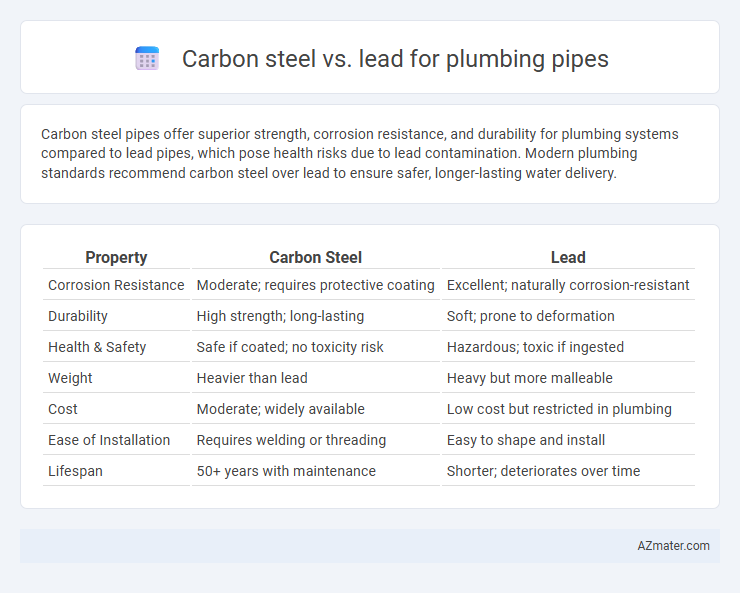
Carbon steel pipes offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability for plumbing systems compared to lead pipes, which pose health risks due to lead contamination. Modern plumbing standards recommend carbon steel over lead to ensure safer, longer-lasting water delivery.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; requires protective coating | Excellent; naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Durability | High strength; long-lasting | Soft; prone to deformation |
| Health & Safety | Safe if coated; no toxicity risk | Hazardous; toxic if ingested |
| Weight | Heavier than lead | Heavy but more malleable |
| Cost | Moderate; widely available | Low cost but restricted in plumbing |
| Ease of Installation | Requires welding or threading | Easy to shape and install |
| Lifespan | 50+ years with maintenance | Shorter; deteriorates over time |
Introduction: Understanding Plumbing Pipe Materials
Carbon steel pipes offer high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for water distribution and heating systems. Lead pipes, once common due to their malleability and ease of installation, pose significant health risks from lead contamination and are now largely banned in plumbing. Selecting carbon steel over lead ensures safer, long-lasting plumbing infrastructure compliant with modern safety standards.
Overview of Carbon Steel Pipes
Carbon steel pipes are commonly used in plumbing due to their high strength, durability, and resistance to high pressure, making them suitable for water supply and gas lines. Unlike lead pipes, carbon steel offers better corrosion resistance when properly coated, reducing the risk of contamination and pipe failure. Their thermal tolerance and structural integrity ensure safe and efficient fluid conveyance in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing systems.
Overview of Lead Pipes
Lead pipes were once commonly used in plumbing due to their malleability and resistance to corrosion but pose significant health risks because lead can leach into drinking water. Carbon steel pipes offer superior strength and durability without the toxic effects of lead, making them a safer and more reliable choice for modern plumbing systems. The transition from lead to carbon steel pipes reflects increasing regulatory standards addressing water quality and public health concerns.
Historical Use of Carbon Steel and Lead in Plumbing
Carbon steel pipes gained prominence in plumbing during the early 20th century due to their strength and resistance to high pressure, making them ideal for water distribution and steam systems. Lead pipes, used since ancient Roman times, were favored for their malleability and corrosion resistance but fell out of favor by the mid-20th century due to health risks associated with lead poisoning. Transitioning from lead to carbon steel marked a significant shift in plumbing materials driven by advancements in public health awareness and industrial manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Carbon steel pipes exhibit superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, making them a preferred choice for long-term plumbing applications. Lead pipes are prone to degradation and pose health risks due to lead leaching, significantly reducing their practical lifespan. Carbon steel's robust structural integrity and resistance to pressure fluctuations contribute to its extended longevity in plumbing systems.
Health and Safety Considerations
Carbon steel pipes offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, significantly reducing the risk of toxic metal leaching into drinking water. Lead pipes pose severe health risks, including lead poisoning, neurological damage, and developmental issues, especially in children. Regulatory agencies strongly discourage the use of lead in plumbing due to its established toxicity and have established strict guidelines for its removal and replacement.
Corrosion Resistance: Carbon Steel vs Lead
Carbon steel pipes exhibit moderate corrosion resistance but are prone to rust and require protective coatings or galvanization for extended durability in plumbing systems. Lead pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance in certain water chemistries, preventing rust and scale buildup, but pose significant health risks due to lead leaching and are largely banned or replaced in modern plumbing. Selecting materials involves balancing carbon steel's mechanical strength with lead's corrosion resistance while considering current safety regulations and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel pipes offer greater durability and recyclability compared to lead pipes, significantly reducing environmental waste and resource consumption over their lifecycle. Lead pipes pose severe health risks due to toxic leaching, resulting in costly remediation and environmental contamination. Sustainable plumbing practices favor carbon steel as it supports circular economy principles and minimizes ecological harm.
Cost and Installation Differences
Carbon steel pipes typically cost more than lead pipes due to higher material durability and long-term reliability in plumbing systems. Installation of carbon steel requires specialized tools and skilled labor because of its rigidity and welding needs, whereas lead pipes are easier to cut and shape but pose health risks and are largely prohibited by modern building codes. Choosing carbon steel ensures compliance with safety standards and offers better corrosion resistance, impacting both upfront costs and future maintenance expenses.
Modern Recommendations for Plumbing Materials
Modern plumbing standards prioritize materials like carbon steel over lead due to health and safety regulations, as carbon steel offers superior durability, corrosion resistance, and is compliant with EPA guidelines. Lead pipes are largely banned in residential plumbing because lead leaching poses severe health risks, including lead poisoning, prompting widespread replacement programs. Contemporary plumbing systems favor carbon steel combined with protective coatings to ensure longevity and potable water safety, aligning with NSF/ANSI 61 certification for drinking water systems.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Lead for Plumbing pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com