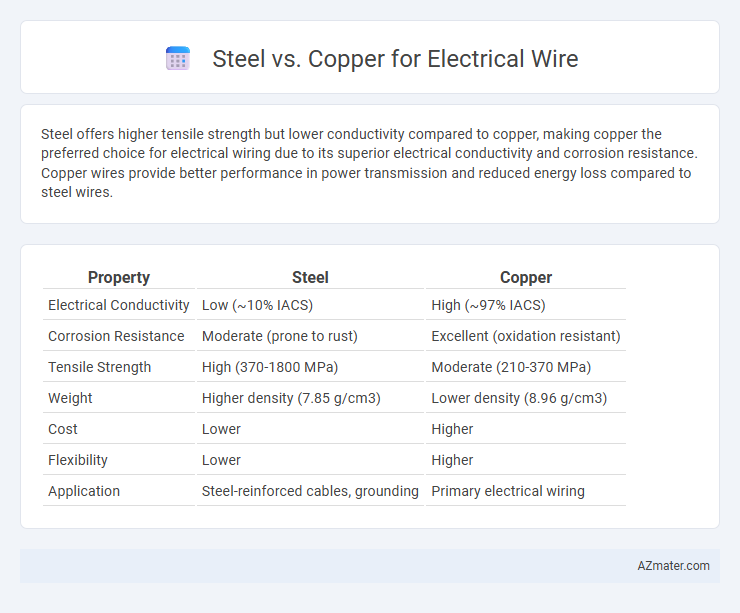
Steel offers higher tensile strength but lower conductivity compared to copper, making copper the preferred choice for electrical wiring due to its superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Copper wires provide better performance in power transmission and reduced energy loss compared to steel wires.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (~10% IACS) | High (~97% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (prone to rust) | Excellent (oxidation resistant) |
| Tensile Strength | High (370-1800 MPa) | Moderate (210-370 MPa) |
| Weight | Higher density (7.85 g/cm3) | Lower density (8.96 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Steel-reinforced cables, grounding | Primary electrical wiring |
Introduction: Steel vs Copper Wires
Steel wires offer higher tensile strength and durability, making them suitable for overhead power lines and applications requiring structural support. Copper wires provide superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, ensuring efficient energy transmission in residential and commercial wiring. Choosing between steel and copper depends on balancing mechanical strength with electrical performance and cost considerations.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity with a conductivity rating of approximately 59.6 million siemens per meter, making it highly efficient for electrical wiring applications. Steel has significantly lower conductivity, roughly 10% of copper's, which results in higher resistance and energy loss in electrical transmission. This conductivity difference directly impacts efficiency, voltage drop, and overall performance in electrical wiring systems.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Steel electrical wire exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to copper, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced tensile strength and resistance to physical stress. Copper offers excellent durability with its high corrosion resistance and long lifespan, ensuring consistent electrical conductivity over time in various environments. While copper is more flexible and easier to work with, steel provides greater toughness and impact resistance, often used in overhead power lines where mechanical robustness is crucial.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Copper exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, maintaining excellent conductivity without significant degradation over time, making it ideal for long-term electrical wiring applications. Steel, particularly galvanized or stainless variants, offers improved mechanical strength but is more prone to rust and corrosion when exposed to moisture, which can compromise electrical performance and reduce lifespan. Copper wiring typically ensures greater longevity and reliable conductivity in environments where corrosion is a concern, while steel may require protective coatings or insulation to mitigate its susceptibility to corrosion.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Steel electrical wire offers higher cost effectiveness compared to copper due to its lower raw material price and durability in specific applications, though it has higher electrical resistance. Copper remains widely preferred in the market for its superior conductivity and flexibility, despite higher costs and price volatility. Market availability favors copper, with extensive infrastructure and supply chain support, while steel wire is often utilized in specialized or cost-sensitive projects.
Weight Differences and Installation
Copper electrical wire is significantly lighter than steel wire, with copper weighing approximately 8.96 grams per cubic centimeter compared to steel's average of 7.85 grams per cubic centimeter, but copper's higher density and flexibility make it easier to handle and install despite the weight difference. Steel wire is stronger and more durable, yet its rigidity and greater weight can complicate installation, requiring additional support and labor. Copper's superior conductivity and lighter weight often result in faster installation times and less mechanical strain on mounting hardware.
Heat Resistance and Fire Safety
Copper electrical wires offer superior heat resistance, maintaining conductivity and structural integrity at higher temperatures than steel wires. Steel has a lower melting point and higher thermal expansion, increasing the risk of deformation and failure during overheating or fire exposure. Copper's excellent thermal conductivity enhances fire safety by dissipating heat more effectively, reducing the likelihood of electrical fires.
Applications in Residential and Industrial Wiring
Steel wiring offers higher tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for structural applications and grounding in residential construction, while copper's superior electrical conductivity and flexibility make it the preferred choice for main electrical wiring and industrial circuits requiring efficient power transmission. Copper wires provide better corrosion resistance and thermal performance, which are critical in maintaining safety and reliability in both residential and industrial electrical systems. Industrial applications often favor copper for sensitive equipment and high-load scenarios, whereas steel wiring is used where mechanical durability is prioritized over conductivity.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Steel electrical wire offers lower environmental impact due to its abundance and lower energy consumption during mining compared to copper, which requires intensive extraction processes causing significant habitat disruption. Copper is highly recyclable with nearly 90% efficiency, enabling repeated reuse without quality loss, whereas steel recycling consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases, enhancing its sustainability profile. Both metals demonstrate strong recyclability, but steel's lower mining footprint and energy-efficient recycling process make it a more eco-friendly choice for electrical wiring applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Choosing between steel and copper for electrical wire depends on the specific project's needs, including conductivity, cost, and durability. Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance and safety-critical applications. Steel is more cost-effective and stronger, but its lower conductivity and susceptibility to corrosion limit its use to grounding or support wiring in construction projects.
Infographic: Steel vs Copper for Electrical Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com