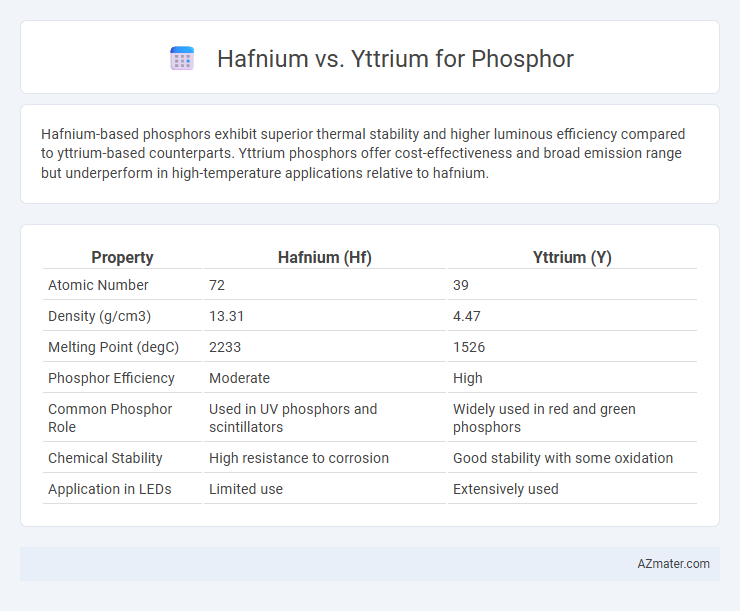
Hafnium-based phosphors exhibit superior thermal stability and higher luminous efficiency compared to yttrium-based counterparts. Yttrium phosphors offer cost-effectiveness and broad emission range but underperform in high-temperature applications relative to hafnium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Yttrium (Y) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 72 | 39 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 13.31 | 4.47 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2233 | 1526 |
| Phosphor Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Common Phosphor Role | Used in UV phosphors and scintillators | Widely used in red and green phosphors |
| Chemical Stability | High resistance to corrosion | Good stability with some oxidation |
| Application in LEDs | Limited use | Extensively used |
Introduction to Hafnium and Yttrium in Phosphor Applications
Hafnium and yttrium are critical elements in phosphor applications due to their unique electronic configurations and luminescent properties. Hafnium oxide is valued for its high refractive index and stability in phosphor layers, enhancing brightness and durability in display technologies. Yttrium commonly acts as a host lattice for activator ions like europium and terbium, crucial for red and green emissions in LED phosphors and fluorescent lighting.
Chemical Properties: Hafnium vs Yttrium
Hafnium exhibits a high melting point of 2233degC and a dense atomic structure with a +4 oxidation state, making it highly stable in phosphor applications. Yttrium, with a lower melting point of 1526degC and a +3 oxidation state, offers excellent compatibility in yttrium-based phosphors such as YAG and YVO4 due to its ability to efficiently host activator ions. The differing ionic radii and oxidation states of Hafnium and Yttrium significantly influence their luminescent efficiency and thermal stability in phosphor materials.
Crystal Structure and Stability Comparison
Hafnium and yttrium phosphors exhibit distinct crystal structures that critically influence their luminescent efficiency and thermal stability. Hafnium phosphors typically crystallize in a monoclinic or tetragonal lattice, offering higher structural stability under high-temperature conditions compared to yttrium phosphors, which commonly adopt a hexagonal or cubic structure prone to phase transitions. The greater lattice rigidity and chemical robustness of hafnium-based phosphors ensure enhanced longevity and consistent emission performance in high-stress applications.
Luminescence Efficiency: Hafnium vs Yttrium Phosphors
Hafnium-based phosphors exhibit higher luminescence efficiency compared to yttrium phosphors due to their superior quantum yield and stronger light emission intensity. The crystal field environment in hafnium phosphors enhances electron transition probabilities, leading to brighter and more stable luminescence under excitation. Yttrium phosphors, while commonly used, often show lower efficiency because of less favorable energy transfer mechanisms and increased non-radiative decay rates.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance in Phosphor Materials
Hafnium-based phosphors exhibit superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures above 1500degC, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Yttrium phosphors provide excellent chemical stability but have lower thermal resilience compared to hafnium, typically degrading beyond 1200degC. The enhanced chemical inertness of hafnium compounds also improves phosphor longevity in aggressive environments, outperforming yttrium under harsh conditions.
Performance in Display and Lighting Technologies
Hafnium-based phosphors exhibit superior thermal stability and longer luminescence lifetimes, enhancing performance in high-brightness LED displays and lighting applications. Yttrium phosphors, particularly yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG), offer efficient blue-to-yellow light conversion with excellent color rendering, making them ideal for white LED illumination. The choice between hafnium and yttrium phosphors hinges on specific display technology needs, balancing hafnium's durability and yttrium's color accuracy for optimal lighting performance.
Cost and Availability of Hafnium and Yttrium
Hafnium is significantly rarer and more expensive than yttrium due to its limited supply and complex extraction process, impacting its cost-effectiveness for phosphor applications. Yttrium is more abundant and widely available, offering a lower-cost alternative with reliable supply chains essential for large-scale phosphor production. The price disparity and availability constraints of hafnium often lead manufacturers to prefer yttrium-based phosphors for commercial use.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Hafnium and yttrium phosphors differ significantly in environmental and safety profiles, with yttrium-based phosphors generally exhibiting lower toxicity and easier recyclability compared to hafnium counterparts. Hafnium compounds often require careful handling due to their potential respiratory hazards and environmental persistence, which complicates disposal and processing. Yttrium's abundance and relatively benign chemical nature contribute to safer manufacturing and reduced ecological impact in phosphor applications.
Industrial Applications and Market Trends
Hafnium and yttrium serve distinct roles in phosphor applications, with yttrium-based phosphors widely used in industrial lighting, displays, and lasers due to their high brightness and thermal stability. Hafnium-enhanced phosphors offer improved durability and performance in harsh environments, making them valuable for specialized industrial sensors and high-performance electronics. Market trends indicate growing demand for yttrium phosphors driven by LED lighting and display technologies, while hafnium phosphors gain attention in niche industrial applications requiring enhanced material resilience.
Future Prospects in Phosphor Technologies
Hafnium and yttrium offer distinct advantages in phosphor technologies, with hafnium showing promising potential due to its ability to enhance thermal stability and luminous efficiency in next-generation phosphors. Yttrium remains a critical component in widely used yttrium-aluminum garnet (YAG) phosphors, essential for LED lighting and display applications, but emerging research into hafnium-doped phosphors suggests improved performance in high-temperature and high-power environments. Future prospects indicate increased integration of hafnium to develop phosphors with superior brightness, color purity, and durability, addressing the demand for advanced lighting and display technologies.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Yttrium for Phosphor
 azmater.com
azmater.com