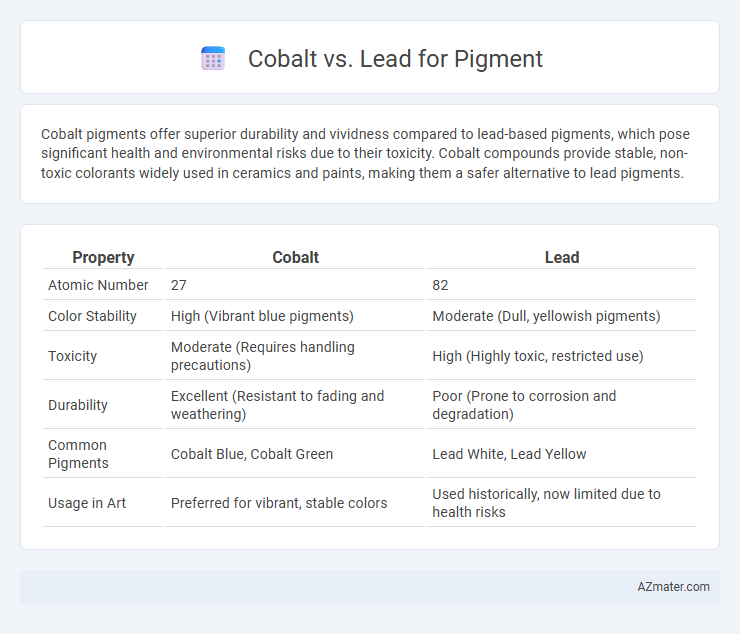
Cobalt pigments offer superior durability and vividness compared to lead-based pigments, which pose significant health and environmental risks due to their toxicity. Cobalt compounds provide stable, non-toxic colorants widely used in ceramics and paints, making them a safer alternative to lead pigments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cobalt | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 27 | 82 |
| Color Stability | High (Vibrant blue pigments) | Moderate (Dull, yellowish pigments) |
| Toxicity | Moderate (Requires handling precautions) | High (Highly toxic, restricted use) |
| Durability | Excellent (Resistant to fading and weathering) | Poor (Prone to corrosion and degradation) |
| Common Pigments | Cobalt Blue, Cobalt Green | Lead White, Lead Yellow |
| Usage in Art | Preferred for vibrant, stable colors | Used historically, now limited due to health risks |
Introduction to Cobalt and Lead Pigments
Cobalt pigments, known for their vibrant blue hues such as cobalt blue and cerulean blue, are prized for their high colorfastness, chemical stability, and non-toxic properties, making them ideal for artistic and industrial applications. Lead pigments, including lead white and lead chromate, historically offered brilliant opacity and brightness but pose significant health risks due to lead's toxicity and have seen reduced use in favor of safer alternatives. Advances in pigment technology have increasingly favored cobalt-based compounds for their durability and safety, while regulatory restrictions limit the use of lead-based pigments in many countries.
Historical Use of Cobalt vs Lead in Art
Cobalt pigments have been prized since ancient times for their vibrant blue hues, found in artifacts dating back to 2,000 BCE, while lead-based pigments, such as lead white, dominated European art from the Renaissance through the 19th century due to their opacity and fast drying properties. Cobalt blue became prominent in the 18th century, replacing the toxic and less stable lead blues that caused health issues among artists. The transition from lead to cobalt pigments marked a significant development in art history, enhancing color stability and safety in painting materials.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Cobalt pigments typically consist of cobalt oxides or cobalt aluminate, offering high stability and vibrant blue hues due to cobalt's +2 and +3 oxidation states, which provide strong resistance to heat and light. Lead pigments, often composed of lead carbonate or lead chromate, exhibit bright yellow and white colors but are less stable under acidic conditions and pose significant toxicity risks due to lead's heavy metal properties. The superior chemical inertness and thermal stability of cobalt compounds make them preferable for durable, non-toxic applications in ceramics and paints compared to the more reactive and hazardous lead-based pigments.
Color Spectrum and Visual Impact
Cobalt pigments offer a rich range of deep blues and violets, providing high color stability and lightfastness suitable for fine art and industrial applications. Lead-based pigments, often seen in yellows, reds, and whites, deliver vibrant hues but pose toxicity risks, limiting their modern use. The visual impact of cobalt pigments is enhanced by their strong opacity and resistance to fading, whereas lead pigments excel in brightness but degrade over time when exposed to light.
Durability and Lightfastness
Cobalt pigments exhibit superior durability and lightfastness compared to lead-based pigments, making them ideal for long-lasting color stability in artworks and coatings. Lead pigments tend to degrade faster under UV exposure, resulting in color fading and discoloration over time. Cobalt's robust chemical structure provides enhanced resistance to environmental factors, ensuring consistent vibrancy and performance across various applications.
Toxicity and Health Concerns
Cobalt pigments exhibit lower acute toxicity compared to lead-based pigments, which are highly toxic and have been linked to severe health issues such as lead poisoning, neurological damage, and developmental delays. Exposure to lead pigments poses significant risks, including carcinogenicity and bioaccumulation, leading to stringent regulations and restrictions in many countries. Cobalt pigments, while less toxic, still require careful handling due to potential cobalt dust inhalation risks, but they present a safer alternative in terms of long-term health impacts.
Environmental Impact of Pigment Production
Cobalt pigments generally exhibit lower environmental toxicity compared to lead-based pigments, which are notorious for their high toxicity and persistence in ecosystems. The extraction and processing of lead pigments release harmful lead particulates, posing significant risks to soil, water, and human health. Cobalt pigment production, while not without environmental concerns such as cobalt mining's ecological footprint, tends to result in fewer hazardous emissions and less bioaccumulation in the environment.
Modern Alternatives and Innovations
Modern alternatives to cobalt and lead pigments emphasize environmental safety and non-toxicity, with innovations including synthetic organic pigments and nanomaterials that provide vibrant, durable colors without heavy metal hazards. Advances in bio-based pigments derived from natural sources offer sustainable options that mimic the color intensity of cobalt and lead while reducing ecological impact. Emerging technologies in pigment encapsulation and stability enhancement further improve the performance and safety profile of lead and cobalt replacements in coatings and plastics.
Availability and Cost Comparison
Cobalt pigments, prized for their vibrant blue hues, often command higher prices due to limited natural reserves and complex extraction processes, making them less readily available than lead-based pigments. Lead pigments, historically abundant and inexpensive, currently face restrictions and declining availability due to toxicity concerns and regulatory measures. The cost comparison favors lead pigments for affordability, but cobalt pigments offer superior stability and colorfastness despite their premium price and limited supply.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pigment
Cobalt pigments offer superior lightfastness, vivid blue hues, and chemical stability compared to lead-based pigments, which pose significant health hazards due to lead toxicity. Despite lead pigments' historical use for opacity and color intensity, stricter regulations have limited their application in favor of safer alternatives like cobalt. Selecting the right pigment depends on balancing performance needs with environmental and health safety, making cobalt the preferred choice in modern pigment formulations.
Infographic: Cobalt vs Lead for Pigment
 azmater.com
azmater.com