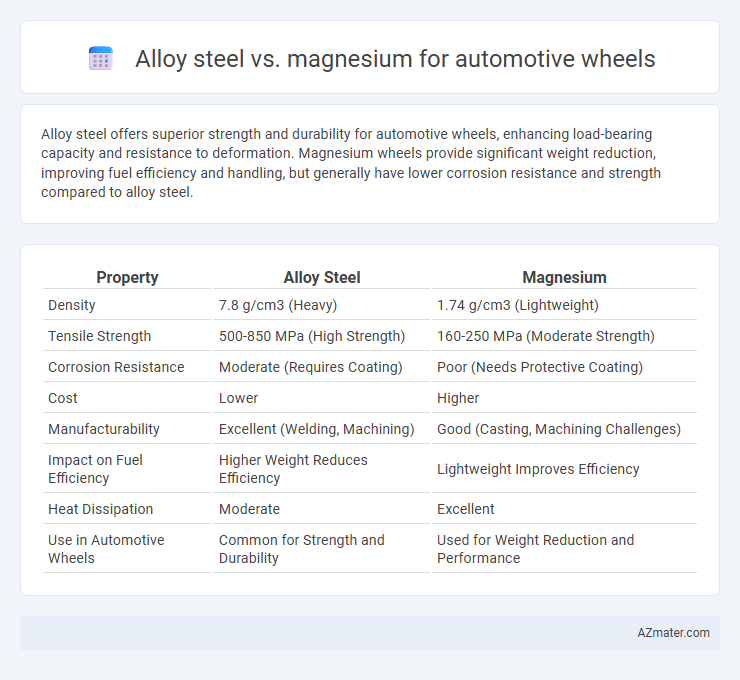
Alloy steel offers superior strength and durability for automotive wheels, enhancing load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation. Magnesium wheels provide significant weight reduction, improving fuel efficiency and handling, but generally have lower corrosion resistance and strength compared to alloy steel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alloy Steel | Magnesium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.8 g/cm3 (Heavy) | 1.74 g/cm3 (Lightweight) |
| Tensile Strength | 500-850 MPa (High Strength) | 160-250 MPa (Moderate Strength) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (Requires Coating) | Poor (Needs Protective Coating) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Manufacturability | Excellent (Welding, Machining) | Good (Casting, Machining Challenges) |
| Impact on Fuel Efficiency | Higher Weight Reduces Efficiency | Lightweight Improves Efficiency |
| Heat Dissipation | Moderate | Excellent |
| Use in Automotive Wheels | Common for Strength and Durability | Used for Weight Reduction and Performance |
Introduction to Automotive Wheel Materials
Automotive wheels require materials with high strength-to-weight ratios, making alloy steel and magnesium prominent choices in the industry. Alloy steel offers excellent durability and resistance to impact, ensuring long-lasting performance, while magnesium provides a lightweight alternative that enhances fuel efficiency and handling. Both materials balance strength and weight differently, influencing vehicle dynamics and manufacturing costs.
Alloy Steel Wheels: Overview and Composition
Alloy steel wheels for automotive use consist primarily of iron combined with elements such as chromium, nickel, and manganese, enhancing strength and corrosion resistance. These wheels offer superior durability and load-bearing capacity compared to magnesium counterparts, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. The dense composition of alloy steel ensures enhanced impact resistance and longer service life under harsh driving conditions.
Magnesium Wheels: Properties and Characteristics
Magnesium wheels boast a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, offering significant weight reduction compared to alloy steel wheels, which improves fuel efficiency and vehicle handling. Their excellent vibration damping properties contribute to a smoother ride, while corrosion resistance is enhanced through specialized coatings, addressing magnesium's natural susceptibility to oxidation. Despite being more costly, magnesium wheels deliver superior performance characteristics ideal for high-performance and racing vehicles.
Weight Comparison: Alloy Steel vs Magnesium Wheels
Magnesium wheels typically weigh 30-50% less than alloy steel wheels, significantly reducing unsprung mass and improving vehicle handling and fuel efficiency. Alloy steel wheels, while heavier, provide greater durability and are more cost-effective for mass production in automotive applications. The substantial weight advantage of magnesium wheels enhances performance in high-end sports cars and racing vehicles, where weight reduction is critical.
Strength and Durability Factors
Alloy steel wheels offer superior strength and exceptional durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to deformation under heavy loads, making them ideal for rugged driving conditions. Magnesium wheels provide a lightweight alternative with good strength-to-weight ratio but generally exhibit lower fatigue resistance and higher susceptibility to corrosion compared to alloy steel. The enhanced toughness and wear resistance of alloy steel ensure longer service life and greater impact resilience in automotive wheel applications.
Performance and Handling Differences
Alloy steel wheels offer superior strength and durability, enhancing vehicle stability and handling under high-stress conditions, while magnesium wheels provide significantly reduced weight, improving acceleration, braking, and overall responsiveness. Magnesium's lightweight nature lowers unsprung mass, resulting in better suspension performance and sharper cornering precision compared to heavier alloy steel wheels. Despite alloy steel's toughness, magnesium wheels excel in performance-oriented applications due to their favorable strength-to-weight ratio and improved dynamic handling characteristics.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Alloy steel wheels exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their high chromium content forming a protective oxide layer, making them less susceptible to rust compared to magnesium wheels. Magnesium wheels, while lightweight, are more prone to galvanic corrosion and require frequent maintenance including protective coatings and regular cleaning to prevent oxidation. The enhanced durability and lower maintenance needs of alloy steel wheels make them preferable for long-term automotive use in harsh environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Alloy steel wheels generally cost less to produce than magnesium wheels due to cheaper raw materials and established manufacturing processes like forging and casting. Magnesium wheels offer superior weight reduction and performance benefits but involve higher costs because of complex handling requirements and specialized casting techniques. Manufacturing challenges in magnesium include corrosion resistance and flammability management, which increase production expenses compared to alloy steel wheels.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alloy steel automotive wheels offer greater recyclability with established infrastructure, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption during recycling compared to magnesium wheels, which require more energy-intensive processes and present challenges in recycling due to their reactivity. Magnesium wheels are lighter, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and lower CO2 emissions over the vehicle's lifetime, yet their extraction involves environmentally hazardous mining and processing activities. Sustainable wheel design must balance magnesium's weight-saving benefits against alloy steel's recyclability to minimize overall environmental impact in automotive manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wheel Material
Alloy steel wheels offer superior strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for heavy-duty and everyday driving conditions. Magnesium wheels provide significant weight reduction, enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency, but come with higher costs and susceptibility to corrosion. Selecting between alloy steel and magnesium wheels ultimately depends on balancing budget constraints, performance goals, and environmental conditions for the specific automotive application.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Magnesium for Automotive wheel
 azmater.com
azmater.com