Ruthenium dental alloys offer superior corrosion resistance and enhanced hardness compared to gold alloys, making them ideal for long-lasting dental restorations. Gold alloys provide excellent biocompatibility and malleability but are softer and more prone to wear than ruthenium-based materials.
Table of Comparison
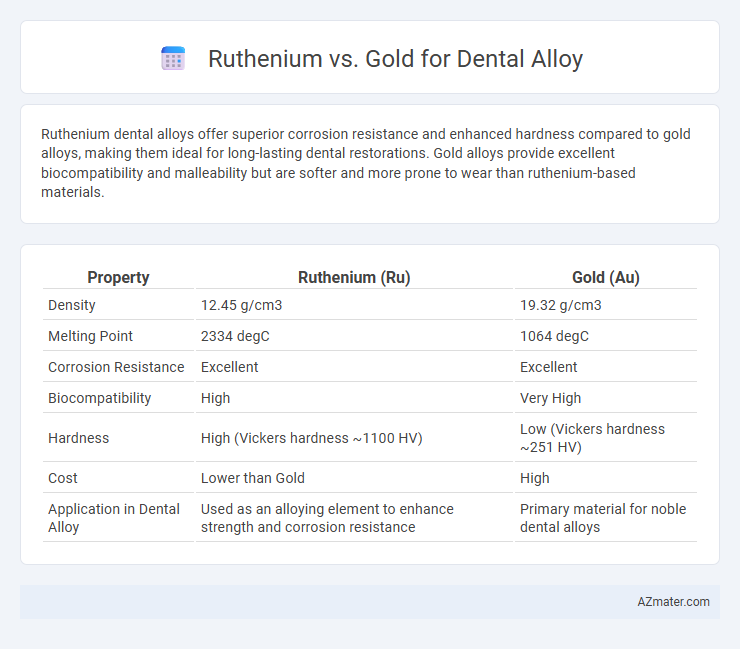
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Gold (Au) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 12.45 g/cm3 | 19.32 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2334 degC | 1064 degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Biocompatibility | High | Very High |
| Hardness | High (Vickers hardness ~1100 HV) | Low (Vickers hardness ~251 HV) |
| Cost | Lower than Gold | High |
| Application in Dental Alloy | Used as an alloying element to enhance strength and corrosion resistance | Primary material for noble dental alloys |
Overview of Dental Alloys: Ruthenium and Gold
Ruthenium and gold are key materials in dental alloys, valued for their biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Gold alloys offer high corrosion resistance, excellent malleability, and aesthetic appeal, making them a traditional choice for crowns and bridges. Ruthenium, often added in small amounts to gold alloys, enhances strength and wear resistance, improving the durability of dental restorations without compromising biocompatibility.
Elemental Properties: Ruthenium vs Gold
Ruthenium exhibits higher hardness and corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it a valuable additive in dental alloys to enhance durability and wear resistance. Gold, known for its excellent biocompatibility and malleability, provides superior ductility and ease of casting in dental applications. Incorporating ruthenium into gold alloys improves mechanical strength while maintaining the chemical stability essential for long-lasting dental restorations.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Dentistry
Ruthenium, a transition metal often used as an alloying element in dental materials, enhances the mechanical strength and corrosion resistance of gold-based dental alloys, improving their long-term biocompatibility. Gold alloys, renowned for their excellent biocompatibility and minimal allergic reactions, provide superior safety in dental restorations due to their inert nature and resistance to tarnish and corrosion in the oral environment. Combining ruthenium with gold in dental alloys optimizes both structural durability and biological safety, making it a preferred choice for crowns, bridges, and other prosthetic applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ruthenium-enhanced dental alloys exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to traditional gold alloys, increasing hardness and resistance to deformation under masticatory forces. The integration of ruthenium improves wear resistance and reduces corrosion rates, significantly enhancing alloy durability in oral environments. Gold alloys, while biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, generally offer lower tensile strength and are more prone to wear, making ruthenium an advantageous additive for long-lasting dental restorations.
Corrosion Resistance in the Oral Environment
Ruthenium enhances the corrosion resistance of dental alloys by forming a stable oxide layer that protects against the acidic and enzymatic conditions in the oral environment. Gold alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance due to their noble metal properties, but their softness can require alloying with elements like ruthenium to improve mechanical strength without compromising durability. Incorporating ruthenium into gold-based dental alloys results in superior resistance to tarnish and degradation, essential for maintaining biocompatibility and longevity in dental restorations.
Workability and Casting Characteristics
Ruthenium enhances dental alloy workability by improving hardness and corrosion resistance, allowing for precise shaping and durability in dental restorations. Gold alloys exhibit excellent casting characteristics due to their low melting point and fluidity, resulting in smooth, detailed dental components. Combining ruthenium with gold in dental alloys balances superior workability with optimal casting performance for high-quality prosthetics.
Aesthetic Considerations: Color and Appearance
Ruthenium enhances dental alloys by providing a subtle grayish hue that can improve the metal's overall strength without significantly compromising aesthetics. Gold alloys maintain a warm, yellow tone prized for its natural tooth-like appearance and resistance to tarnish, ideal for visible restorations. Choosing between ruthenium and gold depends on balancing the desired color with durability, as ruthenium-containing alloys may appear less yellow but offer improved hardness and corrosion resistance.
Cost Analysis: Ruthenium vs Gold Alloys
Ruthenium dental alloys offer a significant cost advantage over traditional gold alloys, with ruthenium prices being substantially lower due to its greater abundance and lower market demand. Gold alloys, while providing excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, often incur higher material and fabrication costs, impacting overall treatment expenses. Dental professionals weigh ruthenium's cost-efficiency against gold's established clinical performance when selecting alloys for restorative applications.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Ruthenium-enhanced dental alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility compared to traditional gold alloys, leading to enhanced clinical performance in restorative dentistry. These alloys demonstrate increased hardness and wear resistance, contributing to improved longevity of dental prosthetics under masticatory stress. Clinical studies indicate that ruthenium-containing alloys maintain structural integrity and aesthetic properties longer than high-carat gold alloys, making them a preferred choice for durable dental restorations.
Choosing the Right Alloy: Key Considerations for Dentists
Ruthenium and gold are popular choices for dental alloys, each offering distinct benefits in durability and biocompatibility. Ruthenium enhances corrosion resistance and hardness when alloyed, making it ideal for patients requiring long-lasting restorations with minimal wear. Gold alloys provide excellent malleability and superior aesthetic appeal, often preferred for crowns and bridges where precision and patient comfort are critical.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Gold for Dental Alloy
 azmater.com
azmater.com