphor
 azmater.com
azmater.com